UUV route planning method with necessary points under obstacle environment
A technology of route planning and must-pass points, applied in three-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve problems such as unreasonable routes, uncertain costs, and difficult to determine the pros and cons of algorithms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
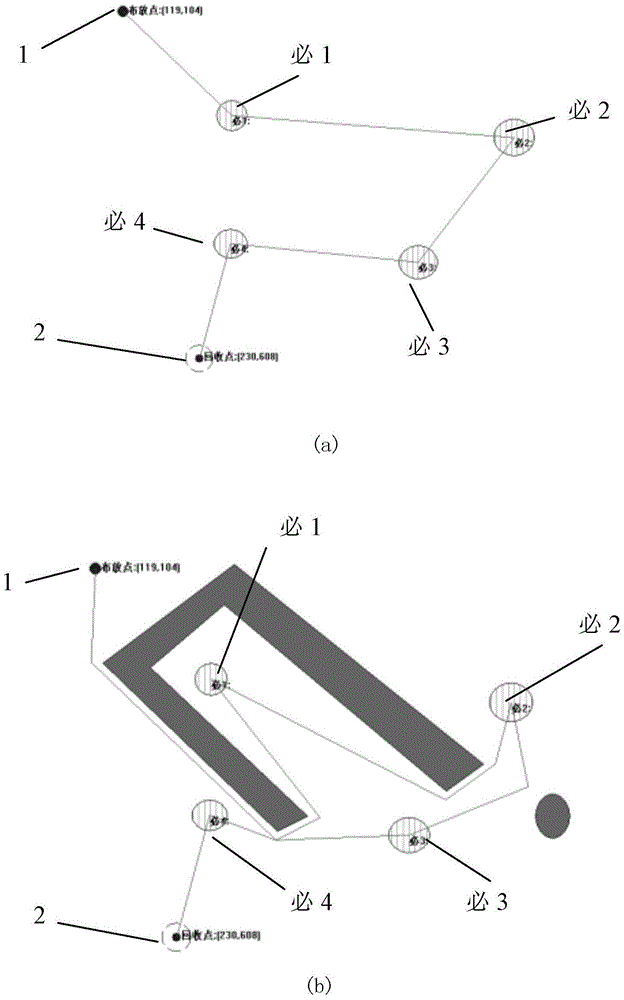
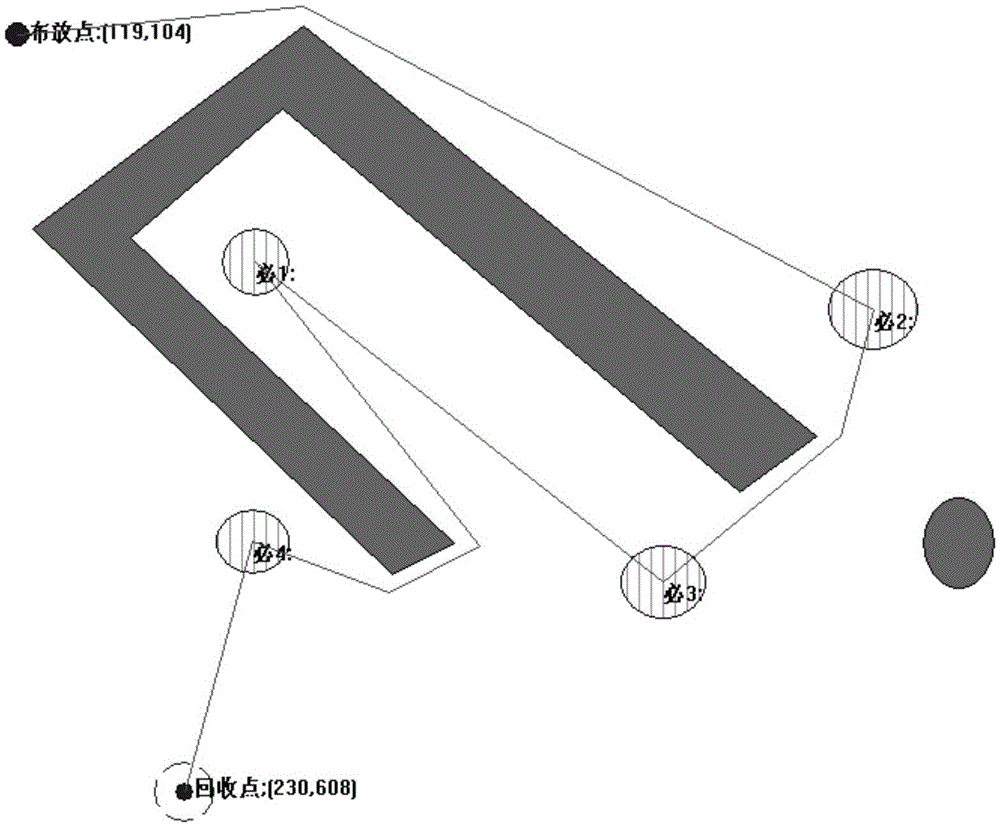
[0027] Specific implementation mode one: as Figure 1~2 As shown, a UUV route planning method with necessary points in an obstacle environment described in this embodiment, the specific process is:
[0028] The obstacle environment where the UUV is located is modeled by a geometric environment model, and the obstacles in the environment are described by closed geometric figures composed of points and lines;
[0029] The implementation process of the UUV route planning method is:
[0030] Step 1. Calculate the estimated distance between the UUV deployment point, the recovery point and all necessary points in the obstacle environment:
