Identification method for clubroot resistance of alpine radish at seedling stage
A technology of clubroot resistance and identification method, applied in the field of identification, can solve problems such as dehydration, rot, death, etc., and achieve strong disease resistance and improve the effect of resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1 Alpine white radish type
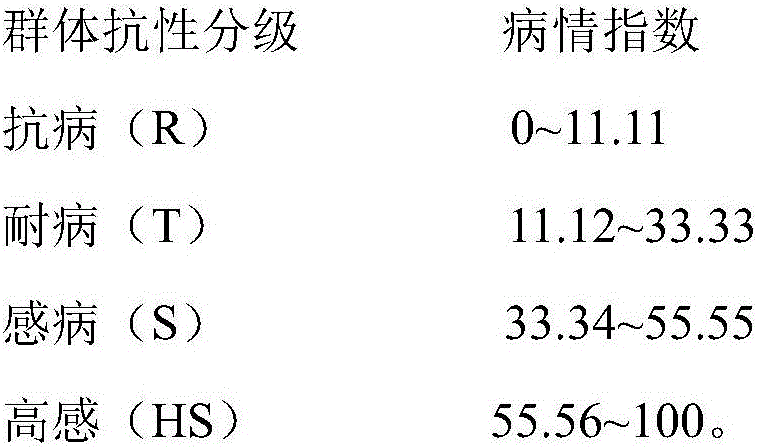
[0056] White-skinned radish participated in 49 test materials, including 20 disease-resistant materials, 18 disease-resistant materials, 12 disease-susceptible materials, and 3 high-sensitivity materials.
[0057]
[0058]
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2 Alpine red-skinned radish type
[0060] There were 8 test materials of red radish, including 4 parts of disease-resistant materials, 1 part of disease-resistant materials, 3 parts of susceptible materials, and 0 parts of high-susceptibility materials.
[0061]
[0062]
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3 Alpine green-skinned radish type
[0064] Green-skinned radish participated in 15 materials, including 4 parts of disease-resistant materials, 5 parts of disease-resistant materials, 5 parts of susceptible materials, and 1 part of high-susceptibility materials.
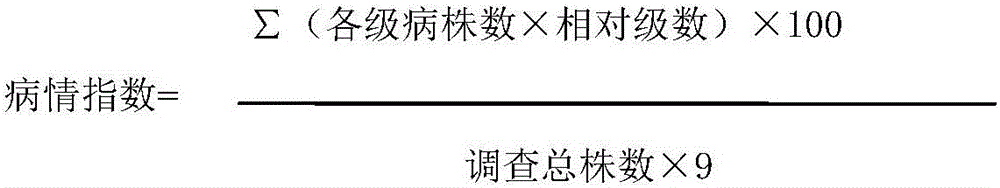
[0065] Numbering product name Diseased strain Total number of plants Disease index 1 Jiaozhou Daqing 15 15 37.78 2 high sugar green 16 16 11.11 3 Candied greens 14 14 11.11 4 Improved Huangzhou 15 15 11.11 5 Silver Daqing 15 15 55.56 6 Green Crisp 50 16 16 30.56 7 spring and autumn polysaccharide brittle 13 13 33.33 8 Yufeng Daqing 16 16 44.44 9 Nanxiang 18 18 35.80 10 Taiyuan 60 early 15 15 15.56 11 Zhao Fuqing 16 16 33.33 12 Deutschland II 14 14 11.11 13 outcropping 15 15 46.67 14 Xinuoqing 30 30 37.78 15 Tender head green-5 series 12 16 16.67 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com