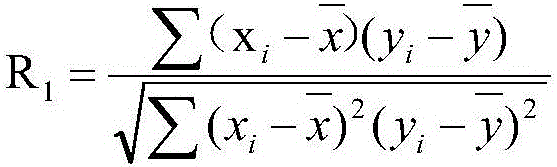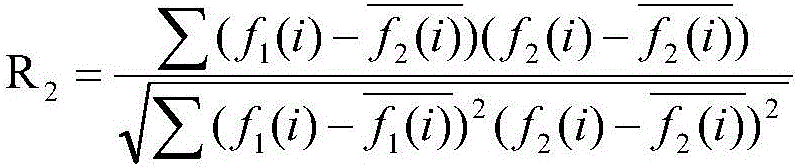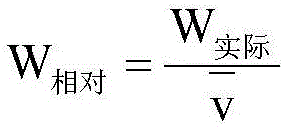Wind generating set performance assessment method based on correlation analysis
A technology for wind turbines and correlation analysis, applied in wind turbines, wind turbine monitoring, engines, etc., can solve the problems of lack of comparison means, not reaching 180 billion kWh, and different wind conditions of wind turbines. Evaluate the effect of reliable results and exclusion of influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] In this embodiment, the method for evaluating the performance of wind power generators based on correlation analysis includes the following steps:
[0046] S1. Collect data through the big data platform, the data is the wind speed, power, actual power generation, turbulence intensity, wind direction and average wind speed of different types of wind turbines in time sequence;
[0047] S2. Determine the generator set to be analyzed, and extract the wind speed, power, actual power generation, turbulence intensity, wind direction and average wind speed of all models of the generator set to be analyzed from the big data platform;
[0048] S3. Use the time-ordered wind speeds of different units to perform correlation analysis on the units that need to be determined:
[0049] S31. Suppose the wind speed sequence of the generator set to be analyzed in time order is x i , the wind speed sequence of the time-ordered unit that needs to determine the correlation is y i , then the...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The present embodiment is similar to embodiment 1, and its difference only lies in:
[0080] S5. Calculate the average value of the relative power generation. When the relative power generation of the generating set to be analyzed is lower than 80% of the average generating capacity, the performance of the generating set to be analyzed is not good and urgently needs rectification, wherein k is a constant.
[0081] In step S5, the calculation method of the average value of the relative power generation is as follows:
[0082]
[0083] Wherein, n is the number of generating units screened by S4, and in this embodiment, k=0.8, when the number of generating units to be analyzed , the performance of the unit to be analyzed is poor.
[0084] The larger the value of k, the stricter the evaluation of the unit, so when k is 0.8, the evaluation of the unit is more relaxed and not strict.
Embodiment 3
[0086] This embodiment is similar to embodiment 1 and / or embodiment 2, and its difference only lies in:
[0087] S5. Calculate the average value of the relative power generation. When the relative power generation of the generating set to be analyzed is lower than 90% of the average generating capacity, the performance of the generating set to be analyzed is not good, and rectification is urgently needed, wherein k is a constant.
[0088] In step S5, the calculation method of the average value of the relative power generation is as follows:
[0089]
[0090] Wherein, n is the number of generating units screened by S4, and in this embodiment, k=0.9, when the number of generating units to be analyzed , the performance of the unit to be analyzed is poor.
[0091] The larger the value of k, the stricter the evaluation of the unit, so when k is 0.9, the evaluation of the unit is stricter.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com