[0031] Step 2. With the deployment point as the starting point and the recovery point as the end point, use the TSP (traditional TSP) algorithm to plan the traversal order of all the necessary points for the UUV, so that the UUV starts from the deployment point, traverses all the necessary points, and then returns to The sum of estimated distan...
Embodiment
[0038] For the UUV route planning method with necessary points in the obstacle environment described in the above specific implementation mode, the following embodiments are given:
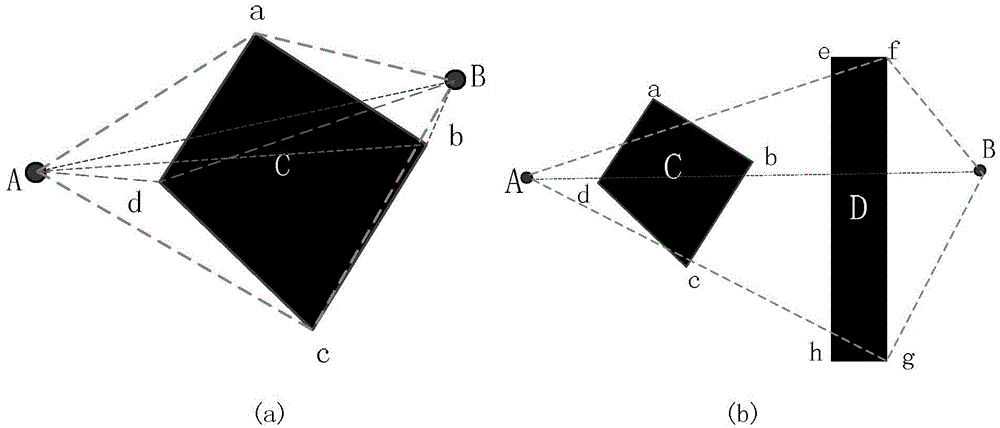
[0039] 1. Estimation method of path cost between two must-pass points
[0040] Such as figure 2 shown. Suppose you want to estimate the path cost between the two necessary points of A and B, the line segment AB intersects with the obstacle C, so the path cost of mutual transfer between A and B cannot directly use the straight-line distance. In this paper, the shortest path required for detour is taken as the transfer cost between A and B. The calculation principle and steps are as follows (with figure 2 (a) as an example):
[0041] 1 According to the coordinates of the necessary points A and B, obtain the AB straight line equation y-Mx-N=0, where Then form an area discriminant function F(x,y)=y-Mx-N that can distinguish a point on the upper side or lower side of the line
[0042] 2 Putti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com