A Free Driving Teaching Method for Industrial Robots Based on Spatial Force Information
An industrial robot and teaching method technology, applied in manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of poor teaching flexibility, increased total cost, poor flexibility, etc., and achieves simple structure, low cost, and flexibility. good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
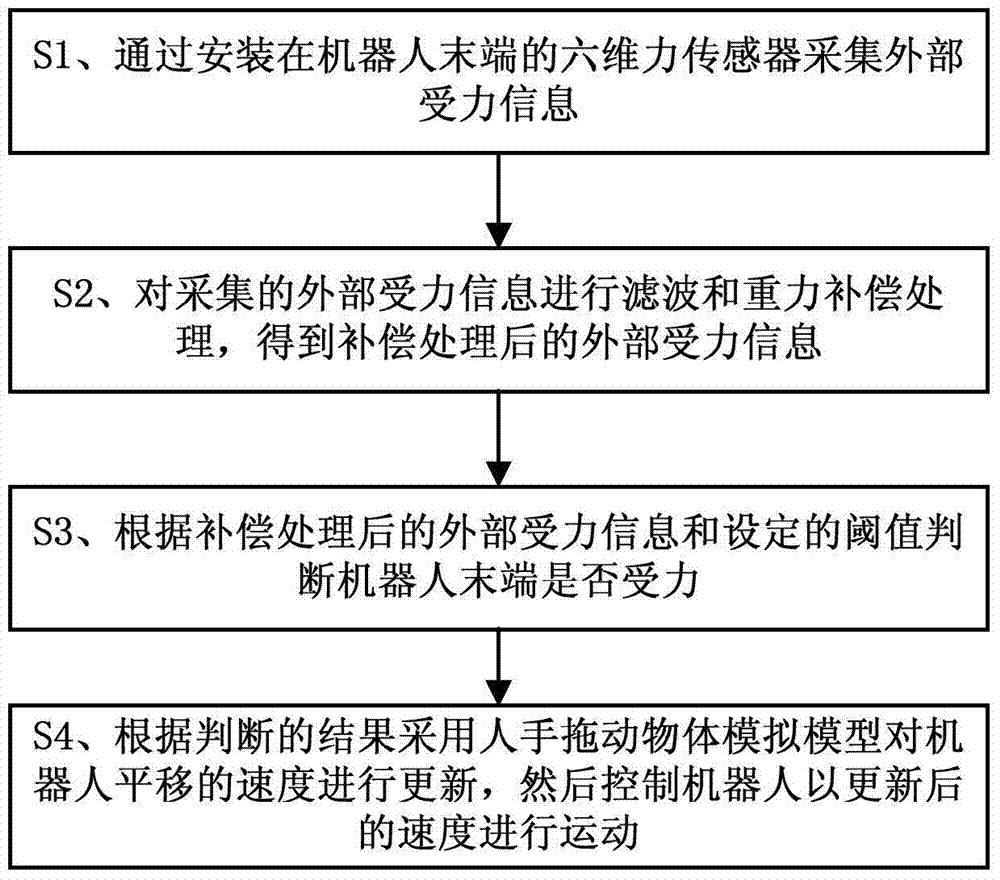
[0077] This embodiment describes in detail the installation of the six-dimensional force sensor of the present invention, the simulation model of the object being dragged by the hand, the mathematical model of the rotational speed of the attitude angle, and the adjustment rule of the teaching compliance.
[0078] (1) Installation of six-dimensional force sensor
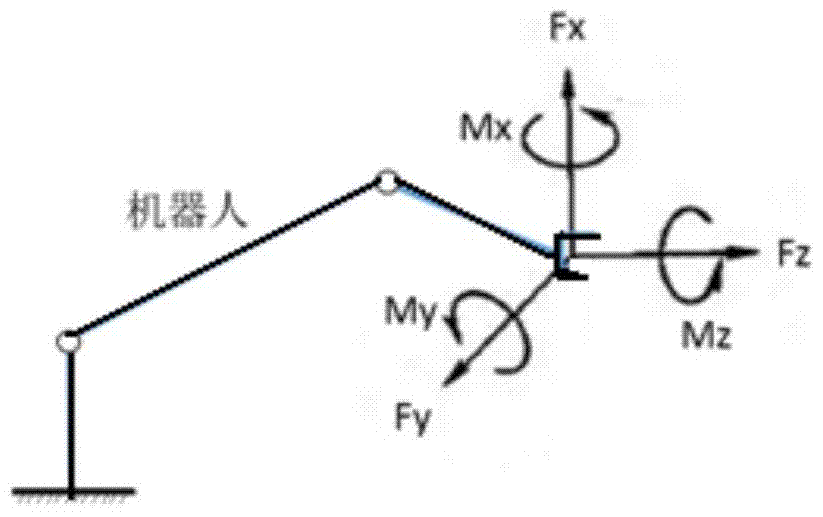
[0079] In order to reduce the cost and improve the flexibility of teaching, the present invention installs a six-dimensional force sensor at the end of the robot to collect the force information of the robot (including the forces Fx, Fy and Fz in the directions of X, Y, and Z axes and the forces around The torques Mx, My and Mz of the three axes, such as figure 2 shown).
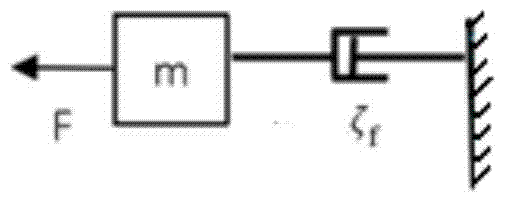
[0080] (2) Human hand dragging object simulation model
[0081] The basic idea of the algorithm proposed by the present invention is to make the motion of the end of the robot simulate the motion of a person pushing an object or dragging an obj...
Embodiment 2
[0098] In this embodiment, the process of updating the speed of the translation of the robot is taken as an example to describe the specific implementation process of the present invention. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the speed update process of robot translation of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0099] A. Collect force information: Collect external force information through a six-dimensional force sensor, which is the data of tension or pressure Fx, Fy and Fz in three directions and three torques Mx, My and Mz.
[0100] B. Kalman filter processing of force information: filter the collected force information to obtain accurate and stable force information. ;
[0101] C. Gravity compensation for the fixture and sensor: Since the collected force information includes the gravity of the fixture and the six-dimensional sensor itself, to obtain real external force information, gravity compensation processing is required to eliminate the fixture and the six-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com