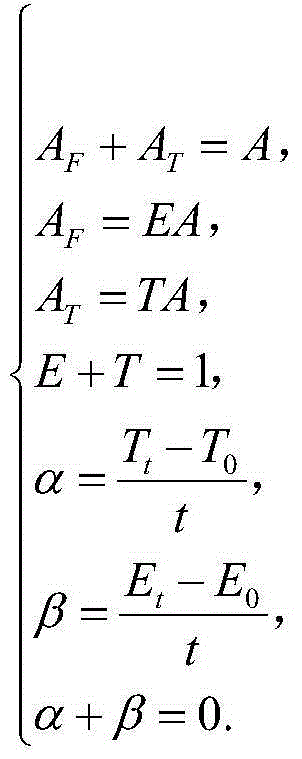Discrimination method for demonstrating correctness of scientific principles and laws
A method of discrimination and correctness, applied in the fields of basic scientific theory and applied basic research, can solve problems such as inaccuracy, cumbersome work, and heavy workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] Example 1. Prove the correctness of the law of buoyancy.
[0040] Archimedes' law of buoyancy: buoyancy F R Equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the floating body (the product of the volume of the liquid displaced by the floating body, the density of the liquid, and the acceleration of gravity). That is, F R =λVg.
[0041] Proof: From the point of view of traditional theory, the law of buoyancy only involves the relationship between action force and reaction force. From the perspective of mechanics, the law of buoyancy involves multiple concepts and their interrelationships. These concepts include action, action, actual action, actual force, imaginary action, imaginary force, resultant force, resistance, deformation, liquid properties (empty or solid). According to functional theory, there are the following relationship rules between these concepts:
[0042] The amount of action A is equal to the force F multiplied by the action time t, that is, A=Ft; whe...
example 2
[0056] Example 2. Prove the scientific nature of the traditional stress-strain theory.
[0057] Proof: ⅰ. Understanding its unscientific nature from the traditional stress-strain relationship itself:
[0058] The basic content of the traditional stress-strain relationship theory: in a unidirectional stress state, the stress-strain relationship of an ideal elastic-plastic material satisfies Hooke's law, that is
[0059] σ=Eε.
[0060] In the formula, σ represents the stress; ε represents the strain; E is the modulus of elasticity. This relational expression does not satisfy the law revealed by Newton's law, the dimensions on both sides of the equation are not unified, the dimensionless parameter E becomes a dimensioned parameter, and the objective meaning of the parameter is lost.
[0061] According to the unified quantitative theory of opposites and opposites in kinetics, the relationship between stress and strain should be
[0062] ϵ = ...
example 3
[0075] Example 3. Demonstrate the correctness of the labor-saving principle of lever and pulley block.
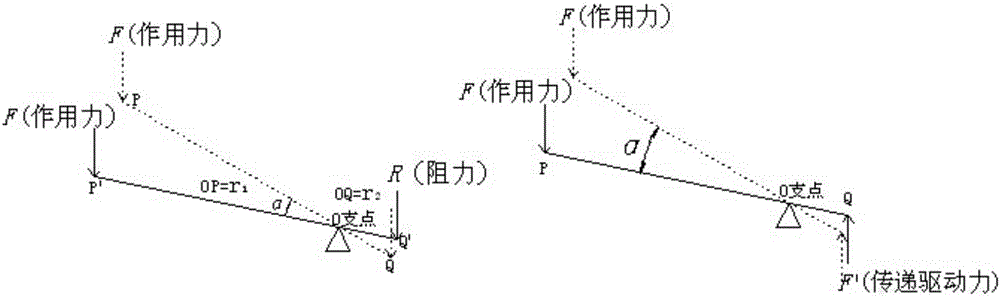
[0076] ⑴. Leverage principle: the working method and principle of using a small force to lift a large weight (a small driving force overcomes a large resistance) with the help of a lever. The lever principle of mechanics refers to the condition of lever balance. The condition of lever balance means that in the leverage system, the product of the driving force received by the lever at the driving end and the driving force arm is equal to the product of the resistance received by the lever at the hindering end and the resistance arm, that is, force × force arm = resistance × resistance arm, whose mathematical expression is r 1 F=r 2 R or Such as figure 1 shown. Mechanics believes that the lever can make the force smaller.
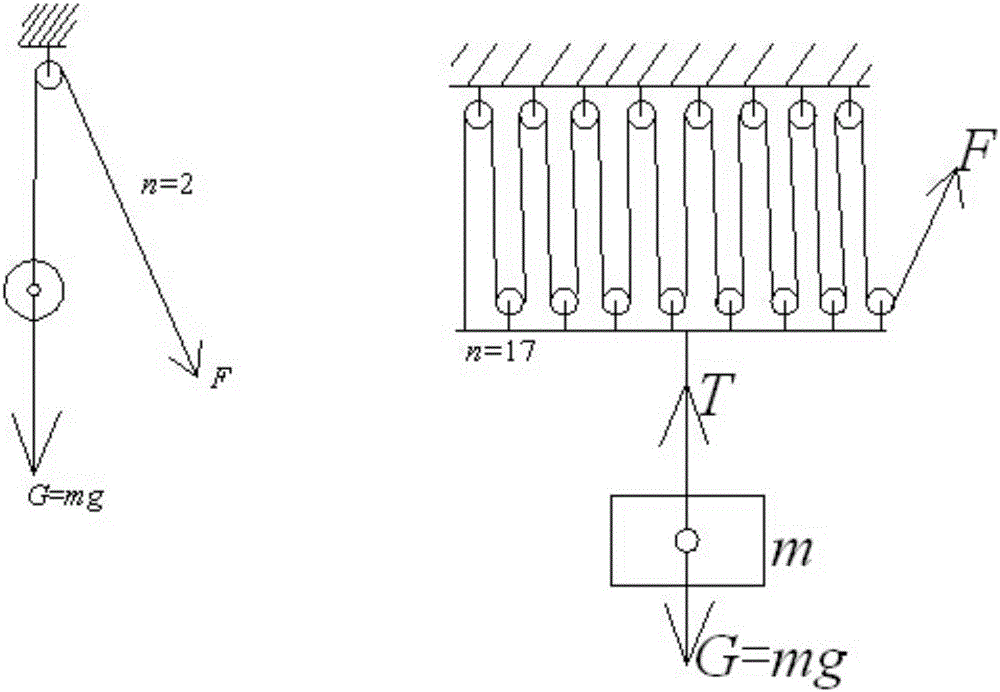
[0077] ⑵. Pulley block labor-saving principle: with the help of pulley block, use a small force to lift a large weight (use a small driving force t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com