Nearest Neighbor Hyperspectral Image Classification Method Based on Dictionary and Band Recombination
A technology of hyperspectral images and classification methods, applied in the field of spectral data classification, can solve the problems of low classification accuracy of hyperspectral images, incomprehensible combination of space-spectral information, and high time complexity, so as to increase the classification accuracy and time complexity. Low, the effect of improving the classification accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The present invention is a space-spectrum combination method based on dictionary and band recombination for rapid classification of nearest neighbor hyperspectral images, see figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0042] Step 1 read hyperspectral remote sensing data image, hyperspectral remote sensing data image referred to as hyperspectral image.
[0043] Step 2: Preprocess the read hyperspectral image first, use the spatial neighborhood information of the hyperspectral image, take the L nearest neighbor pixels for each pixel of the hyperspectral image, and perform L-neighborhood mean processing to obtain the preprocessed hyperspectral image. In the hyperspectral initial image, there are a certain number of pixels polluted by noise. Without preprocessing, these pixels are very destructive to the classification accuracy. Therefore, before classification, the present invention utilizes the hyperspectral image Spatial information, noise pixels are processed.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The nearest neighbor hyperspectral image rapid classification method based on the space-spectrum combination of dictionary and band recombination is the same as embodiment 1, in step 2, each pixel in the hyperspectral image is carried out L-neighborhood mean value processing, used in the present invention The obtained hyperspectral data is the Indian Pines hyperspectral image in the AVIRIS data set, which contains a total of 200 bands, specifically:
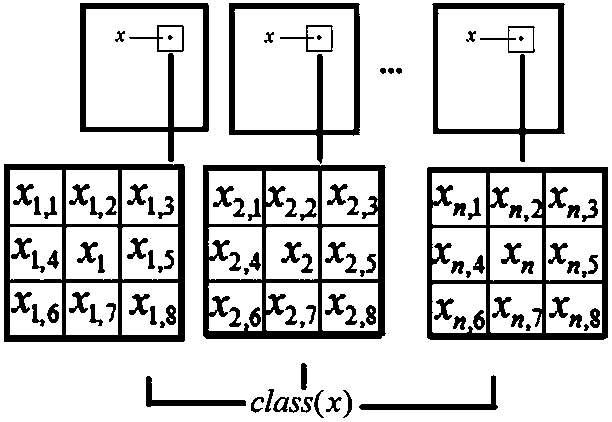
[0051] It is assumed that the hyperspectral image has N wave bands in total, and in the experiments of the present invention, N=200. A certain pixel in the hyperspectral image is x i ={x i,1 ,...,x i,N}, with x i As the center, take the L neighboring pixels {x 1 ,...,x L}, in the experiments done by the present invention, L=24. where x 1 ={x 1,1 ,...,x 1,N}∈R N , R N is the N-dimensional feature space, x 2 ={x 2,1 ,...,x 2,N}∈R N , and so on, for x i Do 24-average processing for all L+1=25 pixels in the 5×5...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The nearest neighbor hyperspectral image classification method based on dictionary and band recombination is the same as in embodiment 1-2, in step 3, there are m pixels {x i,1 ,...,x i,m},make
[0056]
[0057] Perform the above average processing on all bands to get {x 1 ,...,x N}, N=200, for {x 1 ,...,x N} sort from small to large to obtain the hyperspectral image mean sequence, and then rearrange the hyperspectral bands according to this sequence, and divide the reorganized N bands into n equal parts in order to form n sub-bands. In the present invention, the Indian image is divided into 3 equal parts, that is, n=3. The first sub-band is bands 1-66 after band reorganization, the second sub-band is bands 67-133, and the third sub-band is bands 134-200.
[0058] In step 5, let sub-dictionary D=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x d ]exist dimensional feature space, and its category label is ω i ∈{1,2,...,C}. C is the number of categories. Let d be the number of atoms in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com