Super-resolution optical imaging method based on laser-induced transient aperture probe
A small hole probe, laser-induced technology, applied in the field of super-resolution optical imaging, can solve the problem of sample damage, achieve the effect of low cost, remarkable imaging effect and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A super-resolution optical imaging method based on a laser-induced transient pinhole probe, the steps of which include:
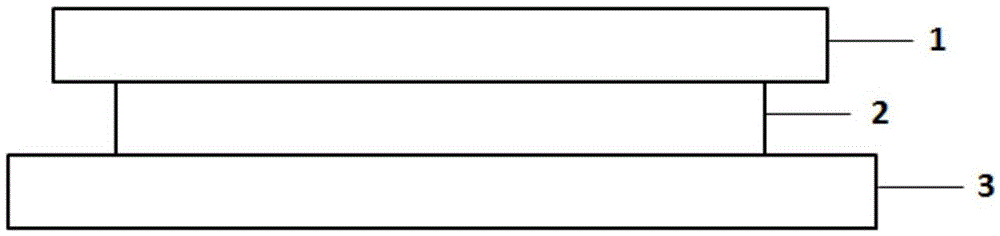
[0036] a) Coating a layer of nonlinear material film 2 on the cover glass 1 by magnetron sputtering;
[0037] b) The above-mentioned cover glass 1 that has been coated with a thin film is closely attached to the surface of the sample 3 to be tested, and the side coated with the thin film is next to the sample;
[0038] c) Scanning and imaging the sample 3 to be tested in a scanning microscope system.
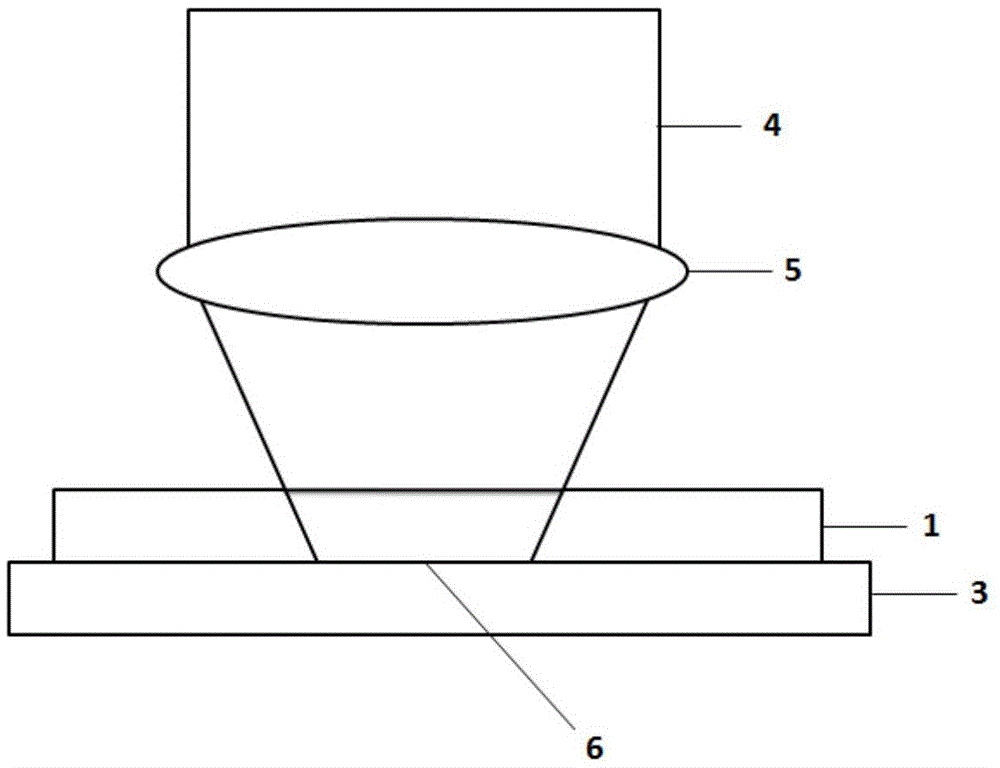
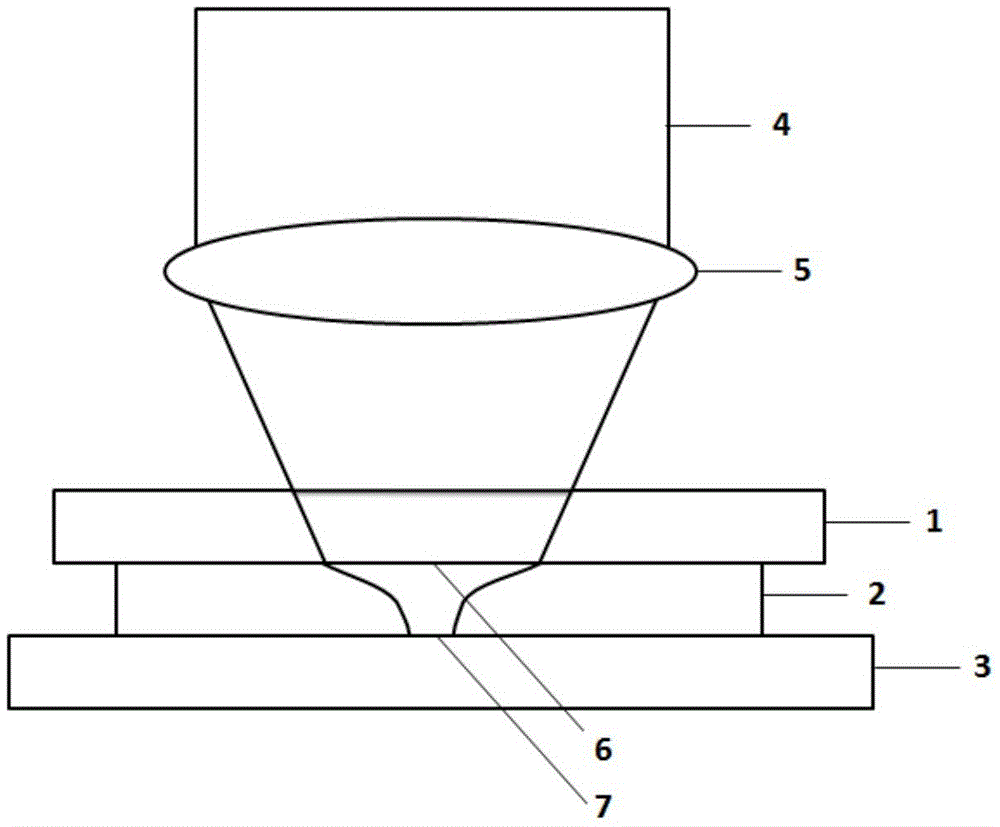
[0039] The cover glass 1 is coated with a nonlinear film 2 and placed on the surface of the sample 3 to be tested, such as figure 1 As shown, the Sb nonlinear thin film material 2 is used, with a thickness of 50 nm, coated on the surface of the cover glass 1, and the coated surface is placed close to the surface of the sample 3 to be tested. When the cover glass 1 is not added with a nonlinear film, its principle is as follows figure 2 As shown, af...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A super-resolution optical imaging method based on a laser-induced transient pinhole probe, the steps of which include:
[0045] a) Coating a non-linear material film 2 on the sample 3 to be tested by magnetron sputtering;
[0046] b) Scanning and imaging the sample 3 to be tested in a scanning microscope system.
[0047] Directly plate the Sb nonlinear thin film 2 on the surface of the sample 3 to be tested, such as Figure 5As shown, just like the sample to be tested in the scanning electron microscope system needs to be coated with a layer of carbon film or gold film on its surface to enhance its conductivity and remove the charge effect. In the scanning microscope system, the Sb nonlinear film 2 can be directly plated on the surface of the sample 3 to be tested, and its thickness is selected as 50nm as in Figure 1, and the same film thickness can be ignored in the test. When the focused laser spot 6 passes through the Sb nonlinear film 2, based on the nonlinear sa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com