Method and system for correcting brightness and chromaticity of LED display device based on human vision
A display device and human vision technology, applied to static indicators, cathode ray tube indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, improve calibration efficiency, shorten adjustment time, and eliminate differences in brightness and chromaticity between regions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
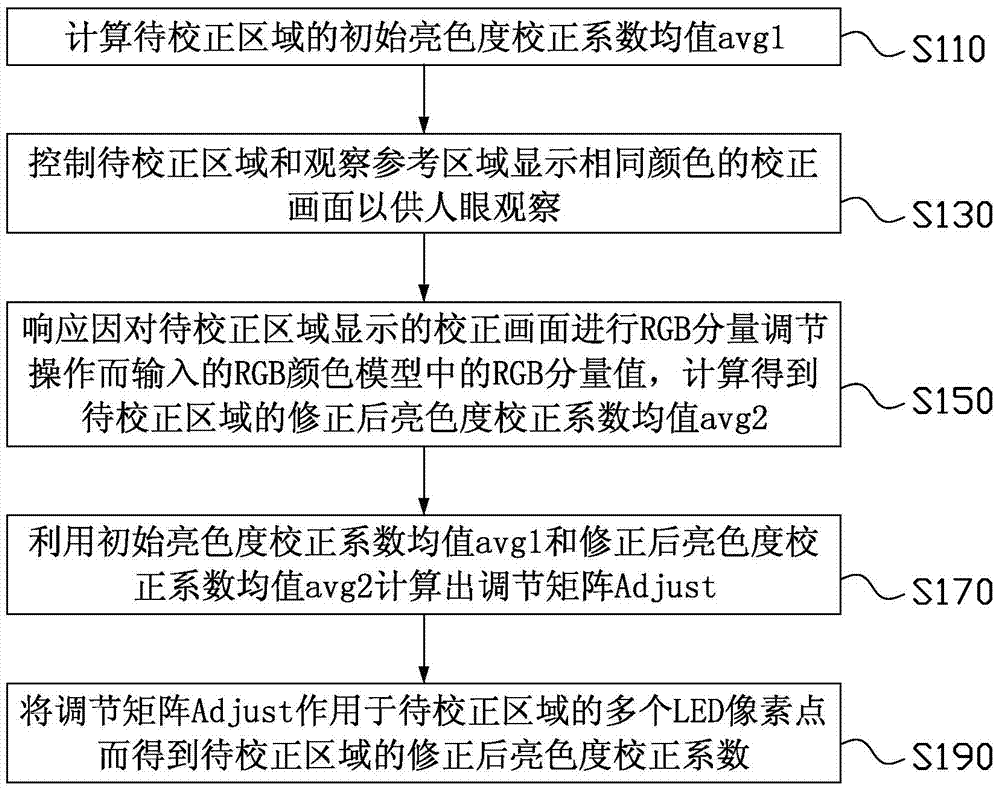
[0031] see figure 1, which is a schematic flowchart of steps of a method for correcting brightness and chromaticity of an LED display device based on human vision according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The method for correcting brightness and chromaticity of an LED display device in this embodiment is suitable for use in an LED display device including multiple splicing units, and the calibration method can be performed after splicing multiple splicing units into an LED display device, or after combining multiple splicing units. Before the splicing unit is spliced into an LED display device. And a plurality of splicing units can be a plurality of LED cabinets (comprising one or more LED light boards) for splicing into LED display screens, or a plurality of LED lamp boards for splicing into LED cabinets, and these splicing units are mutually There are brightness and chromaticity differences between the splicing units, and the method for correcting the br...
