A method for fabricating low-friction superhydrophobic surface-enhanced Raman substrates using micro-nanoparticle coatings
A technology of micro-nano particles and super-hydrophobic surface, applied in the field of analysis and detection, can solve the problems of complex preparation process, insufficient sensitivity and repeatability, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Weigh 6 g of commercial silica pellets with a diameter of 1 μm and 100 nm each, and disperse them in 99 g of absolute ethanol, then add 1 g of 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecylmercaptan, and stir for 2 hours. Put the stirred suspension into the paint tank of a commercial air pump airbrush, and spray it on the glass to form a uniform liquid film; after the absolute ethanol volatilizes, heat the glass to 160°C for 5 hours, and the surface is coated Multiscale micro-nanospheres of 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorodecylthiol form uniform superhydrophobic coatings. The silver with a thickness of 40nm is slowly deposited on the coating by vacuum thermal evaporation, and the deposition rate is about 2nm / min. This substrate has good low-friction superhydrophobicity, can effectively realize the SHD effect, and finally realize the Raman detection of trace analytes.
Embodiment 2
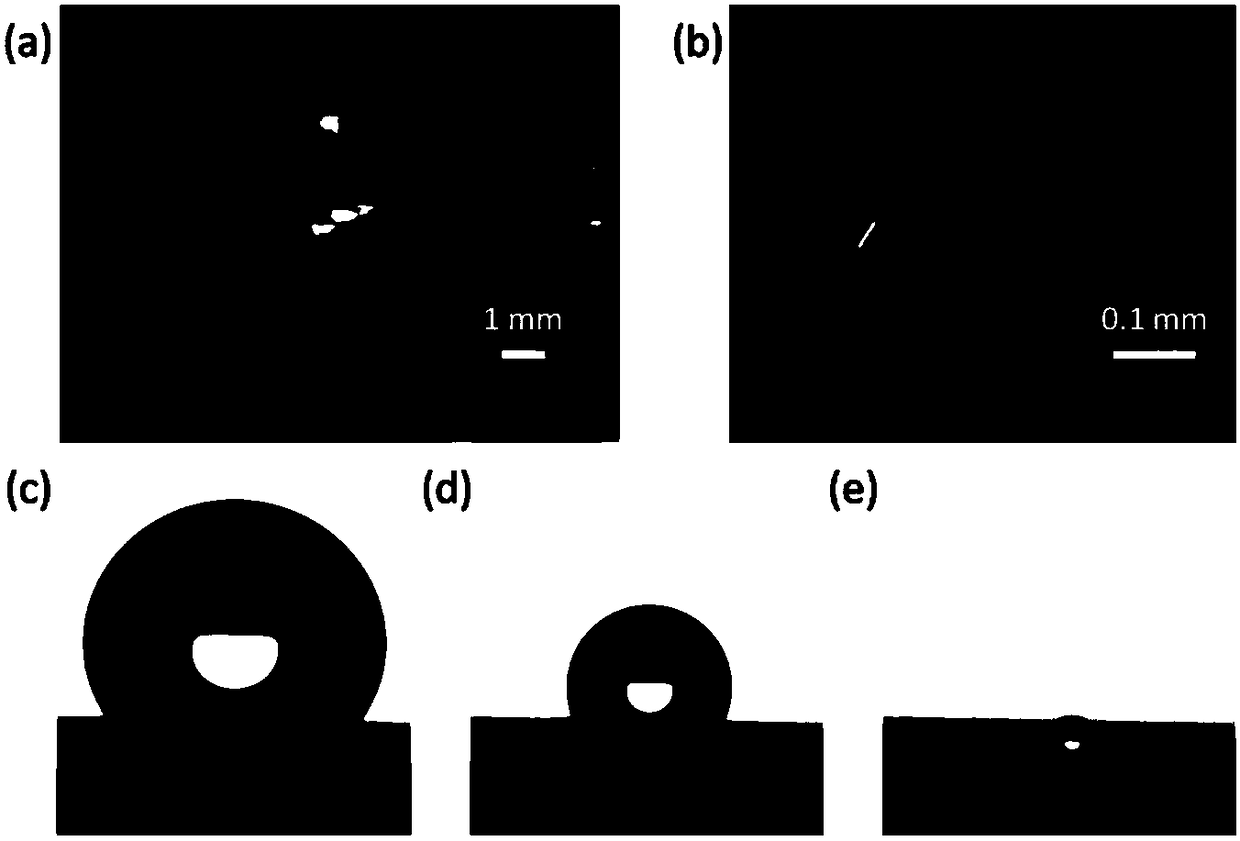
[0037] Such as figure 2 As shown in (a), 15 μL of rhodamine 6G (R6G) solution was dropped on the surface of the substrate prepared in Example 1, almost in a spherical shape with a diameter of 3.34 mm. After the solvent evaporates to dryness, the