Rotating electric machine control device
A technology for rotating electrical machines and control devices, which is applied in motor control, AC motor control, control systems, etc., and can solve problems such as control without description
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
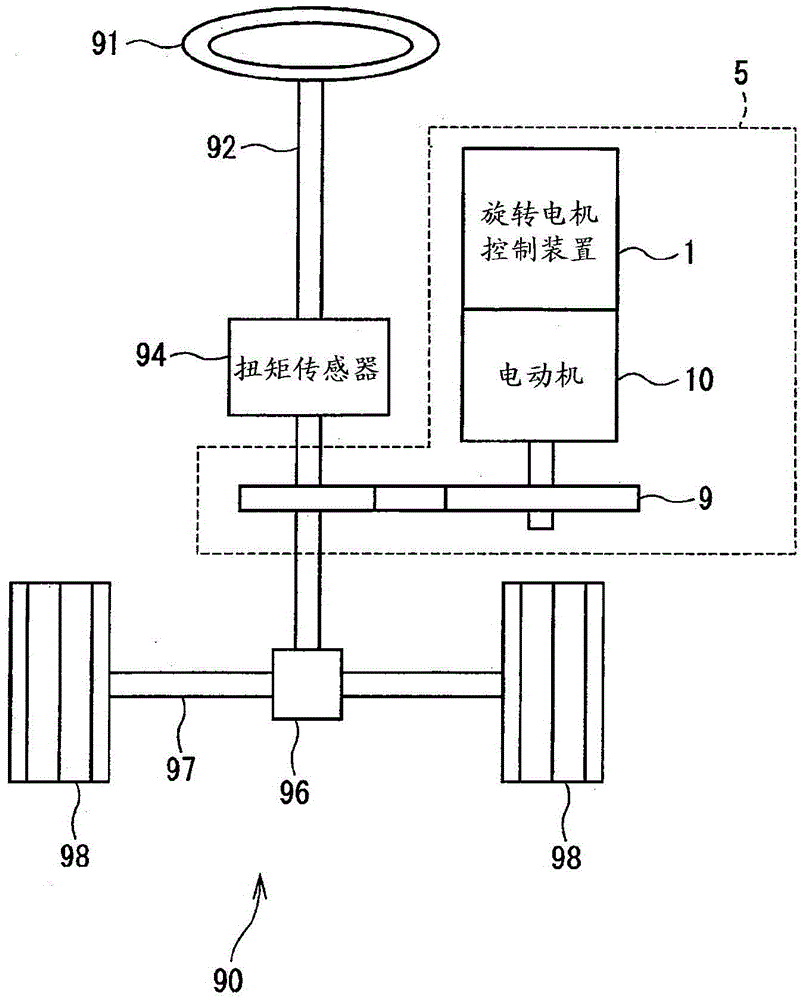
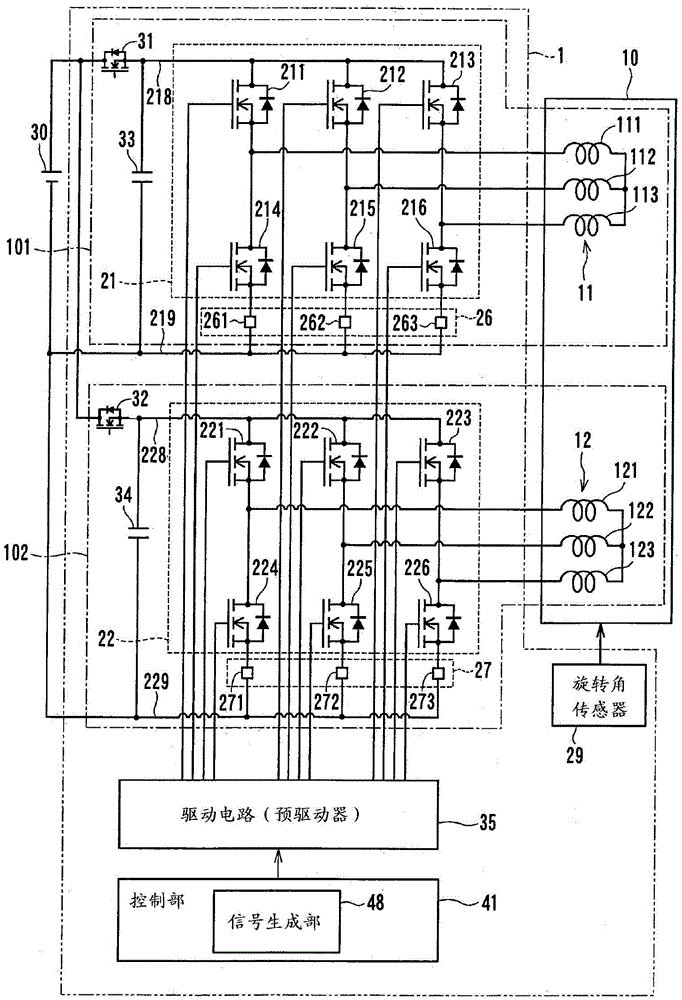
[0020] Figure 1 to Figure 3 A rotating electric machine control device according to a first embodiment of the present disclosure is shown. The rotating electric machine control device 1 of the present embodiment is applied to an electric power steering apparatus 5 for assisting a driver's steering operation together with an electric motor 10 as a rotating electric machine.
