Dynamic closing curve optimizing method of guide vanes
A technology of guide vane closing and optimization method, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of insufficiency and low efficiency of guide vane dynamic closing curve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, this embodiment discloses:
[0042] The method for optimizing the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane includes the following steps:
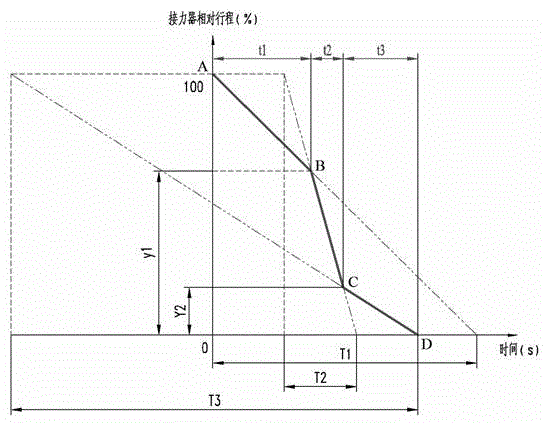
[0043] Step A: Parametrize and vary the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane: the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane is composed of N straight lines; the parameterization and variableization refer to transforming the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane into (2N-1 ) control variables, the (2N-1) control variables include N time variables T 1 , T 2 , T 3 …T N and (N-1) inflection point variables Y 1 , Y 2 , Y 3 ...Y N-1 ; N≥1, N is an integer; T 1 , T 2 , T 3 …T N Respectively refer to the time when the 1st, 2nd, 3rd...N straight line in the guide vane closing curve is closed from 100% of the full stroke to 0 relative to the servomotor; the inflection point variable Y 1 , Y 2 , Y 3 ...Y N-1 Respectively refer to the servomotor travel corresponding to the inte...
Embodiment 2
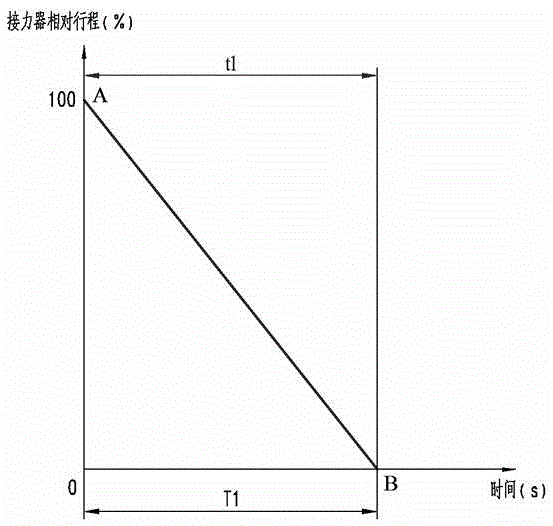
[0058] As another preferred embodiment of the present invention, with reference to the attached figure 1 , this embodiment discloses: when the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane is composed of a straight line, the optimization method for the dynamic closing of a straight line of the guide vane is:
[0059] Step A: Parametrize and change the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane, so that the closing curve of the guide vane can be transformed into the control variable T 1 ,T 1 Refers to the time from 100% of the full stroke to 0 relative to the servomotor;
[0060] Step B: Set T 1 is a one-dimensional array, that is, T 1 =T 1 [M 1 ], length M 1 ;
[0061] Step C: Initialize T 1 [m 1 ](0≤m 1 1 ) to make it from m 1 =0 start loop calculation till m 1 = M 1 -1 ends; one-to-one correspondence will be T 1 [M 1 ] converted to t 1 [m 1 ],t 1 [m 1 ] is the time consumed by the servomotor from 100% off to 0 position;
[0062] Step D: Set the control variable t ...
Embodiment 3
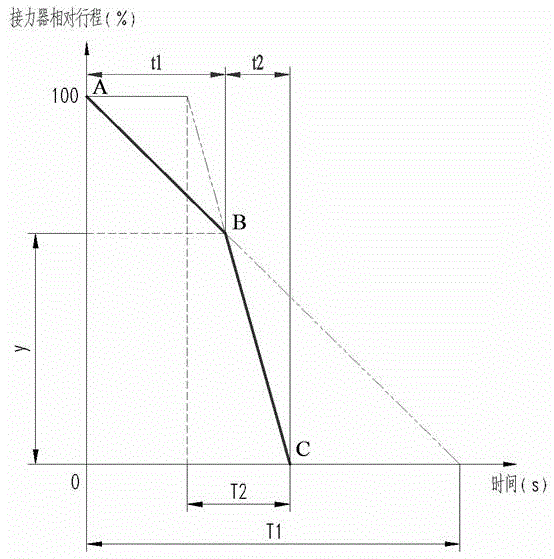
[0065] As another preferred embodiment of the present invention, with reference to the attached figure 2 , this example discloses:
[0066] When the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane is composed of two broken lines, the optimization method for the dynamic closing of the two broken lines of the guide vane is:
[0067] Step A: Parametrize and change the dynamic closing curve of the guide vane, so that the closing curve of the guide vane can be transformed into the control variable T 1 , T 2 and Y 1 ,T 1 Indicates the time when the first segment of the closing line is closed from 100% of the full stroke to 0 relative to the servomotor, T 2Indicates the time when the second segment of the closing line is closed from 100% of the full stroke to 0 relative to the servomotor, Y 1 Indicates the stroke of the servomotor corresponding to the intersection of the first segment and the second segment of the straight line;
[0068] Step B: Set T 1 is a one-dimensional array, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com