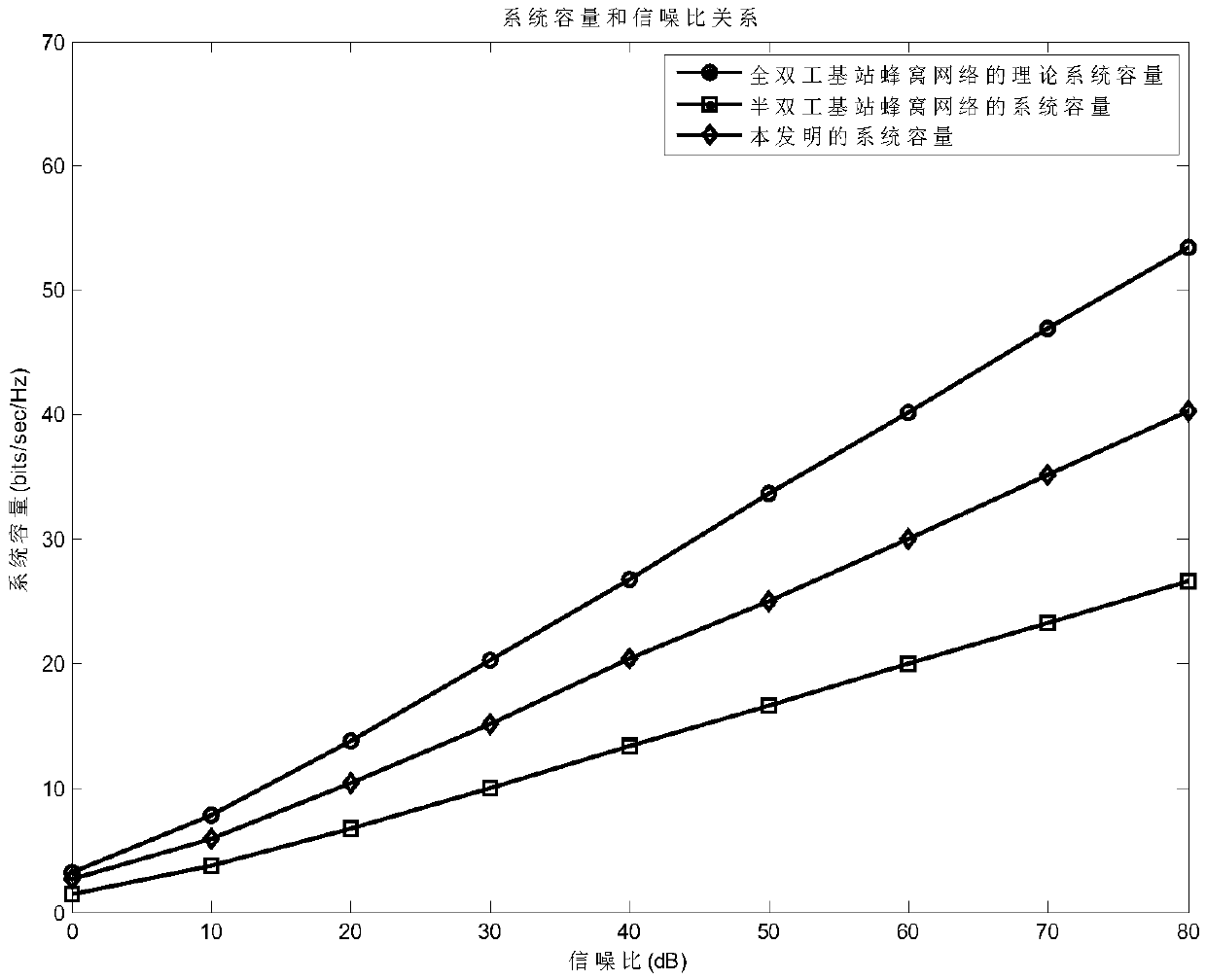
A Time Division Interference Alignment Method for Full-duplex Base Station Cellular Networks
A cellular network, interference alignment technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of reducing system rate, high overhead, incompatibility of single-antenna users, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing compatibility and overcoming incompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0051] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
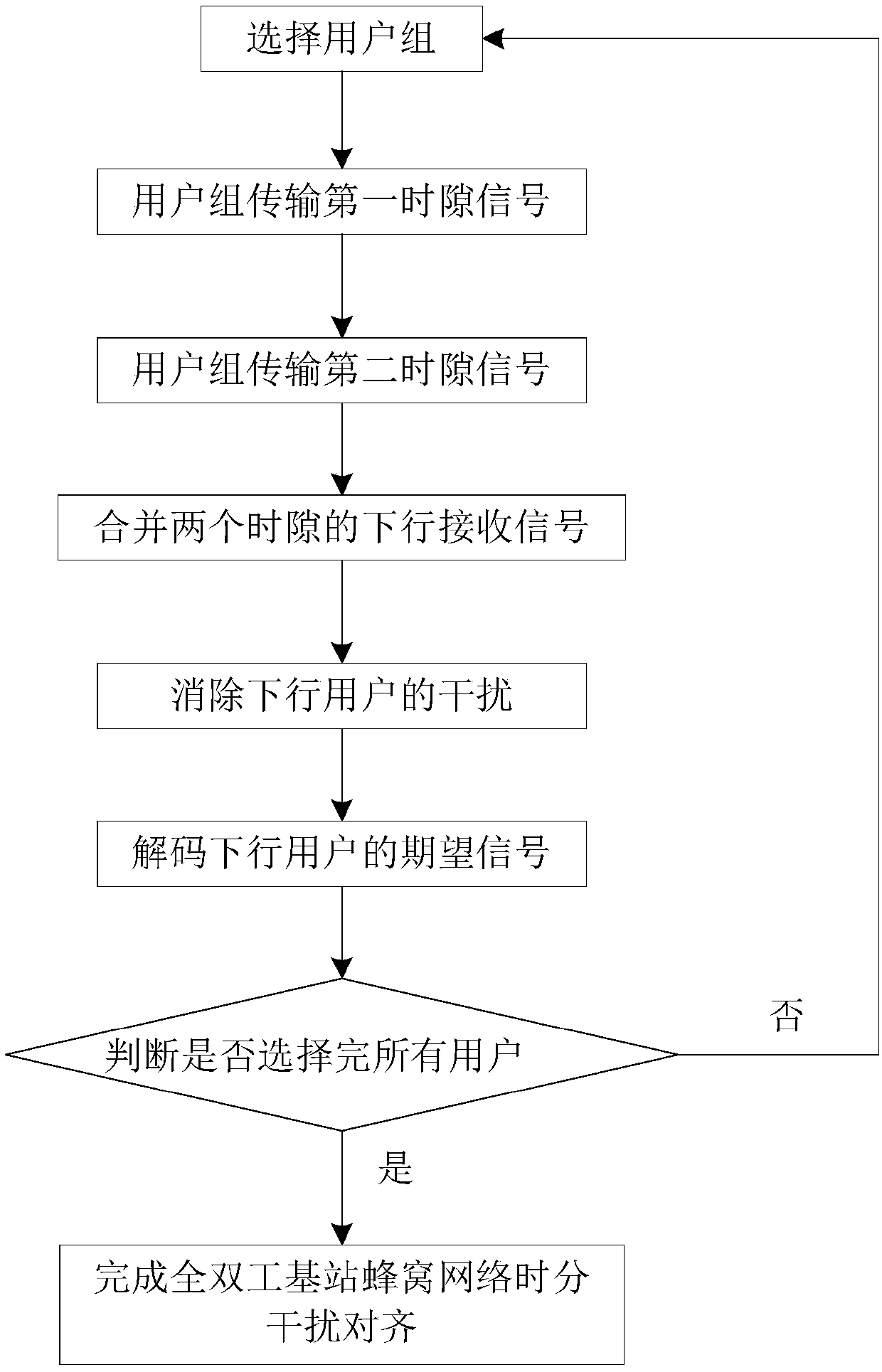
[0052] Refer to attached figure 1 , to further describe the specific steps for realizing the present invention.
[0053] Step 1. Select a user group.
[0054] Randomly select one uplink user from all the uplink users of the full-duplex base station cellular network, randomly select two downlink users from all the downlink users of the full-duplex base station cellular network, and combine the selected one uplink user and the two downlink users A user group.
[0055] The number of uplink and downlink antennas at the base station is both M, and the number of antennas at the uplink and downlink user terminals is also M, where M≥1, and M=1 is adopted in the embodiment of the present invention.
[0056] Step 2, the user group transmits the signal of the first time slot.
[0057] Uplink users in the user group send uplink signal s to the base station 1 .
[0058] The b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com