A Locality Repair Coding Method Based on Pyramid Codes
A technology of partial repair and encoding method, applied in the computer field, can solve the problem of high disk I/O overhead, achieve the effect of small repair bandwidth overhead and ensure storage overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
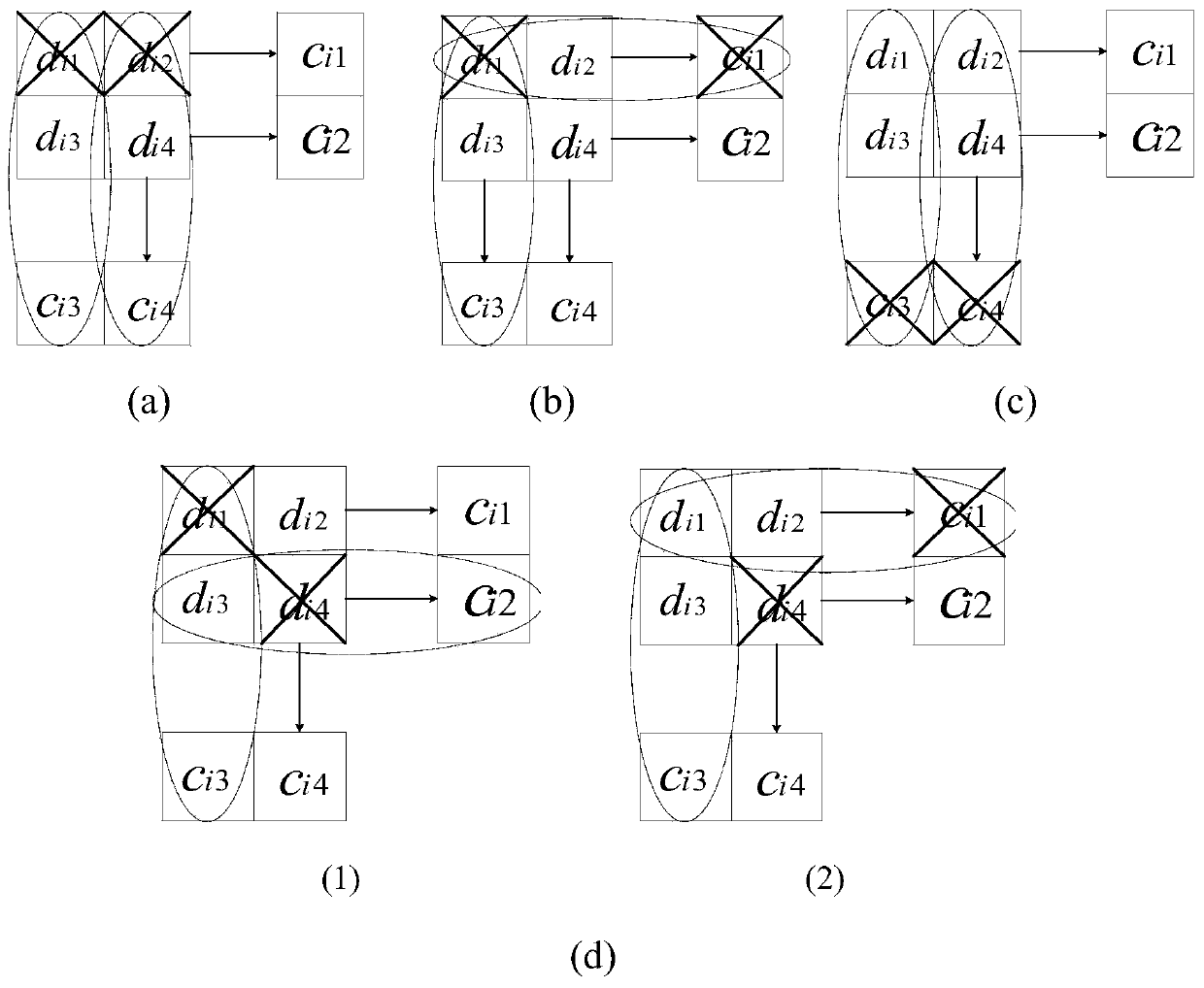
[0035] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, in accordance with the above technical solution, this embodiment provides a localized repair coding method based on Pyramid codes. The minimum coding structure of Pyramid codes refers to the ability to quickly repair the Pyramid code coding method and ensure that the least number of nodes participate in the repair process.
