An Inner-Cavity Optical Fiber Fabry-Perot Sensor for Slip Measurement
A sensor and optical fiber technology, applied in the field of sensors, can solve problems such as strong electromagnetic interference, and achieve the effects of not affecting measurement accuracy, high anti-shake and anti-vibration technology, and strong practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
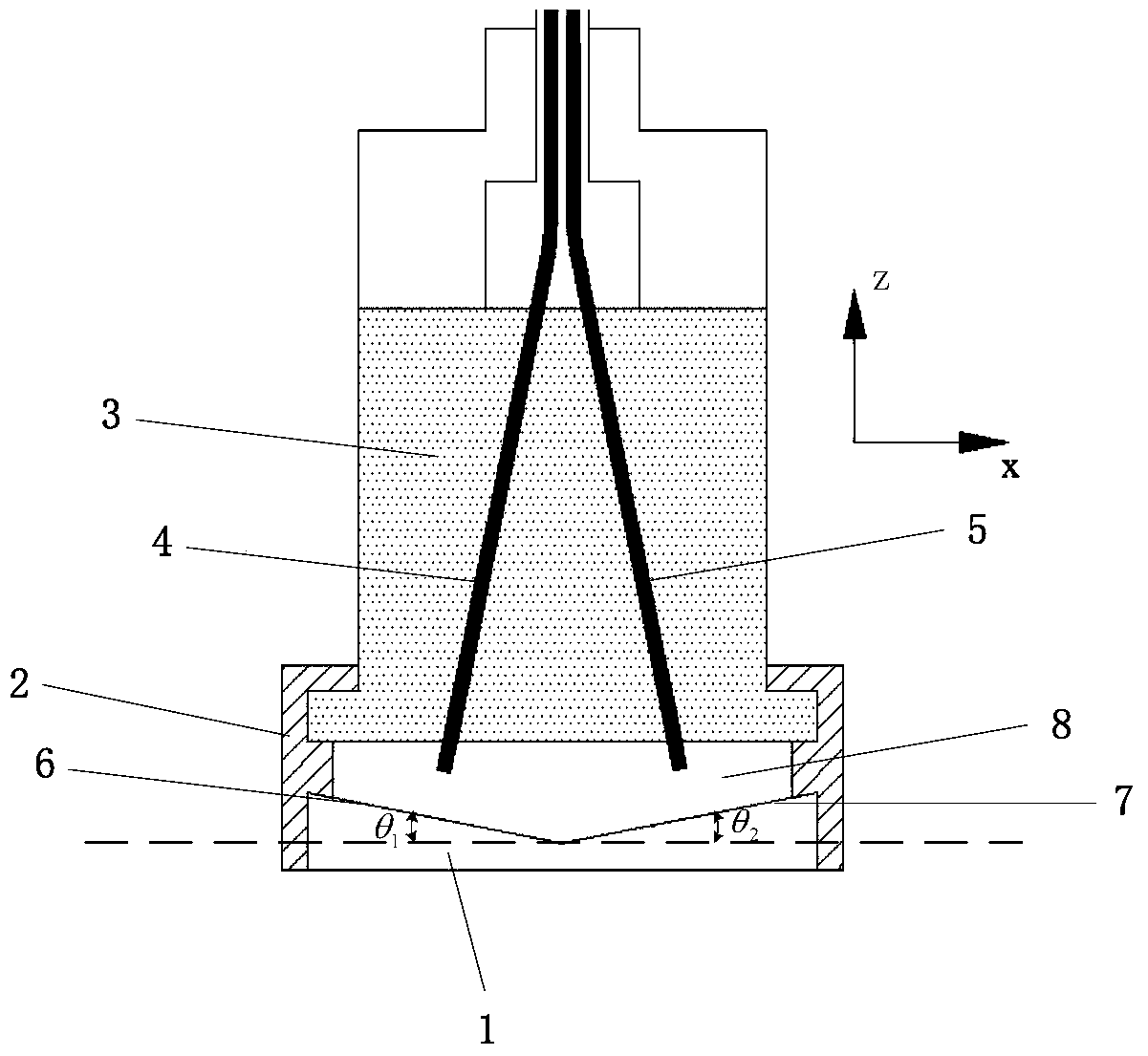
[0042] The invention provides a sensor for measuring slip in an inner cavity optical fiber Fabry Perot, such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, it includes a reflective slope 1, a sealed dust cover 2, a sensor body 3, a first optical fiber 4, and a second optical fiber 5, wherein:
[0043] The material of the reflective slope and the sensor body can be metal.
[0044] The sealed dustproof cover 2 is a flexible pipe body with a cavity 8 inside and two ends connected through. One end of the flexible pipe body is sealed and connected to the sensor body 3, and the other end is sealed and connected to the reflective slope 1;
[0045] The bottom side of the reflective inclined surface 1 is a plane, and its upper side is provided with an inclination angle of θ with its bottom side plane. 1 The first inclined plane 6, the inclination angle is θ 2 The second inclined plane 7 is provided with a reflective surface on the upper side surfaces of the first inclined plane 6 and the second ...
