Motor imagery brain electrical signal recognition method based on dual-tree complex wavelet energy difference
A dual-tree complex wavelet and EEG signal technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, etc., can solve the problem of poor anti-aliasing, inability to accurately separate adjacent frequency bands, and inability to correctly reflect time-frequency features Problems such as brain imagination and movement achieve the effect of low feature dimension, which is conducive to real-time application and overcomes the effect of poor anti-aliasing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
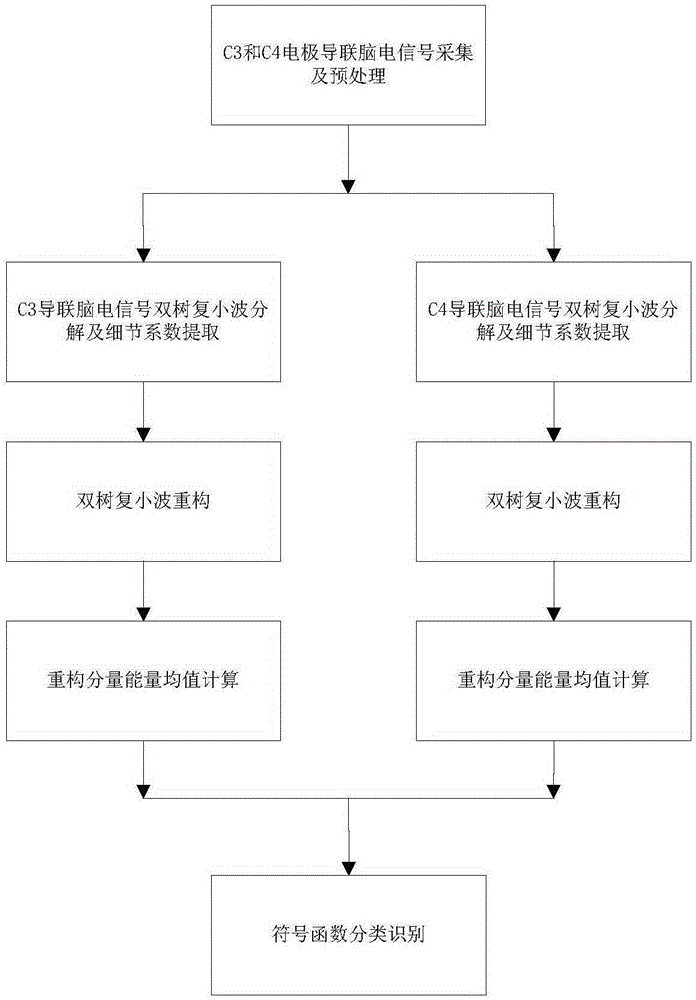
[0039] Such as Figure 1-10 As shown, the present invention is based on the motor imagery EEG signal recognition method of dual-tree complex wavelet energy