Calculating method for electric current field distribution of soil grounds in partitions and layers
A technology of partition layering and calculation method, applied in the field of high-voltage electricity, can solve problems such as difficulty in finite element calculation, and achieve the effect of avoiding inaccurate calculation and simple calculation method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
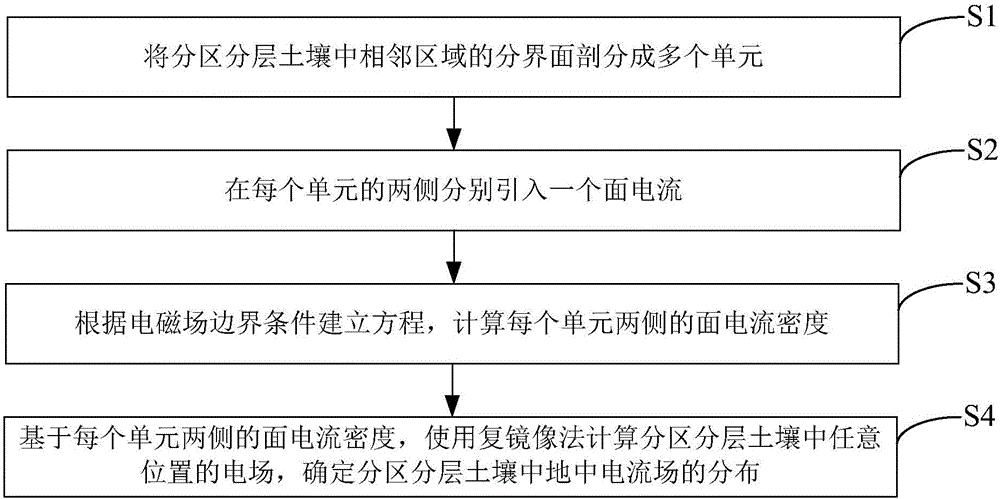
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a calculation method for the distribution of the ground current field in the divided and layered soil, which is used to calculate the ground current generated in the ground by the grounding device of electrical engineering (including substations, converter stations, towers, grounding poles, etc.) A wide range of voltage distribution; which includes:
[0041] S1. Divide the interface of adjacent areas in the partitioned and layered soil into multiple units, and the units meet the unique boundary condition. The only boundary condition is that the soil resistivity of any side of the area on both sides of the unit is unique.
[0042] S2. Introduce a surface current on both sides of each unit, and the surface currents on both sides correspond to the regions on both sides of the unit;
[0043] S3. Establish an equation according to the electromagnetic field boundary conditions, and calculate the surface current densit...
Embodiment 2
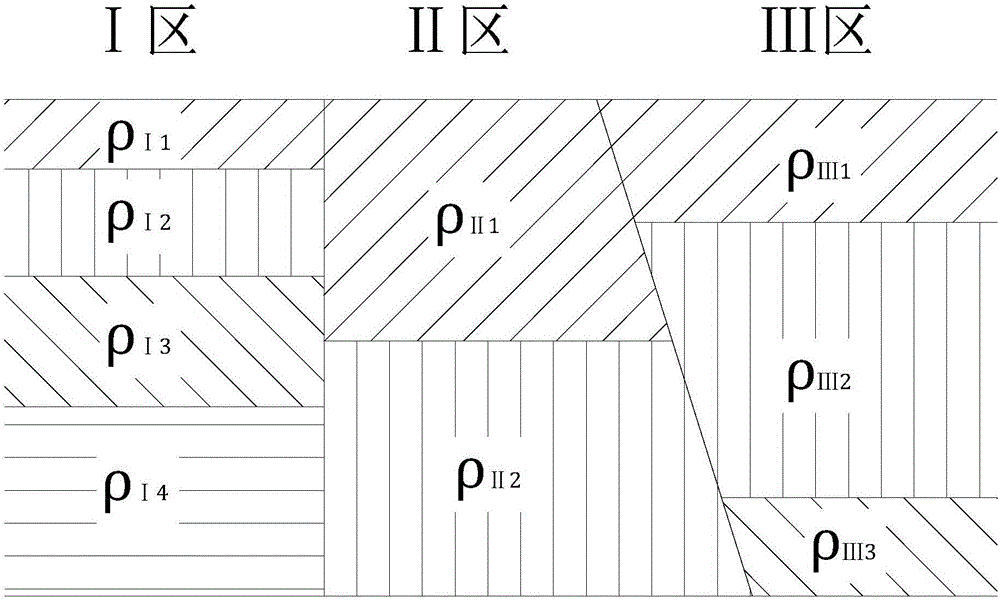
[0064] Algorithm of the present invention and the calculation result of COMSOL software are contrasted, and the soil condition of each partition and conductor location are as follows: Figure 6 shown; Figure 6 Among them, the soil in area Ⅰ is divided into two layers in the horizontal direction. The soil resistivity of the first layer is 10Ω·m, the thickness is 300m, and the resistivity of the second layer is 100Ω·m. The resistivity of the second layer is 50Ω·m and the thickness is 100m. The resistivity of the second layer is 20Ω·m and the thickness is 400m. The resistivity of the third layer is 500Ω·m. The resistivity is 100Ω·m, the thickness is 200m, and the resistivity of the second layer of soil is 1000Ω·m. The position of the conductor and the position of the observation line are the same as in Example 1. The calculation result of the inventive method and the calculation result of COMSOL are as Figure 7 shown.
[0065] From Figure 7 It can be seen that when the so...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com