Embodiment 2
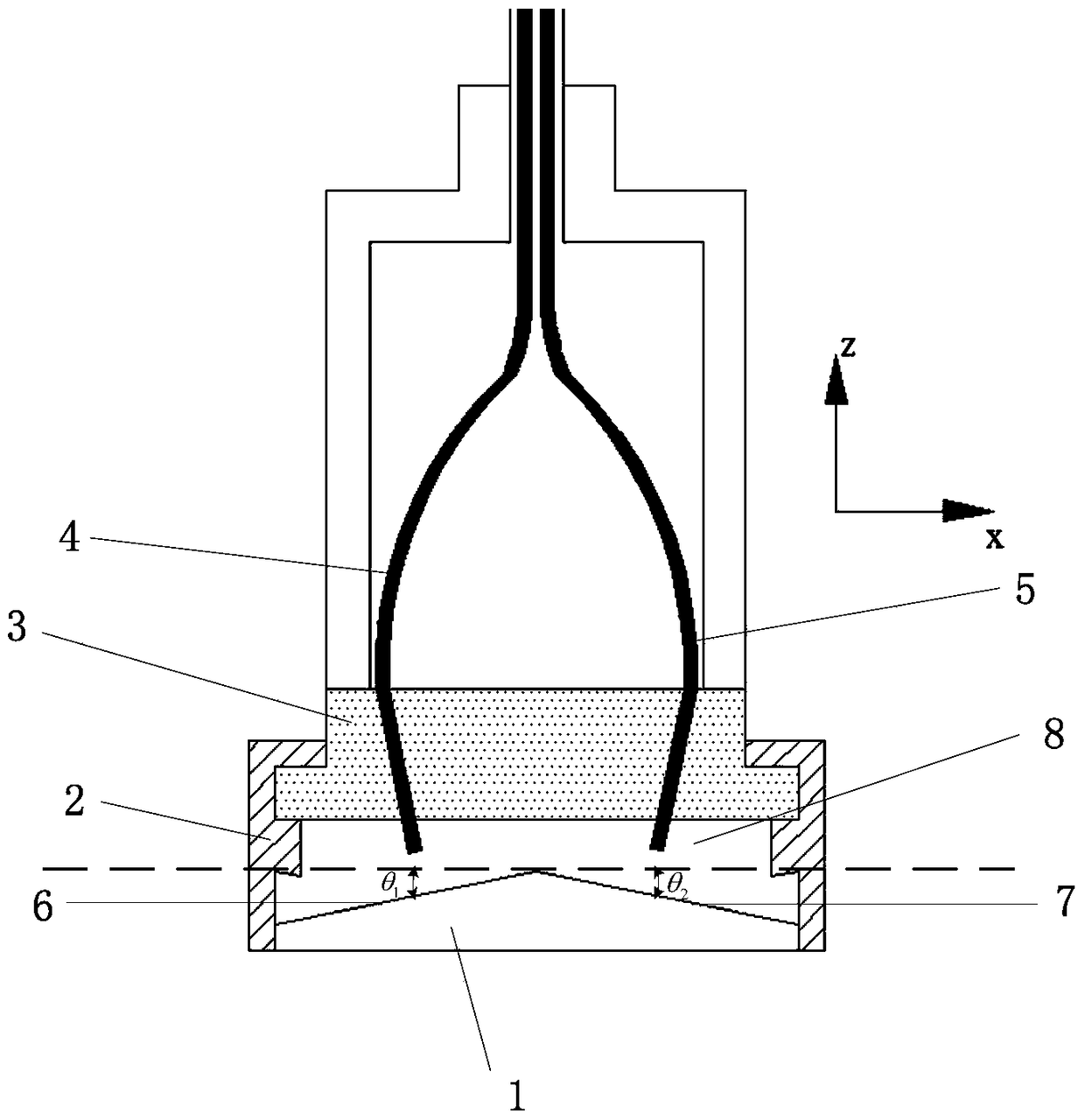
[0070] This embodiment has been improved on the basis of embodiment 1, as Figure 5 As shown, the specific improvements are as follows:
[0071] The first intersection line between the plane where the first slope 6 is located and the plane on the bottom side is perpendicular to the second intersection line between the plane where the second slope 7 is located and the plane on the bottom side,
[0072] and θ 1 ,θ 2 The condition that must be satisfied is sinθ 1 sinθ 2 ≠0.
[0073] Such as Figure 5 As shown, in actual use, in order to be able to simultaneously measure the slip in the x and y directions, the sensor uses two optical fibers and two reflective surfaces to measure the slip in one direction. During specific measurements (such as: To measure the displacement between object A and object B), you can grind a small groove with a flat bottom surface on object B (in fact, it does not necessarily have to be polished, there is another method, which is to weld the reflec...
