A method for stimulating the efficient proliferation of peripheral blood γδt cells in vitro and its application
A high-efficiency proliferation and peripheral blood technology, applied in the field of medical bioengineering, can solve the problems of poor anti-tumor cytotoxicity and poor amplification ability, and achieve the effect of complete anti-tumor cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1: Construction of K562 transgenic cell line
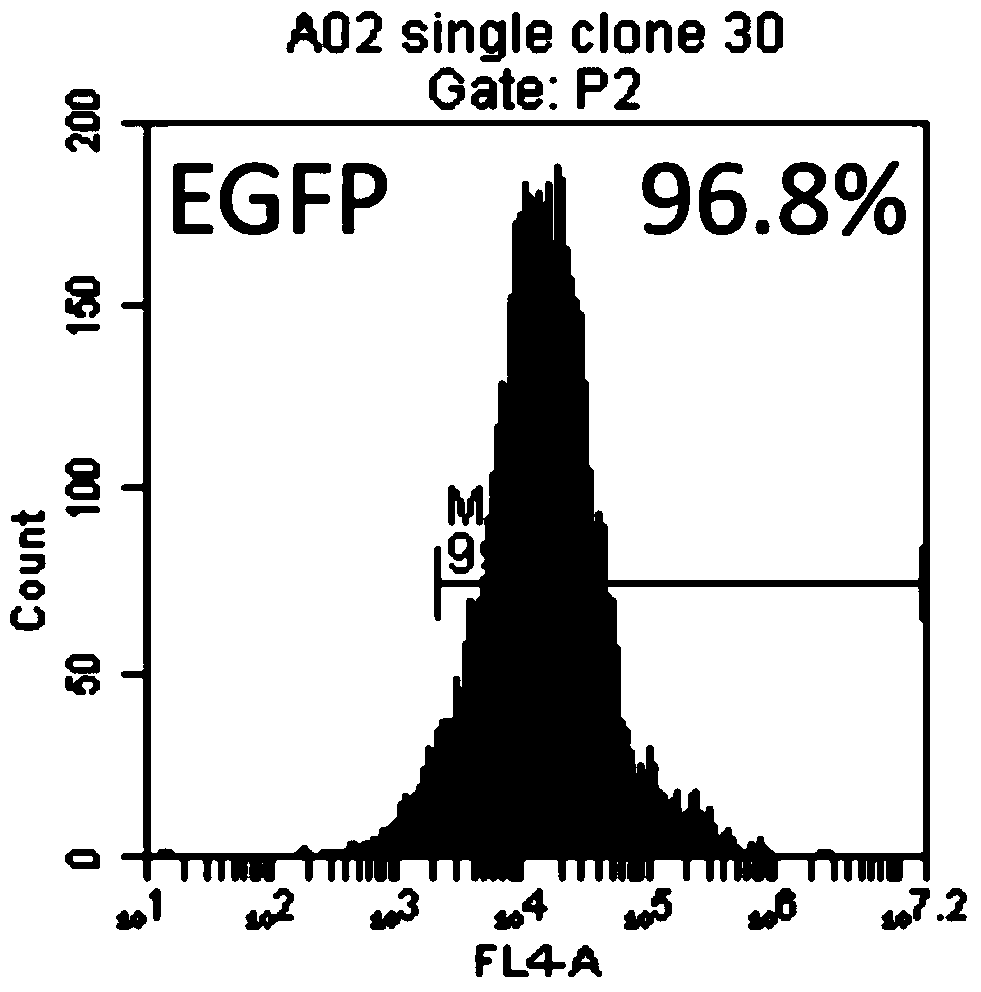
[0062] A K562 transgenic cell line was constructed, which expresses CD64, CD86 and CD137L (4-1BBL) on the surface of the cell line. First, the gene coding sequences of CD64 (FcγRI, GenBank accession no.BCO32634), CD86 (B7-2, GenBank accession no.NM_175862) and CD137L (4-1BBL, GenBank accession no.NM_003811) were obtained from peripheral blood mononuclear cells using PCR technology The cDNA library was amplified and then cloned into the pFastBac1-CMV-EGFP vector to construct the pFastBac1-CMV-aAPC3-PuroEGFP plasmid containing the CD64, CD86, and CD137L genes. Using zinc finger nuclease technology, site-specific integration of CD64, CD86 and CD137L gene expression structures was performed at the AAVS1 locus of chromosome 19 in K562 cells. The genetically modified cells were selected for puromycin, followed by cell sorting using anti-CD64 antibody and seeding of single cells into 96-well plates. The 96-well plate ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2: Selection of Phosphorylated Antigens for Expansion of Vγ9Vδ2 T Cells
[0064] After comparing the efficacy of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and zoledronic acid on the expansion of Vγ9Vδ2T cells, 5 μM zoledronic acid showed relatively high efficiency in activating and expanding γ9Vδ2T cells, achieving 600-fold expansion within 10 days. increase. 48% of the expanded cells were Vγ9Vδ2T cells ( Figure 13 , 14 , 15, 16, 17, 18). Condition optimization of phosphorylated antigen treatment to expand Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. Comparison of the effects of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and zoledronic acid treatment. The peripheral blood mononuclear cells were treated with different concentrations of these two drugs in AIM-V culture supplemented with 5% human AB serum for 10 days. Figure 19 γδT cell expansion fold and γδT cell percentage after using different treatment methods.
