Method for removing heavy metal chromium in water body
A heavy metal and water technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the pollutant removal ability of nZVI, hindering the contact reaction of nZVI, etc., to achieve good reduction and removal effect, promote Corrosion reaction and co-precipitation inhibition effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A kind of method of removing heavy metal chromium in water body of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0028] (1) Preparation of nanometer zero-valent iron (nZVI), the specific steps are:
[0029] 1.1. Weigh 2.71×10 -2 g NaBH 4 Dissolved in 10 mL deionized water to prepare NaBH with a concentration of 0.072 mol / L 4 solution.
[0030] 1.2. Take FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in 10 mL deionized water to prepare FeSO with a concentration of 0.036 mol / L 4 solution.
[0031] 1.3. Under electric stirring at room temperature and normal pressure, mix 10 mL of NaBH prepared in step 1.1 4 The solution was added dropwise at a rate of 0.05 mL / s into the 10 mL FeSO solution prepared in step 1.2. 4 In the three-necked flask of the solution, during the dropwise addition of FeSO 4 The solution gradually turned black. After the dropwise addition was completed, the stirring was continued for 30 min, and ultrasonic treatment was performed at the same time to ma...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A kind of method of removing heavy metal chromium in water body of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0040] (1) Preparation of nanometer zero-valent iron (nZVI): same as in Example 1.
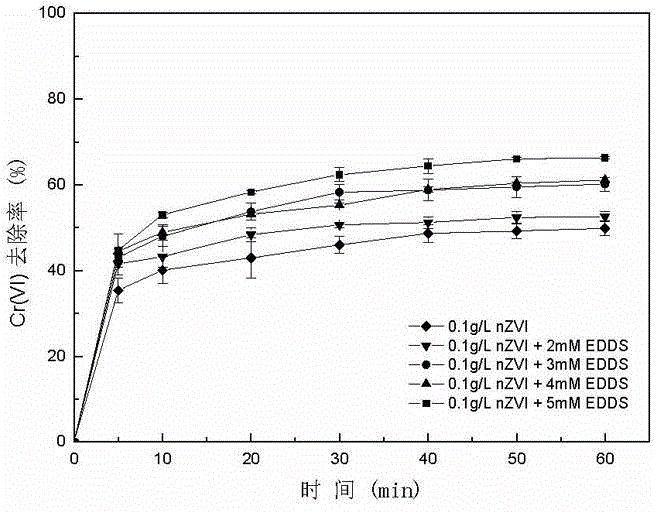
[0041] (2) Add nZVI and ethylenediamine disuccinic acid (EDDS) to the chromium-containing water body with a pH value of 7 and a Cr(VI) concentration of 10 mg / L, and mix well to obtain a reaction solution, wherein the initial concentration of EDDS in the reaction solution The concentrations were 3 mM, 4 mM, and 5 mM, respectively, and the initial concentration of nZVI was 0.1 g / L.
[0042] In the above step (2), the concentration of Cr(VI) is 0.05 mg / L-50 mg / L, and the initial concentration of nZVI is 0.1 g / L-1 g / L, both of which can achieve the same or similar technical effects.
[0043] (3) The reaction solution in step (2) was placed in a digital display water bath constant temperature oscillator for constant temperature oscillation treatment. The temperature of ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] A kind of method of removing heavy metal chromium in water body of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0049] (1) Preparation of nanometer zero-valent iron (nZVI): same as in Example 1.
[0050] (2) Add nZVI and ethylenediamine disuccinic acid (EDDS) to the chromium-containing water body with a pH value of 9 and a Cr(VI) concentration of 10 mg / L, and mix well to obtain a reaction solution, wherein the initial concentration of EDDS in the reaction solution The concentrations were 2mM, 3mM, 4mM, 5mM, respectively, and the initial concentration of nZVI was 0.1 g / L.
[0051] In the above step (2), the concentration of Cr(VI) is 0.05 mg / L-50 mg / L, and the initial concentration of nZVI is 0.1 g / L-1 g / L, both of which can achieve the same or similar technical effects.
[0052] (3) The reaction solution in step (2) was placed in a digital display water bath constant temperature oscillator for constant temperature oscillation treatment. The temperature of co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com