no. 2 example
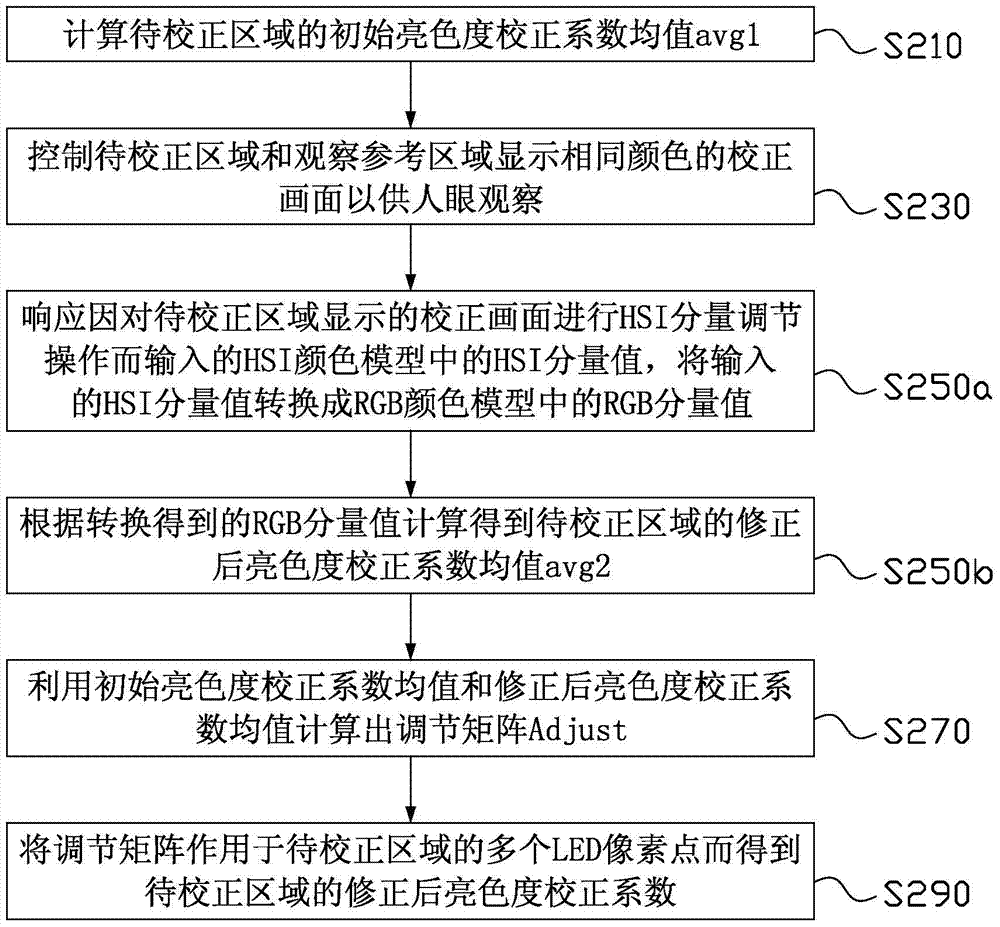
[0045] see figure 2 , which is a schematic flowchart of steps of a method for correcting brightness and chromaticity of an LED display device based on human vision according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The method for correcting brightness and chromaticity of an LED display device in this embodiment is suitable for use in an LED display device including multiple splicing units, and the calibration method can be performed after splicing multiple splicing units into an LED display device, or after combining multiple splicing units. Before the splicing unit is spliced into an LED display device. And a plurality of splicing units can be a plurality of LED cabinets (comprising one or more LED light boards) for splicing into LED display screens, or a plurality of LED lamp boards for splicing into LED cabinets, and these splicing units are mutually There are brightness and chromaticity differences between the splicing units, and the method for correcting the...
no. 3 example
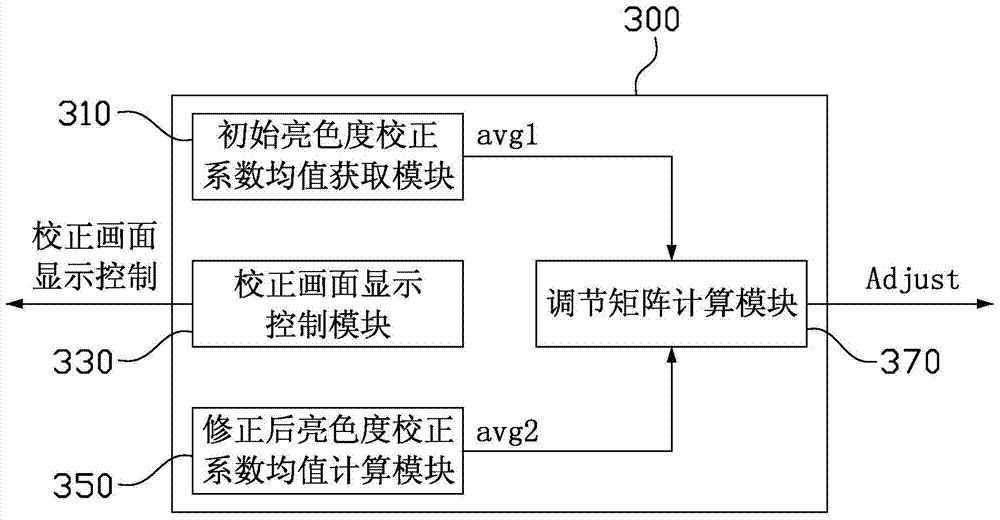
[0063] see image 3 , which is a block diagram of a brightness and chromaticity correction system for an LED display device based on human vision according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, the brightness and chromaticity correction system 300 of an LED display device based on human vision is, for example, implemented by software installed in a computer system, for example, installed in the playback computer of the synchronous control system or other computer systems linked to the playback computer, or is Installed in the computer system connected to the asynchronous control card of the asynchronous control system.
[0064] Specifically, the brightness and chromaticity correction system 300 of an LED display device based on human vision in this embodiment includes: an initial brightness and chromaticity correction coefficient mean value acquisition module 310, a correction screen display control module 330, a corrected brightness and c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com