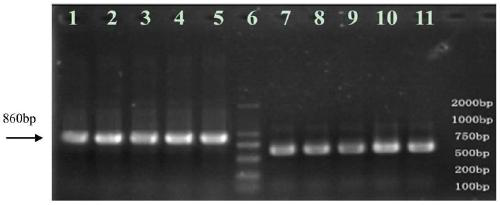
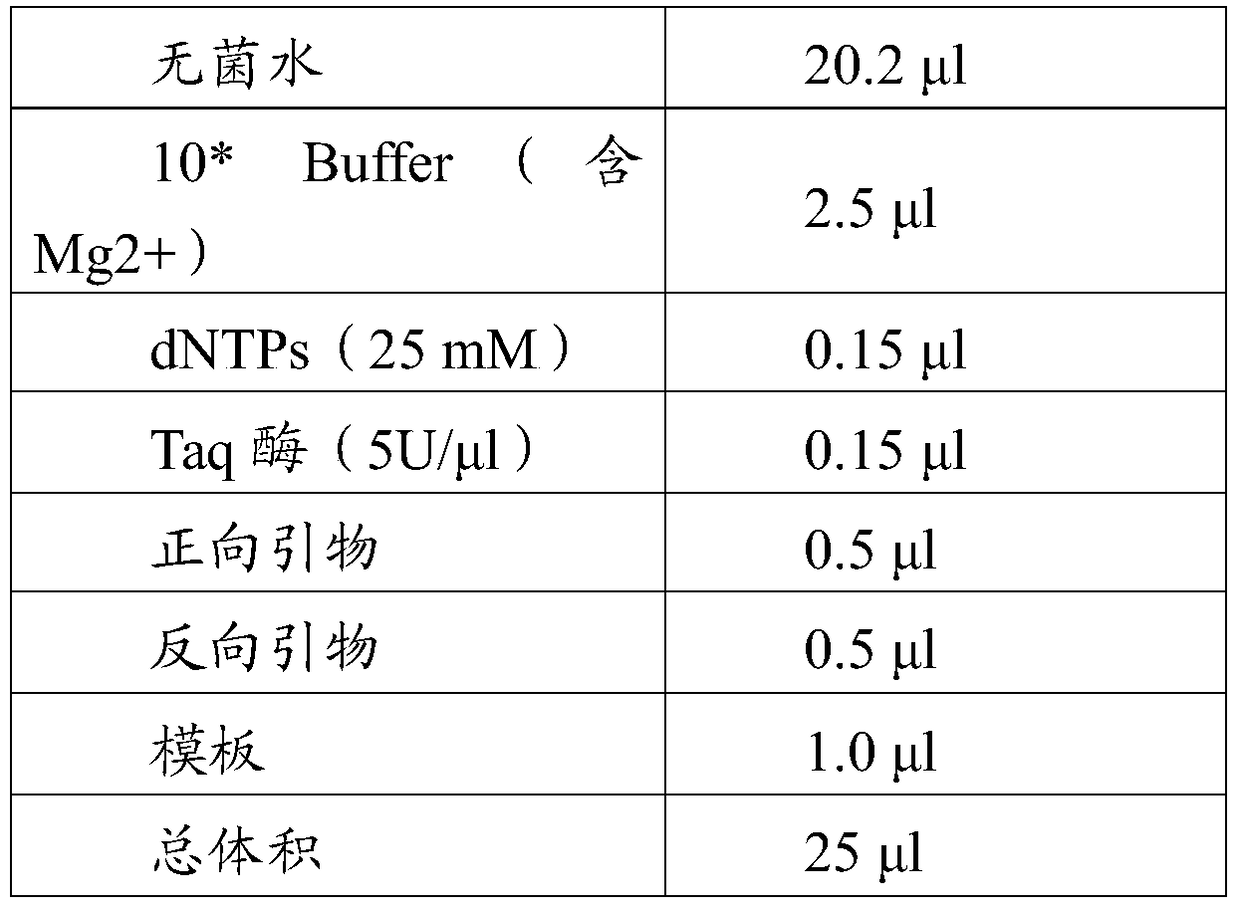
Molecular marker osblb-sv1 tightly linked to rice bacterial blight resistance gene
A technology of resistance to bacterial blight and molecular markers, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as the complexity and lack of genetic mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: Construction of rice RIL population
[0040] Male parent: 801, resistant to bacterial blight, purchased from Shenzhen Huada Agriculture and Circular Economy Technology Co., Ltd.
[0041] Female parent: R15, not resistant to bacterial blight, purchased from Shenzhen Huada Agriculture and Circular Economy Technology Co., Ltd.
[0042] RIL population construction: The F1 generation was obtained by crossing the male parent and the female parent, and 188 recombinant inbred RIL strains (F7 generation) were obtained from the F1 generation by single seed transmission.
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: rice bacterial blight inoculation identification
[0044] A representative strain of dominant pathogenic type IV of bacterial blight of rice in Hunan Province (gifted by Hunan Hybrid Rice Research Center) was selected. Cultivate the strain with Wakimoto Tetsu's potato semi-synthetic medium at a constant temperature of 28°C for 72 hours, wash the bacterial lawn with sterile water, and dilute the bacterial suspension to 10 by McNerbidimetric method. 8 ~10 9 cells / ml of bacteria solution.
[0045] Wakimoto Tetsu’s potato semi-synthetic medium formula: 300 grams of potatoes, 15 grams of sucrose, 5 grams of peptone, 0.5 grams of Ca(NO3)2.4H2O, 2.0 grams of Na2HPO4.12H2O, 16 grams of agar powder, adjusted to 1000 ml with distilled water .
[0046] For the RIL population obtained in Example 1, the artificial leaf-cutting inoculation method was used to inoculate at the seedling stage of the plant, and 14 to 20 days after inoculation, the investigation was perfo...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Extraction of Genomic DNA from Parents and RIL Individual Plants
[0050] The genomic DNA of the parents and 188 RIL individual plants were extracted by CTAB method, the specific method is as follows:
[0051] (1) Weigh 1.0g of fresh leaves, cut them into pieces and put them into a mortar, grind them with liquid nitrogen, add 3mL1.5×CTAB, grind them into a homogenate and transfer them to a 15mL centrifuge tube, then add 1mL1.5×CTAB into the mortar Wash with ×CTAB and transfer to a centrifuge tube. After mixing, place in a water bath at 65°C for 30 minutes, and shake slowly from time to time during this period.
[0052] Among them, the formula of 1.5×CTAB is as follows (1L):
[0053] CTAB
15g
1mol / L Tris.Cl (pH 8.0)
75mL
0.5mol / L of EDTA
30mL
NaCl
61.4g
[0054] Add deionized water to make up to 1 L, and add mercaptoethanol with a final concentration of 0.2% (2 ml) before use.
[0055] (2) After cooling to r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com