Electromagnetic vector-sensor linear array de-coherent multiple signal classification (MUSIC) parameter estimating method
An electromagnetic vector and parameter estimation technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems such as limiting the application range of the method, increasing computational complexity, and reducing the resolution of the array
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] In order to make the above and other objects, features and advantages of the present invention more apparent, the following specifically cites the embodiments of the present invention, together with the accompanying drawings, for a detailed description as follows.
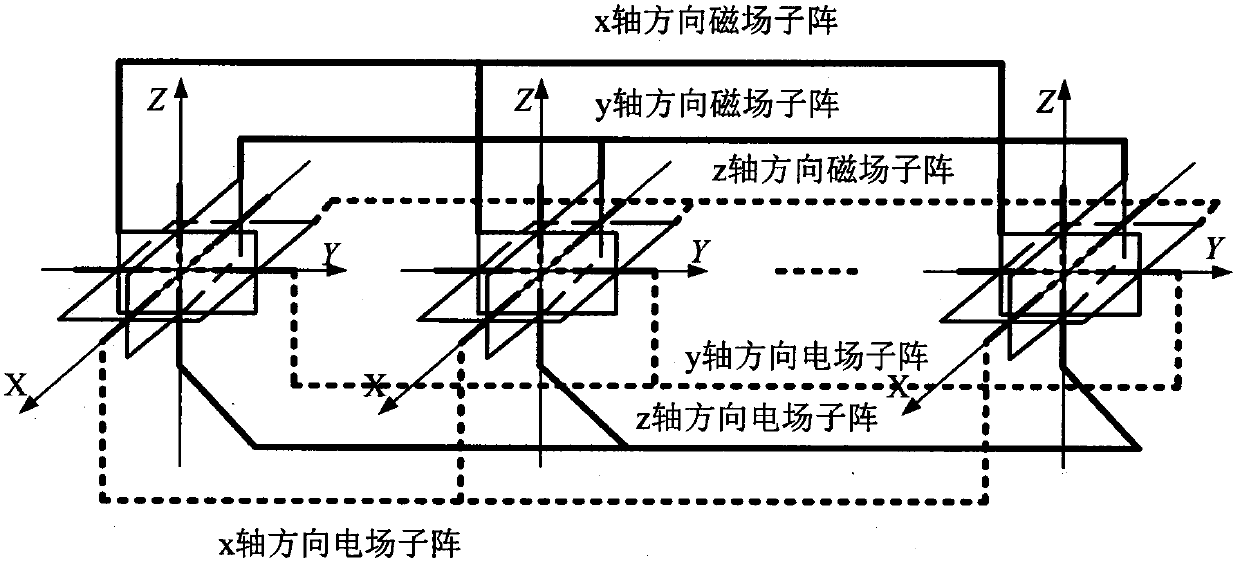
[0024] figure 1Shown is a schematic diagram of an electromagnetic vector sensor array according to an embodiment of the present invention. The array of the present invention is composed of M arbitrarily distributed electromagnetic vector sensor array elements on the y-axis, and the array elements are electric dipoles in the direction of x-axis, y-axis and z-axis and x-axis, y-axis and z-axis at the same point in space. The electromagnetic vector sensor composed of magnetic dipoles in the axial direction, the corresponding channels of all sensors are parallel to each other: all the x-axis electric dipoles are parallel to each other, all the y-axis electric dipoles are parallel to each other, and all the z-axi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com