Designing method of cylindrical blade with controllable inlet setting angle
A design method and a technology of placing angles, which are applied to mechanical equipment, parts of pumping devices for elastic fluids, non-variable pumps, etc., can solve the problem of reducing water flow pressure, limiting the use range of cylindrical blades, and blade inlet impact Loss and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following description.
[0058] In order to achieve the design goals and principles of the new cylindrical blade, the blade design should be completed according to the following calculation and drawing process, which is quite different from the traditional cylindrical blade design steps.
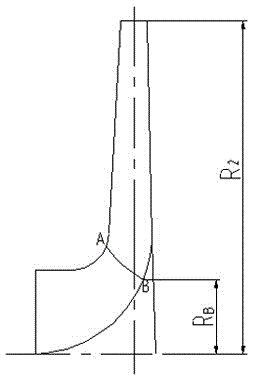
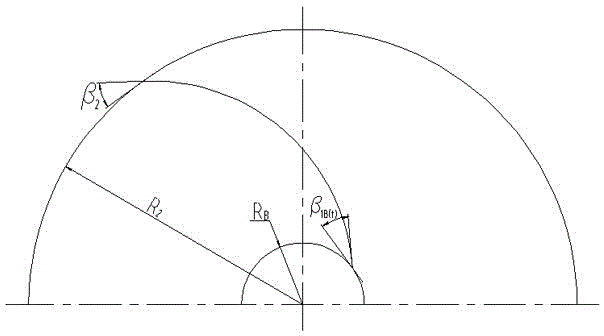
[0059] (1) According to the main geometric parameters of the blade obtained in the previous calculation, including the impeller radius R 2 , the impeller outlet width b 2 , impeller inlet radius R 0 etc. After repeated revisions and checks, a satisfactory projection of the axial plane of the blade was obtained. According to certain principles, draw the blade inlet edge on the blade axial plane projection diagram, and measure the distance R from the intersection point A and B of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com