Method and system for protecting DRAM stored data of embedded system software
An embedded system and a technology for storing data, which is applied in the direction of data error detection, protection of storage content to prevent loss, and response to error generation, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in meeting the cost requirements of ordinary products, rising system costs, Software errors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with specific embodiments and drawings. In the following description, more details are set forth in order to fully understand the present invention. However, the present invention can obviously be implemented in many other ways different from the description herein. Those skilled in the art can make similar promotion and deduction according to actual application conditions without violating the connotation of the present invention. Therefore, the content of this specific embodiment should not limit the protection scope of the present invention.
[0017] have to be aware of is, figure 1 These are only examples, and they are not drawn on the condition of equal proportions, and should not be taken as limiting the scope of protection actually required by the present invention.
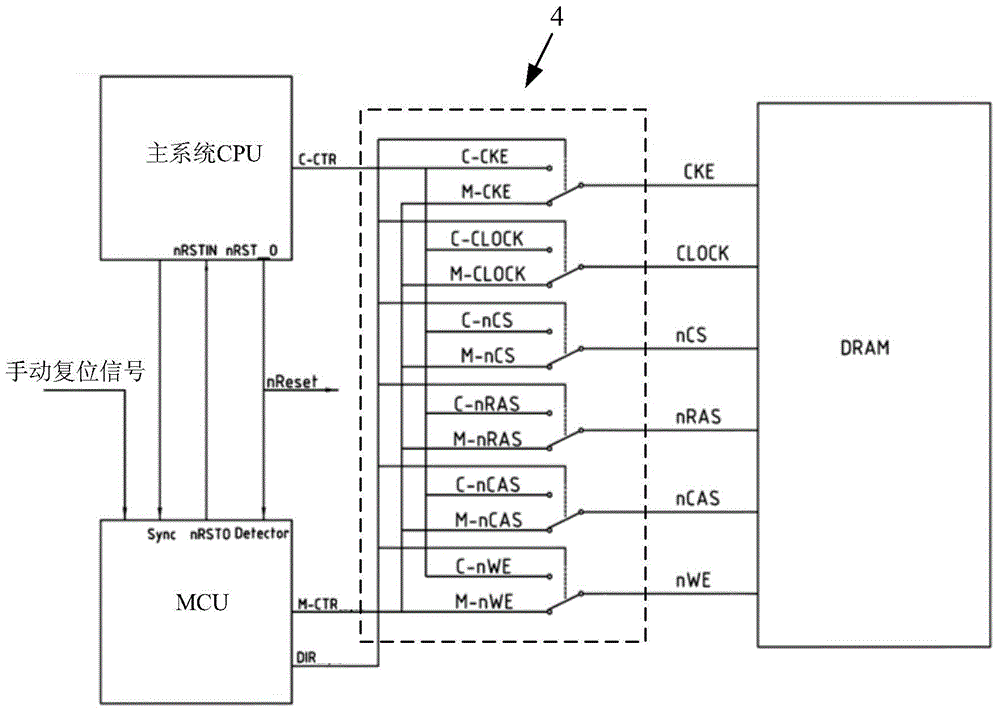
[0018] The DRAM storage data protection system of embedded system software includes the main system CPU and DRAM of the embedded syste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com