Method for improving aftertaste of fruit and vegetable juice, method for improving aftertaste of food and drink, and food and drink
A technology for food and vegetables, which is applied in the fields of improving the aftertaste of fruit and vegetable juice, improving the aftertaste of food and beverages, and can solve problems such as difficult drinking and residual tomatoes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0120] The change of guanylic acid content was studied by treating tomato juice with acid phosphatase. As the acid phosphatase, "Sumizyme (registered trademark) PM" (manufactured by Shin Nippon Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) was used. Specifically, 250 mg of Sumizyme PM was weighed and completely dissolved in 5 mL of ultrapure water to prepare a 5% (mass / volume) enzyme stock solution, and this enzyme stock solution was added to the squeezed juice.
[0121] First, the ripe tomatoes are washed and crushed with a hammer crusher. The resulting crushed product was squeezed with a pulper to remove pulp to obtain tomato juice [1A] (Brix value: 29).
[0122] Next, weigh 20 mL of tomato juice [1A] in a 100 mL beaker, add 40 μL of the enzyme stock solution (final enzyme concentration: 0.01% (mass / volume)), and let stand at 60°C for 1 hour to perform the enzyme reaction (test sample). In addition, 20 mL of tomato juice [1A] which was left still at 60 degreeC for 1 hour without adding an...
Embodiment 2
[0142] Change the conditions of the reaction time of the enzyme reaction and the amount of enzyme added, and observe the influence on the content of guanylic acid.
[0143] Specifically, for the amount of enzyme added, the final concentration of the enzyme is 0.01%, 0.05%, or 0.1% (mass / volume), the enzyme reaction temperature is set to 4°C or 20°C, and the enzyme reaction time is set to Except having been 0, 10, 20, 30, 60, 180, 480, or 960 minutes, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and carried out phosphatase treatment with respect to tomato juice [1A].
[0144] The guanylic acid content in the tomato juice after the enzyme reaction was calculated in the same manner as in Example 1. The calculated results are shown in figure 2 . The vertical axis represents the guanylic acid concentration (ppm) per tomato juice [1A] (Brix value: 29), and the horizontal axis represents the reaction time (minutes). The results can be confirmed: if figure 2 As shown, the more enzyme ...
Embodiment 3
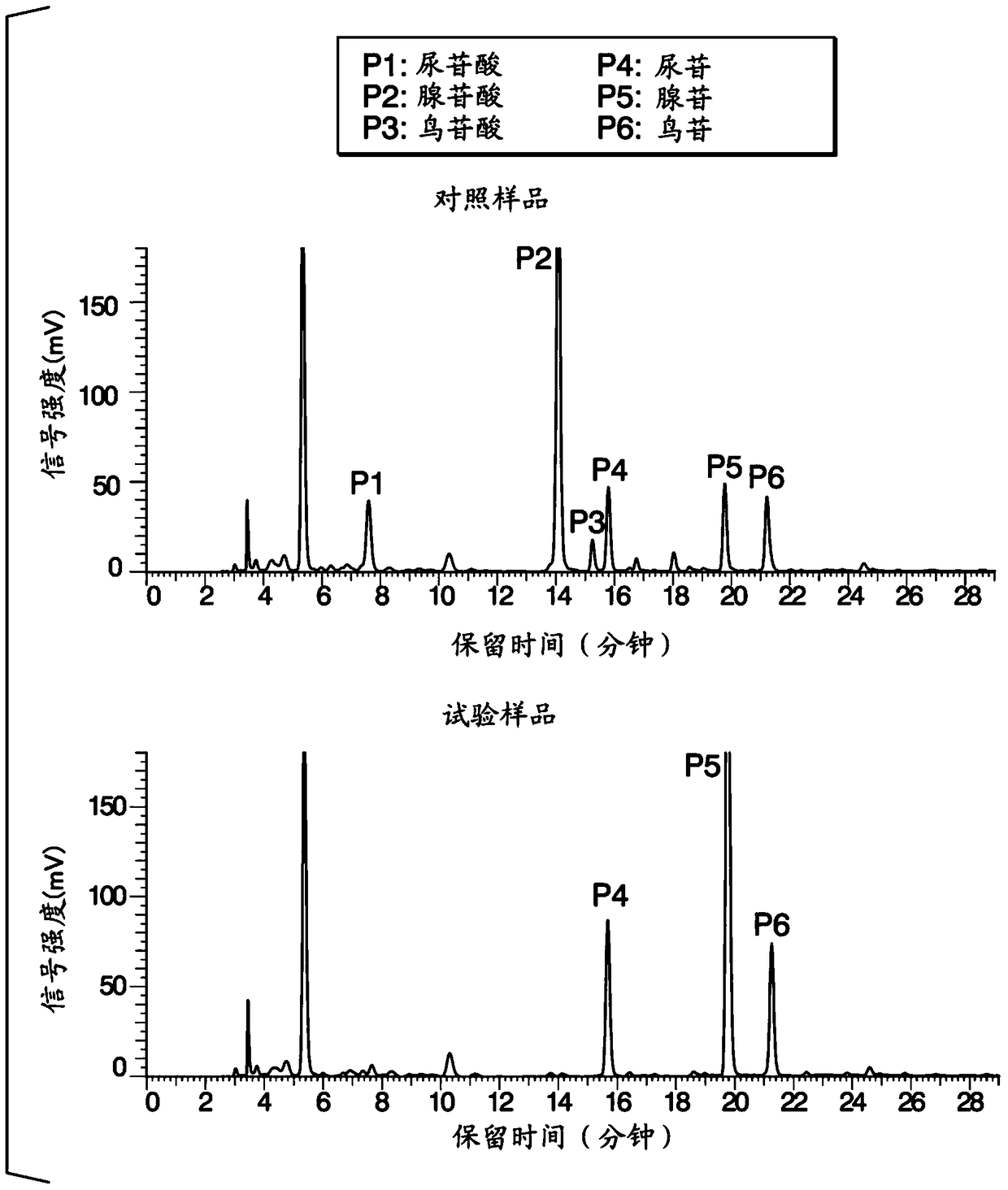
[0146] The acid phosphatase used in Example 1 was added to commercially available tomato juice (salt-free) (manufactured by Kagome Co., Ltd.) so that the final concentration of the enzyme was 0.1% (mass / volume), and carried out at 60°C. Enzyme reaction was carried out for 1 hour (test sample 1). In addition, distilled water was added instead of the enzyme stock solution, and a sample incubated at 60° C. for 1 hour in the same manner as Test Sample 1 was used as a control sample.
[0147] The guanylic acid content of both samples was measured in the same manner as in Example 1. As a result, in Test Sample 1, guanylic acid was completely decomposed and no peak was detected in the HPLC chromatogram.
[0148] In addition, the glutamic acid content of the two samples was analyzed under the following analysis conditions. In addition, the filtrate obtained by filtering with the membrane filter (manufactured by Advantec Corporation) with a pore diameter of 0.45 nm was subjected to HP...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com