difference, using dual-tree complex wavelet decomposition and reconstruction to extract C3, C4 lead energy mean difference as a feature, and finally using a sign function to classify; specifically Include the following steps:
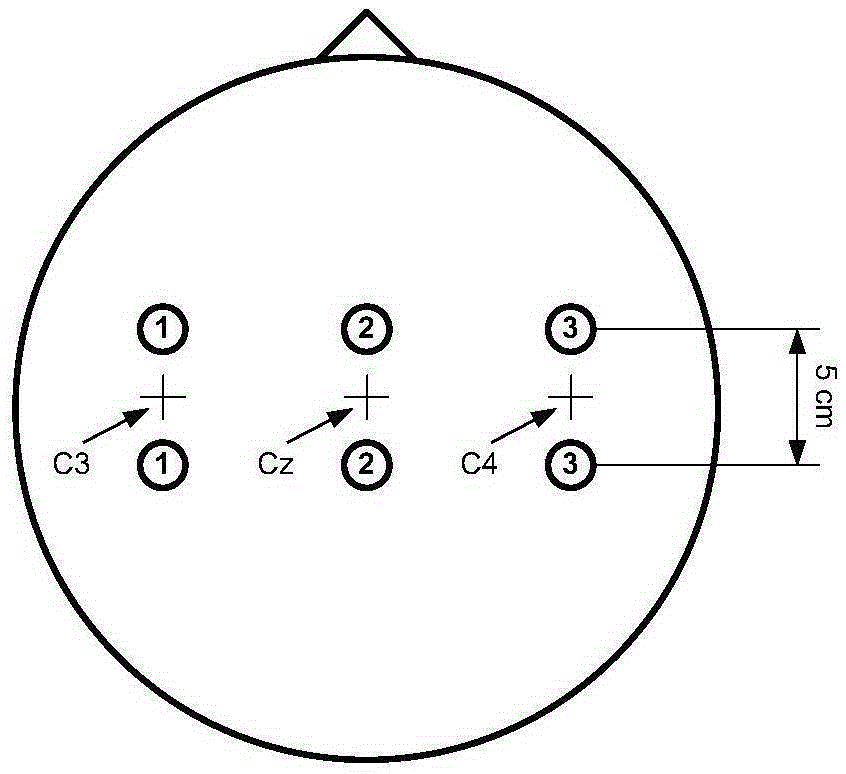
[0040] Step 1. EEG signal collection and pre-filtering: use electrode leads C3 and C4 to collect EEG signals on the left and right sides of the subject respectively, and perform band-pass filtering on the EEG signals collected by C3 and C4. Specifically:
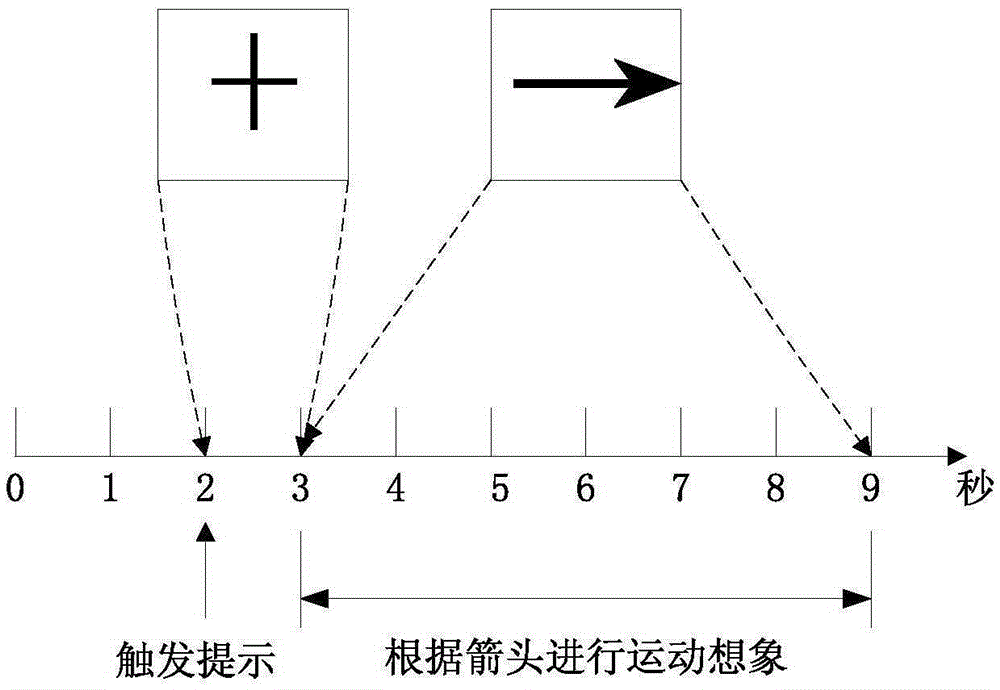
[0041] Such as Figure 2-3 As shown, the EEG motor imagery EEG signals are collected through the electrode leads C3, Cz and C4 on the multi-channel collector. The electrode leads C3, Cz and C4 are placed from lef...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com