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Vγ9Vδ2 T cell expansion experiment
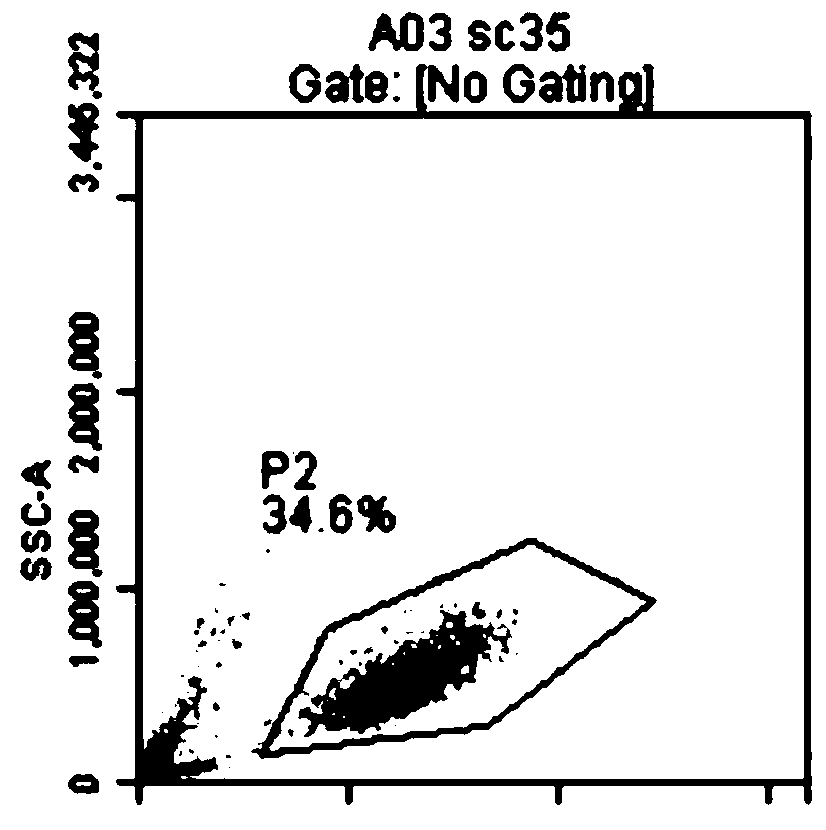
[0066] This example consists of two parts: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were treated with 5 μM zoledronic acid and 300 IU / mL human recombinant interleukin-2 for 7 days, and then the treated cells were mixed with inactivated K562a cells for 1 : 200 for 14 days, in which 5 μM zoledronic acid and 300 IU / ml human recombinant interleukin-2 were added. Treatment of K562a cells with gamma irradiation or Mitomyces C can inactivate it. After expanding the cells using this standard protocol, the in vitro expanded cells were analyzed ( Figure 20 , 21 , 22) composition. A representative study using peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 4 donors showed that after 7 days of treatment, most of the expanded cells expressed the Vδ2 T cell receptor (80.67%± 4.85% amplified cell expression, 78.73% ± 3.09% amplified cell expression after mitomycin C treatment). By the 21st day, the percentages of Vδ2 T cell receptor-positive cel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com