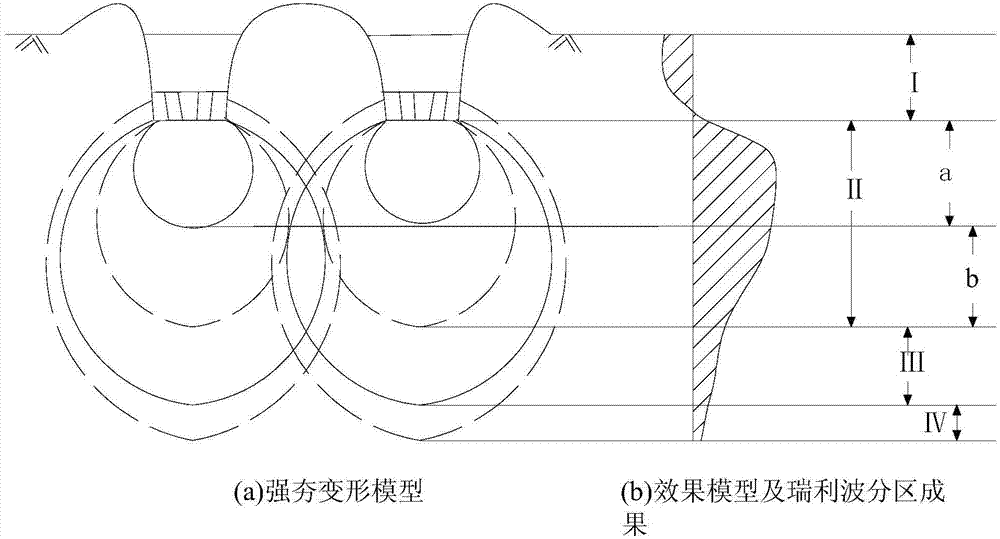
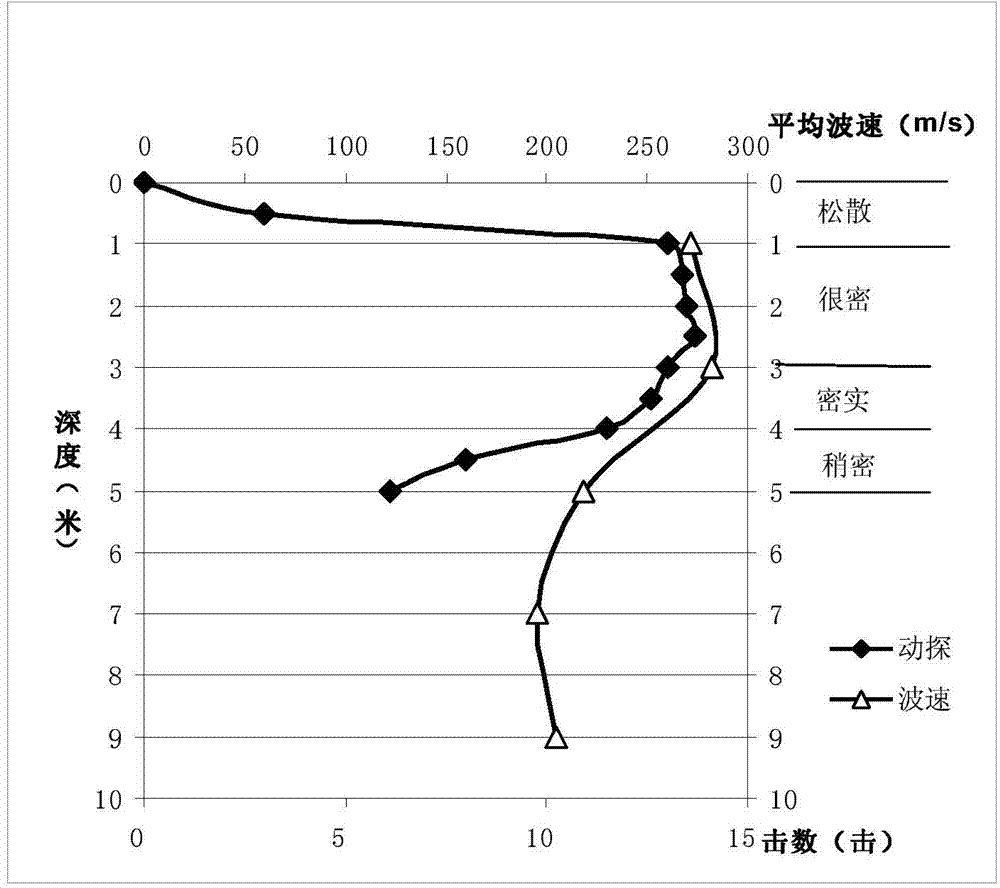
Method for dividing density degrees of gravelly soil foundations through surface-wave inversion shear wave velocities
A technology of shear wave and compactness, which is applied in the engineering field, can solve the problems of difficult drilling, low detection efficiency, and limited detection depth, and achieve the effect of overcoming the difficulty of drilling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
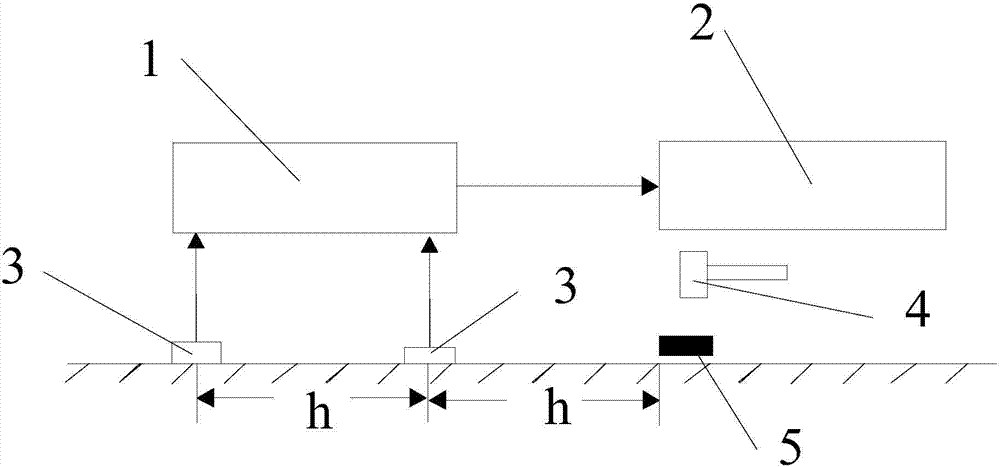
[0063] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the on-site detection layout of the ground transient Rayleigh wave measurement. In the figure, 1 is the seismograph, 2 is the analyzer, 3 is the geophone, 4 is the heavy hammer, and 5 is the backing plate. The Rayleigh shear wave velocity is collected according to the operating procedures, and this process should be completed through field operations. We adopt the single-ended excitation method, arrange 24 channels of detectors, the detector frequency is 4Hz, the channel spacing is 1m, the offset distance is 5m, the number of sampling points is 2048, and the sampling interval is 250us. Taking the measuring point as the center of symmetry, the detector is evenly placed on the ground in a straight line, so that it fits tightly with the ground and stands upright. Impact the ground vertically with a heavy hammer, and the seismograph records the ground vibration signals received by the geophone. Repeat the above steps 3 to 5 times to ...
Embodiment
[0066] The test was carried out in three different sites, so the test sites were all with less earthwork and more stonework, and the stonework was mainly backfilled. The construction overview of dynamic compaction is shown in Table A and Table B, and there are three kinds of fillers.
[0067] Table A List of dynamic compaction parameters for soil-rock mixed fill area
[0068]
[0069] Note: The particle size of gravel in gravel soil is less than 500mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com