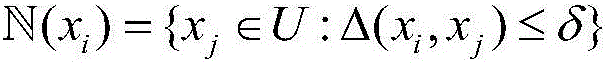Method and system for carrying out face fatigue state recognition by relative coverage element reduction
A fatigue state and face technology, which is applied in the system field of face fatigue state recognition, can solve the problems of face fatigue expression recognition, too many rules and a large amount of calculation, etc., and achieve excellent generalization performance, fast classification speed, and calculation Small amount of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
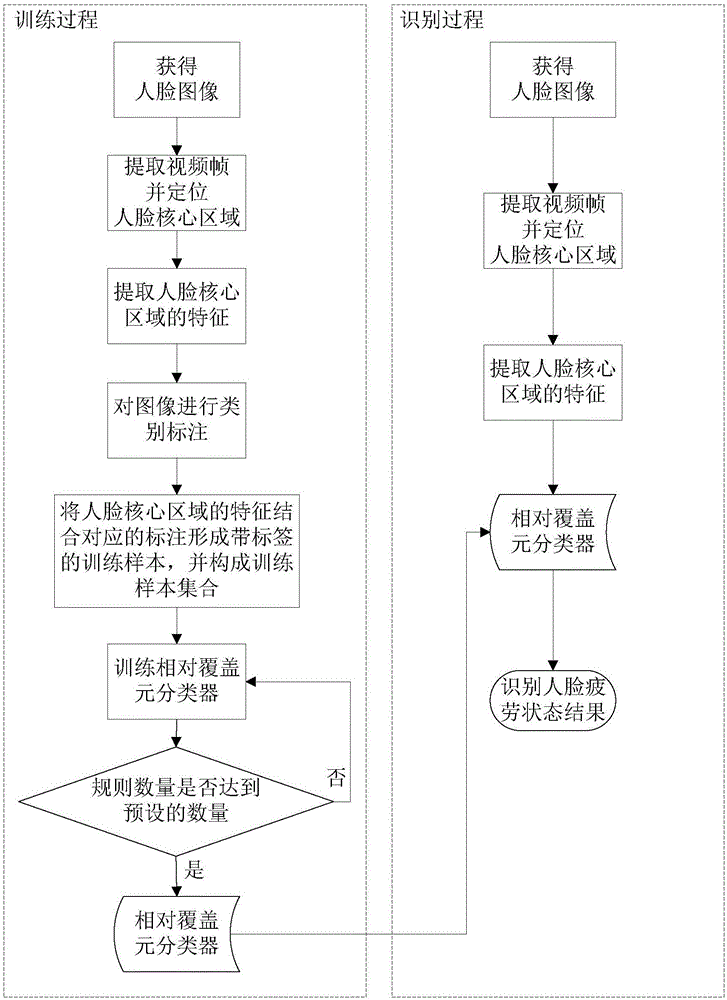
[0046] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To describe this embodiment,
[0047] The method for identifying the fatigue state of a human face by using relative coverage element reduction described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0048] 1. Train a relative coverage meta-classifier:
[0049] Step 1, obtain the human face video frame of the video image in the video recording device;
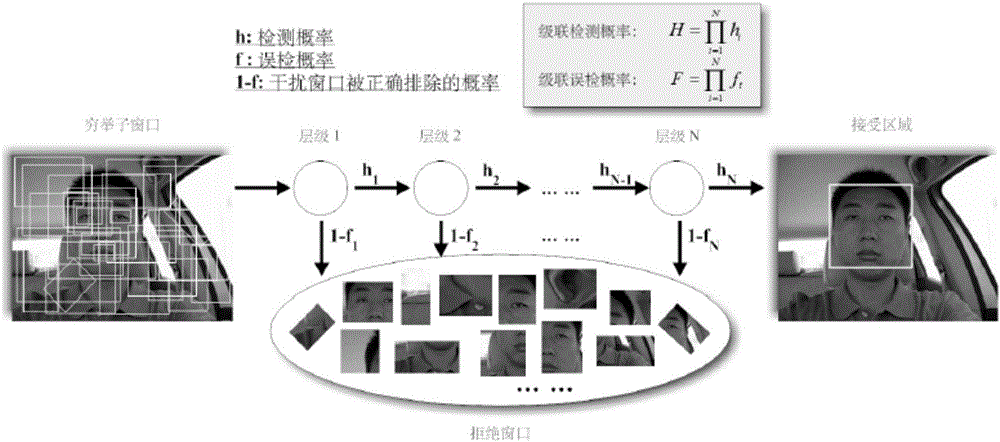
[0050] Step 2, detect the face core area in each face video frame;
[0051] Step 3, extracting the features of the core area of the face;
[0052] Step 4, based on the state of the face in each face video frame, classify each frame of image;
[0053] Step 5, combine the features of the core area of the face with the corresponding annotations to form labeled training samples, and form a training sample set;
[0054] Step 6, generating a neighborhood covering element for each sample in the training sample set, and counting the samples covered by the neighborhoo...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0067] The neighborhood covering element described in step 6 of this embodiment is as follows:
[0068]
[0069] where x i ,x j Represents two arbitrary samples without category labels (only feature attributes and no category attributes); U represents the sample set; Δ(x i ,x j ) is a distance function, and δ is a function that depends on x i The parameter that represents the distance threshold.
[0070] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0072] Δ(x) described in step 6 described in this embodiment i ,x j ) is calculated using the Euclidean distance.
[0073] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com