A method for simultaneous determination of glutathione and free amino acids in shellfish
A technology of free amino acid and glutathione, which is applied in the field of simultaneous determination of glutathione and free amino acid in shellfish, can solve the problem that there is no fast and effective method for simultaneous determination, and achieves the advantages of separation, measurement of a wide range of The effect of accurate measurement data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040]Preparation of mixed standard solution: Accurately weigh 76.83 mg of glutathione standard substance, dilute it to a 100 ml volumetric flask with ultrapure water to obtain a 2.5 μmol / ml standard solution, accurately take out 2 ml of the mixed solution, add 2 ml2. 5μmol / mL mixed solution containing multiple standard amino acid components, dilute to 50ml with ultrapure water, that is, 0.10μmol / mL mixed standard solution, and store in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0041] Preparation of buffer:
[0042] (1) Preparation of B1 reagent: Weigh 6.0g of sodium citrate dihydrate, 7ml of 1mol / L sodium hydroxide, 5.66g of sodium chloride, 19.80g of citric acid, and 135.0ml of ethanol, mix thoroughly and dilute to volume with ultrapure water to 1 L at a pH of 3.5;
[0043] (2) Preparation of B2 reagent: Weigh 7.80g of sodium citrate dihydrate, 20ml of 1mol / L sodium hydroxide, 7.07g of sodium chloride, 22.00g of citric acid, and 25.0ml of ethanol, mix thoroughly and dilute to volume with ul...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Preparation of buffer:
[0053] (1) Preparation of B1 reagent: Weigh 6.40g of citric acid dihydrate, 6ml of 1mol / L sodium hydroxide, 5.66g of sodium chloride, 21.50g of citric acid, and 135.0ml of ethanol. 1L, pH 3.1;
[0054] (2) Preparation of B2 reagent: Weigh 7.60g of citric acid dihydrate, 20ml of 1mol / L sodium hydroxide, 7.07g of sodium chloride, 24.00g of citric acid, and 25.0ml of ethanol. 1L, pH 3.0;
[0055] (3) Preparation of B3 reagent: Weigh 13.31g of citric acid dihydrate, 3.74g of sodium chloride, 15.60g of citric acid, and 9.0ml of ethanol, mix well, and dilute to 1L with ultrapure water, with a pH of 4.0;
[0056] (4) Preparation of B4 reagent: Weigh 26.80 g of citric acid dihydrate, 54.35 g of sodium chloride, and 6.30 g of citric acid and mix them thoroughly, then dilute to 1 L with ultrapure water, and the pH is 4.5;
[0057] (5) Preparation of B5 reagent: Weigh 8.0 g of sodium hydroxide and 100.0 ml of ethanol, mix well, and dilute to 1 L with ul...
Embodiment 3
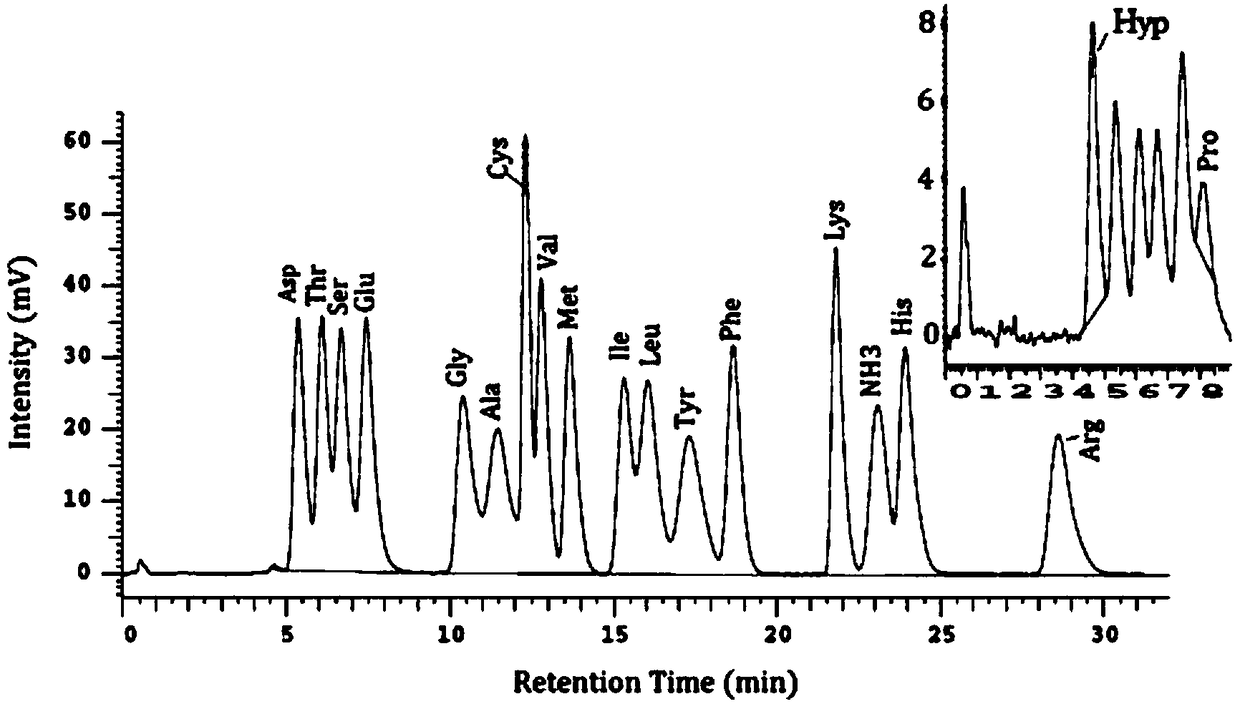
[0063] Take 20 μl of the standard mixed solution obtained in Example 1, use the original reagent and its system parameters, measure it with an automatic amino acid analyzer, perform 3 parallel experiments, and take the average value of the measurement results. Specific test results such as figure 1 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com