figure 2 As shown in (b), R6G molecules are deposited in an approximately circular region with a diameter of 0.34 mm. From the droplet evaporation process, the contact angle photos at different times ( figure 2 (c)-(e)) It can be seen that due to the sufficiently low frictional force of the substrate surface on the solution, the contact area between the droplet and the substrate gradually decreases during the evaporation and shrinkage process. This phenomenon proves that this substrate has good SHD function.
Embodiment 3
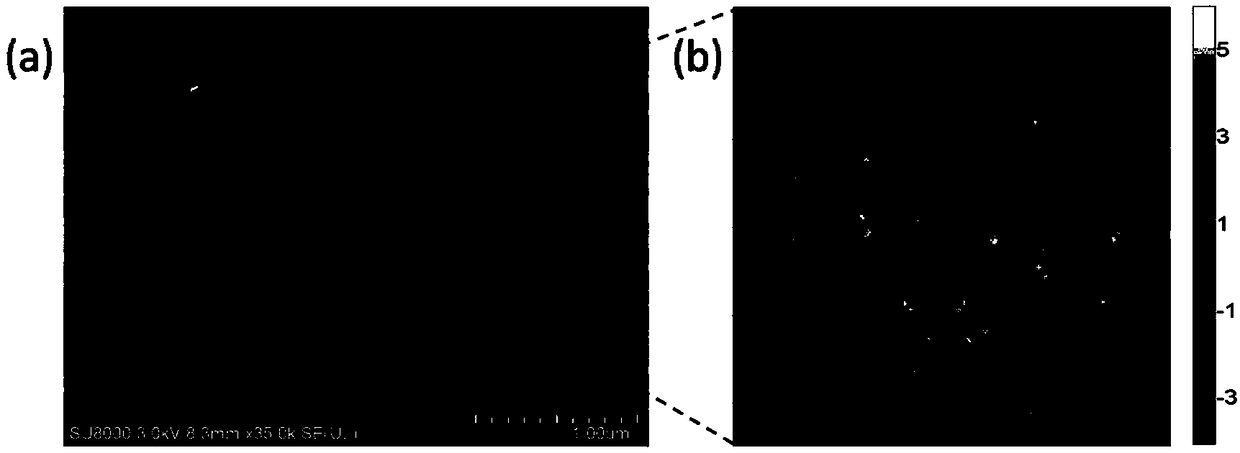
[0039] Using scanning electron microscopy to characterize the microscopic morphology of substrates, such as image 3 (a) shown. Silica spheres with diameters of 1μm and 100nm are aggregated together, and their surface is covered with a mottled silver film. The silver film is not dense and continuous, but is composed of many island structures with a size of tens to hundreds of nanometers. On the one hand, these island structures increase the surface roughness of the substrate, making it maintain good Cayce state superhydrophobic properties; on the other hand, they have good surface plasmon resonance properties. Under laser irradiation, they can form many The sites of the electromagnetic field, they are the SERS hotspots. We simulated the electromagnetic field distribution on a part of Yindao through the finite time domain difference method (FDTD), such as image 3 (b) shown. The brighter areas in the figure represent higher electromagnetic field strengths. Most of these re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com