[0036] It mainly includes the following steps: there are many storage nodes in the distributed storage system, assuming that there are n storage nodes in the distributed storage system, each storage node stores a data block, and every 8 storage nodes are regarded as a minimum coding structure C, where C=D·G, D=[d 11 , d 12 ,...,d ij ,...,d tj ], d ij j data blocks stored for the i-th partial repair group, i represents the i-th partial repair group, i≤t, j represents the number of data blocks stored in the local repair group, 1≤j≤4 and is an integer; there are t local repair groups, G=[I|P] represents the generation...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This embodiment provides a storage node failure recovery method in a distributed storage system, including the following steps:
[0045] Step 1: Encoding all n storage nodes in the distributed storage system by using the local repair encoding method described in Embodiment 1;
[0046] Step 2, storage node failure repair;
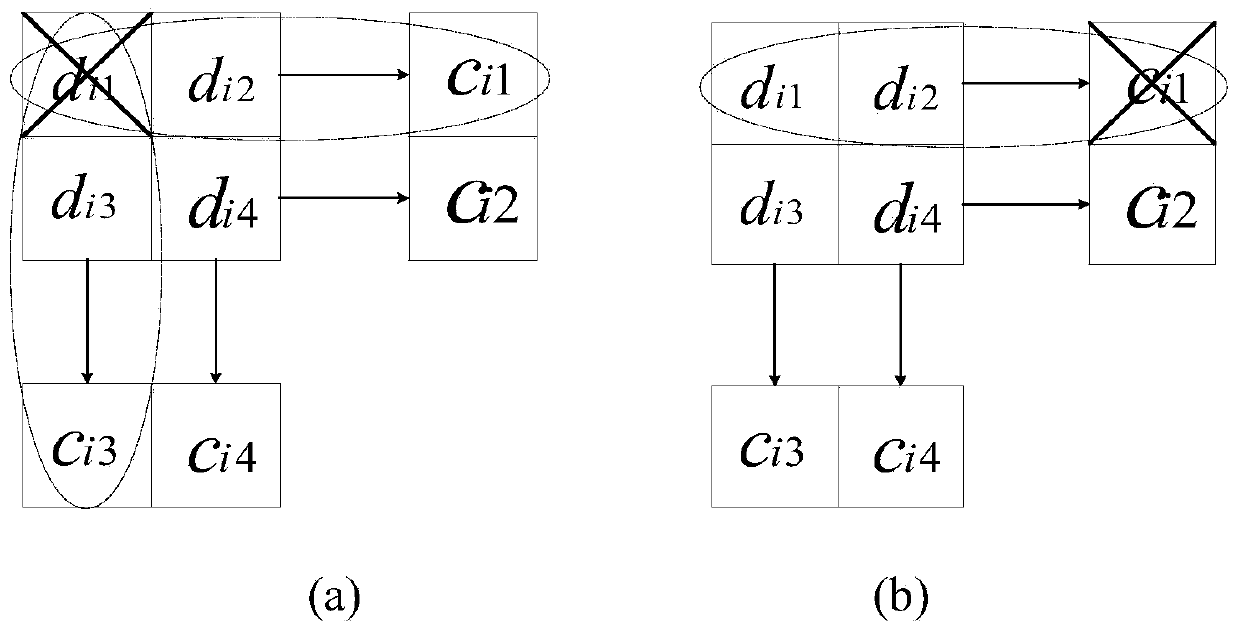
[0047] Assume that in the i-th local repair group of t local repair groups, there is a storage node failure, and the non-failure storage node is a surviving storage node; the i-th local repair group contains four data blocks d i1 、d i2 、d i3 and d i4 and four check blocks c i1 、c i2 、c i3 and c i4 , where d i1 、d i2 、d i3 and d i4 It is a data block arranged in two rows and two columns, c i1 for d i1 and d i2 Generated by linear encoding of the generator matrix G, c i2 for d i3 and d i4 Generated by linear encoding of the generator matrix G, c i3 for d i1 and d i3 Generated by linear encoding of the generator matrix G, c i4 for d ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Such as Figure 4 , the present embodiment assumes that there are 8 storage nodes in the distributed storage system, and the Pyramid code is constructed in a storage structure in which the minimum coding structure is 8 storage nodes, and D=[d 1 , d 2 , d 3 , d 4 ] represents the data block stored by the storage node in the minimum coding structure, where d 1 , d 2 , d 3 , d 4 respectively represent the information of a single data block; G=[I|P] represents the generator matrix required to generate the coded data block C, where I is the identity matrix and P is the 4×4 sub-matrix. Then C is recorded as: C=[d 1 , d 2 , d 3 , d 4 ,c 1 ,c 2 ,c 3 ,c 4 ],
[0057] Generate matrix here
[0058]
[0059] where the variable g 12 , g 13 , g 21 , g 24 , g 31 , g 34 , g 42 and g 43 Indicates the coding coefficient of the Pyramid code. The expression of the check block can be known from the generator matrix, c 1 =g 12 d 1 +g 21 d 2 , c 2 =g 34 d 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com