[0021] figure 1 An overall configuration of a steering system 90 provided with the electric power steering device 5 is shown. The steering system 90 has a steering wheel 91 , a steering shaft 92 , a pinion 96 , a rack shaft 97 , wheels 98 , an electric power steering device 5 , and the like.
[0022] The steering wheel 91 is connected to a steering shaft 92 . The steering shaft 92 is provided with a torque sensor 94 for detecting a steering torque input by the driver operating the steering wheel 91 . The pinion gear 96 is provided at the tip of the steering shaft 92 and meshes with the rack shaft 97 ....
no. 2 approach
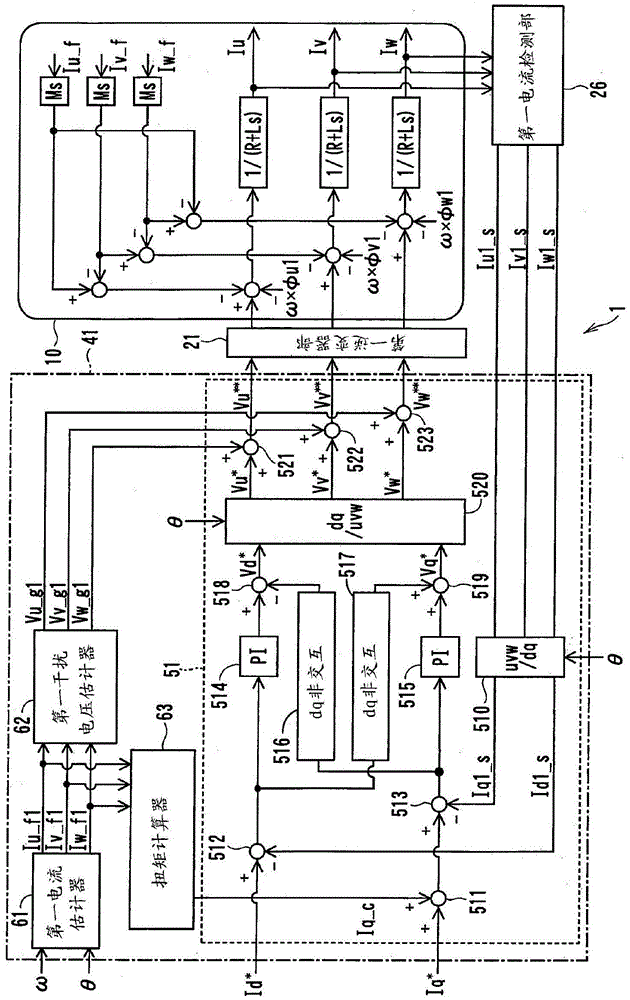
[0101] will refer to Figure 4 A second embodiment of the present disclosure will be described.
[0102] The control unit 42 of the present embodiment includes a command calculation unit 53 , a second disturbance voltage estimator 71 , a bandpass filter 73 , a second current estimator 75 , and a three-phase to two-phase conversion unit 77 .
[0103] The command calculation section 53 has: a three-phase to two-phase conversion section 510, current command value correction sections 531, 532, subtractors 533, 534, controllers 514, 515, dq non-alternative voltage calculation sections 516, 517, non-alternative voltage correction Sections 518 and 519, a two-phase to three-phase conversion section 520, and disturbance voltage correction sections 541, 542, and 543.
[0104] The d-axis current command value correcting section 531 adds the d-axis second current command value Id_f2 and the d-axis current command value Id* to calculate the corrected d-axis current command value Id**, whi...
no. 3 approach
[0153] will refer to Figure 5 A third embodiment of the present disclosure will be described. The difference is that the d-q axis voltage equation is used in the present embodiment, whereas the three-phase voltage equation is used in the second embodiment. Using the d-q axis model instead of the three-phase model allows the number of arithmetic expressions to be reduced.
[0154] as in Figure 5 As shown in , the control unit 43 has: a command calculation unit 55 , a second disturbance voltage estimator 72 , a bandpass filter 74 , and a second current estimator 76 .
[0155]The command calculation section 55 has: a three-phase to two-phase conversion section 510, current command value correction sections 531, 532, subtractors 533, 534, controllers 514, 515, dq non-alternative voltage calculation sections 516, 517, non-alternative voltage correction Sections 518, 519, interference voltage correction sections 551, 552, and two-phase to three-phase conversion section 553.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com