Embodiment 3
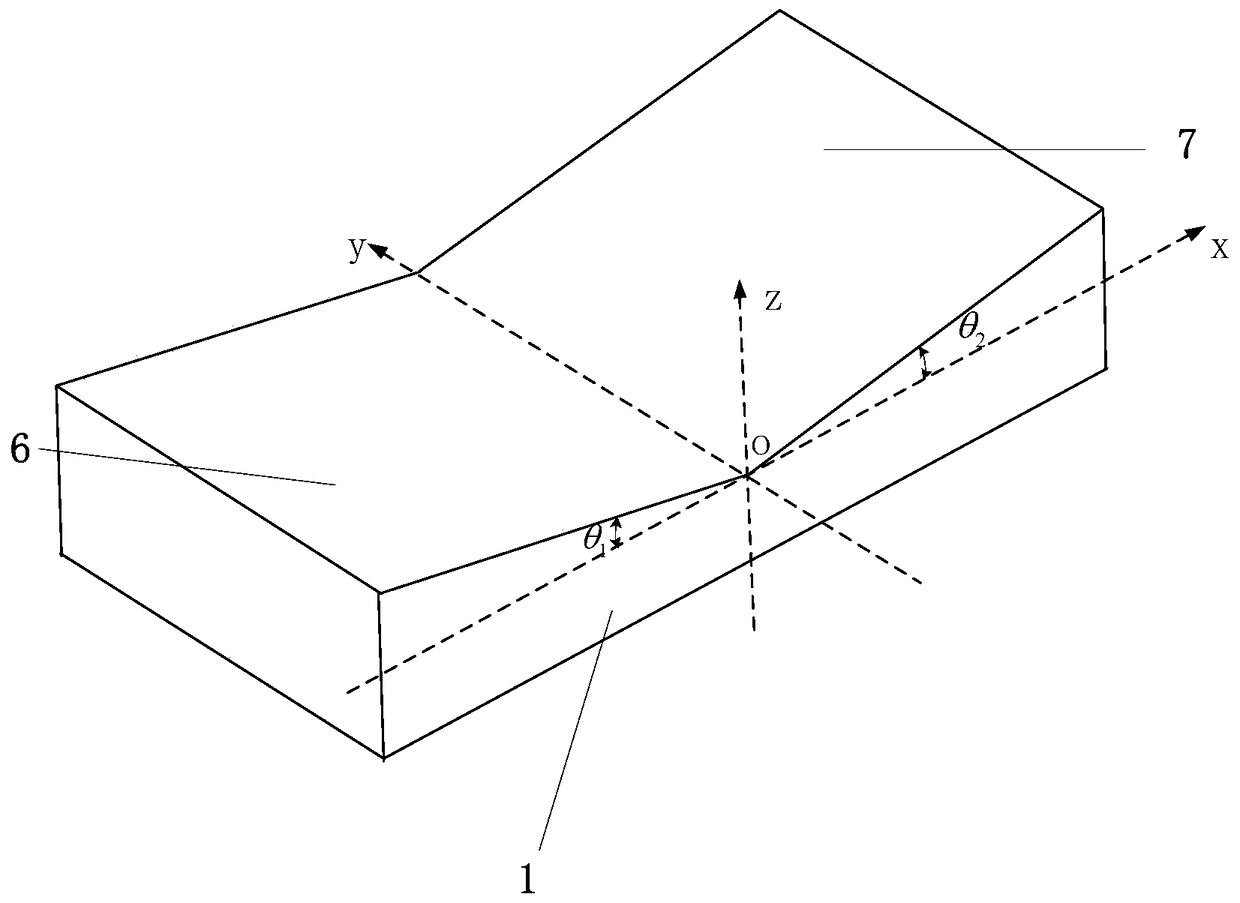
[0076] This embodiment has been improved on the basis of embodiment 1, as Figure 6 As shown, the specific improvements are as follows:
[0077] The sensor also includes a third optical fiber, and the bottom of the third optical fiber is provided with a reflective end face, and the third optical fiber passes through the sensor body 3 and extends into the cavity 8;
[0078] The upper side of the reflective inclined surface 1 is also provided with an inclination angle of θ with its bottom side plane. 3 The third inclined plane 9 is provided with a reflective surface on the upper side surface of the third inclined plane 9;
[0079] And the first inclined plane 6, the second inclined plane 7 and the third inclined plane 9 must satisfy the condition that the determinant is not equal to 0, where (l 1 ,m 1 ,n 1 ), (l 2 ,m 2 ,n 2 ), (l 3 ,m 3 ,n 3 ) are respectively the normal vectors of the first, second and third slopes;
[0080] The optical axis of the third optical fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com