Dual-core dual-drive flood forecast method
A flood forecasting and flooding technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical and digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of complex model structure, many parameters, and many input data, etc., to achieve simple methods, improve accuracy, and reduce uncertainty. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
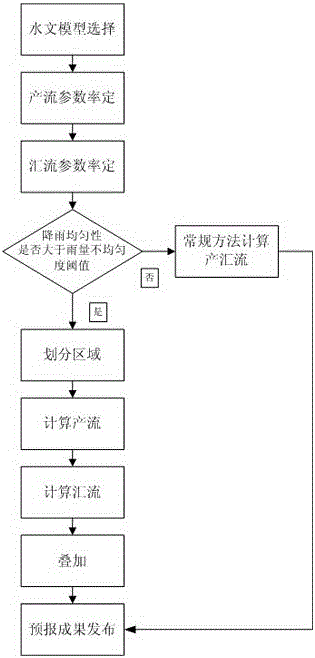
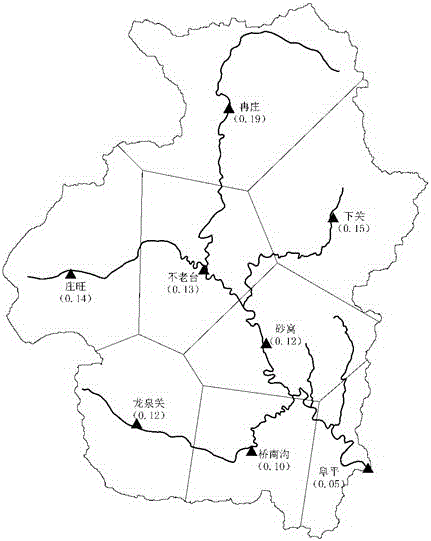
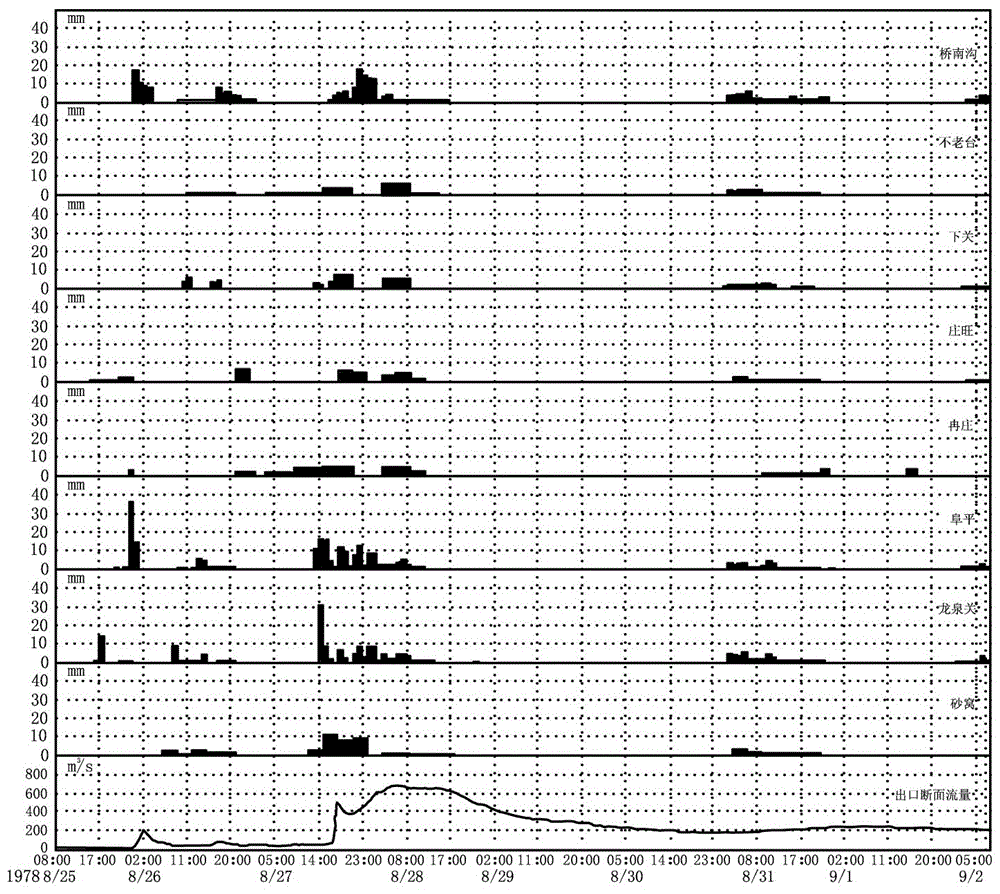
[0035] This embodiment is a dual-core and dual-drive flood forecasting method for the uneven rainfall threshold of the runoff model. The process is as follows figure 1 shown. For a specific non-uniform rainfall, the rainfall is always concentrated in a certain area of the watershed. This area has a large amount of rainfall and high intensity, which is the core area of runoff production; while other areas of the watershed have relatively small rainfall and weak rainfall intensity. Or no rainfall occurs at all, resulting in less runoff. According to the characteristics of non-uniform rainfall and runoff, the "dual-core and double-drive" method divides the watershed into a "rainstorm core area" and a "non-rainstorm core area". Then synthesize the total runoff at the outlet section of the basin. However, since only the hydrological stations at the outlet section of the watershed have actual flow data, the key to the "dual-core dual-drive" method is to solve the problem of c...
Embodiment 2
[0073] This embodiment is an improvement of the first embodiment, and is a refinement of the first embodiment on the runoff model and the confluence model. The runoff model described in this embodiment is: three water sources full storage runoff model SMS_3, and the confluence model is: three water sources lag calculation model LAG_3.
[0074] SMS_3 is a lumped conceptual hydrological model that has been widely used in humid and sub-humid regions in many countries. The model adopts the concept of full storage runoff, and believes that during the rainfall process, runoff can only be produced when the water storage in the aerated zone reaches the field capacity. After runoff production, the part of the rainfall that exceeds the infiltration intensity forms surface runoff, the infiltration part is underground runoff, and the underground part is divided into soil midflow and underground runoff according to the speed of water retreat. The model proposes the concept of watershed st...
Embodiment 3
[0076] This embodiment is an improvement of the above embodiment, and is a refinement of the calculation method of the rainfall non-uniformity coefficient in the above embodiment. The coefficient of rainfall unevenness described in this example PU Calculated according to the following formula:
[0077]
[0078] in: PS It is the rainfall of runoff when the watershed is the driest, and its value is equivalent to the average maximum soil water storage capacity of the watershed, N is the total number of rainfall stations in the basin, large ( N , i ) is a statistical function that returns the number i the maximum accumulated rainfall value, the same small ( N , j ) is a statistical function that returns the number j minimum cumulative rainfall value, n with m is the maximum and minimum number of rainfall stations selected, and its value can be selected according to the total amount of rainfall stations in the basin. Generally, n with m The control area should be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com