Telescopic-leg energy-saving 2D under-actuated traveling device and control method thereof
A walking device and underactuated technology, which is applied in the field of underactuated walking devices, can solve the problems of heavy leg mass, unsuitable for practical large-scale promotion, complex transmission structure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] A non-limiting embodiment is given below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings to further illustrate the present invention. It should be understood, however, that these descriptions are exemplary only, and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. Also, in the following description, descriptions of well-known structures and techniques are omitted to avoid unnecessarily obscuring the concept of the present invention.
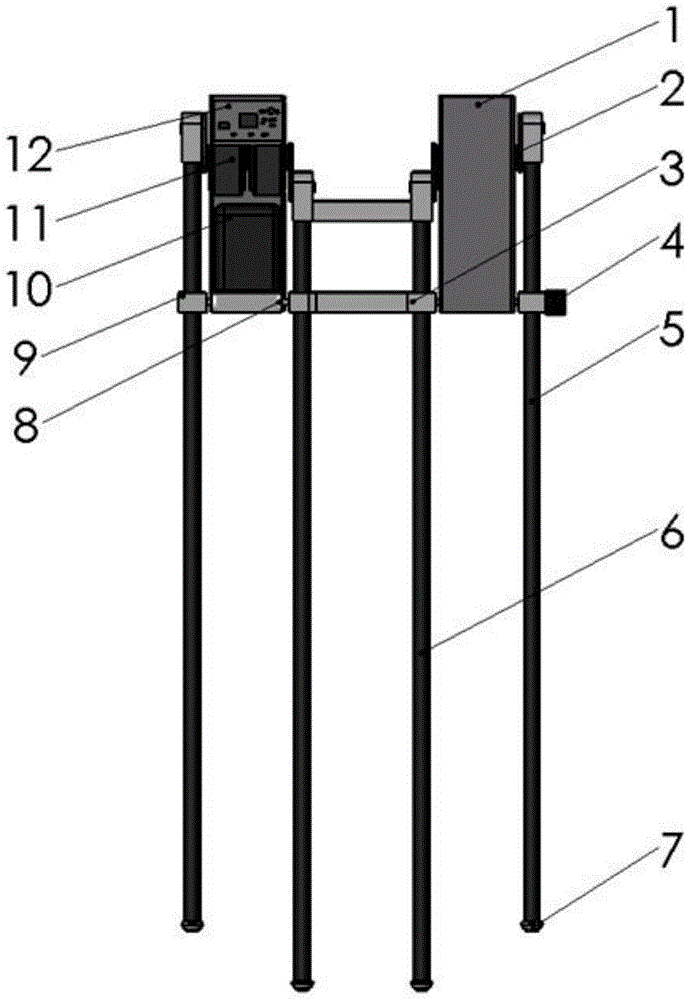
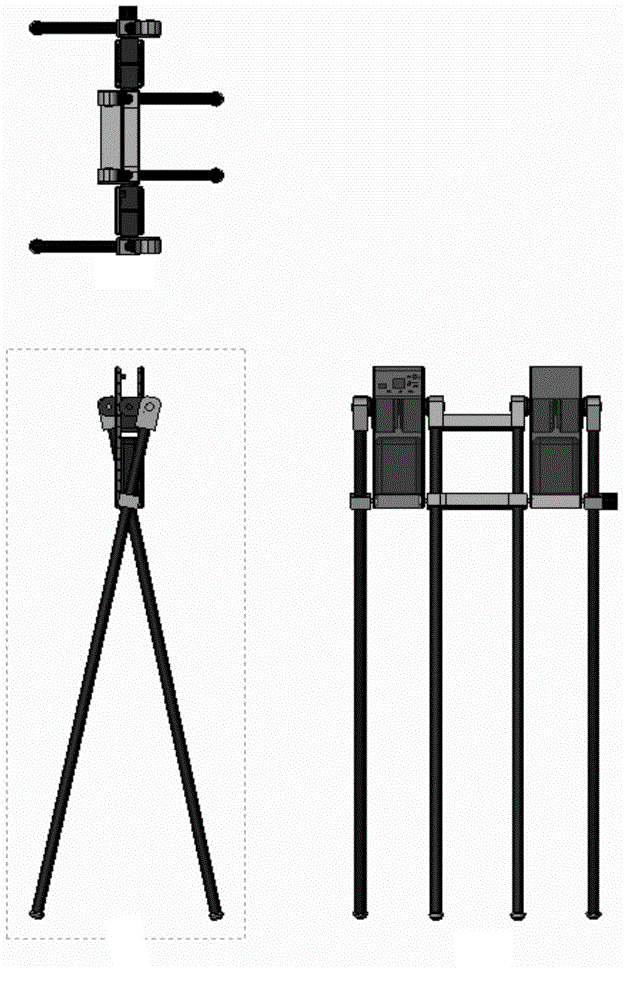
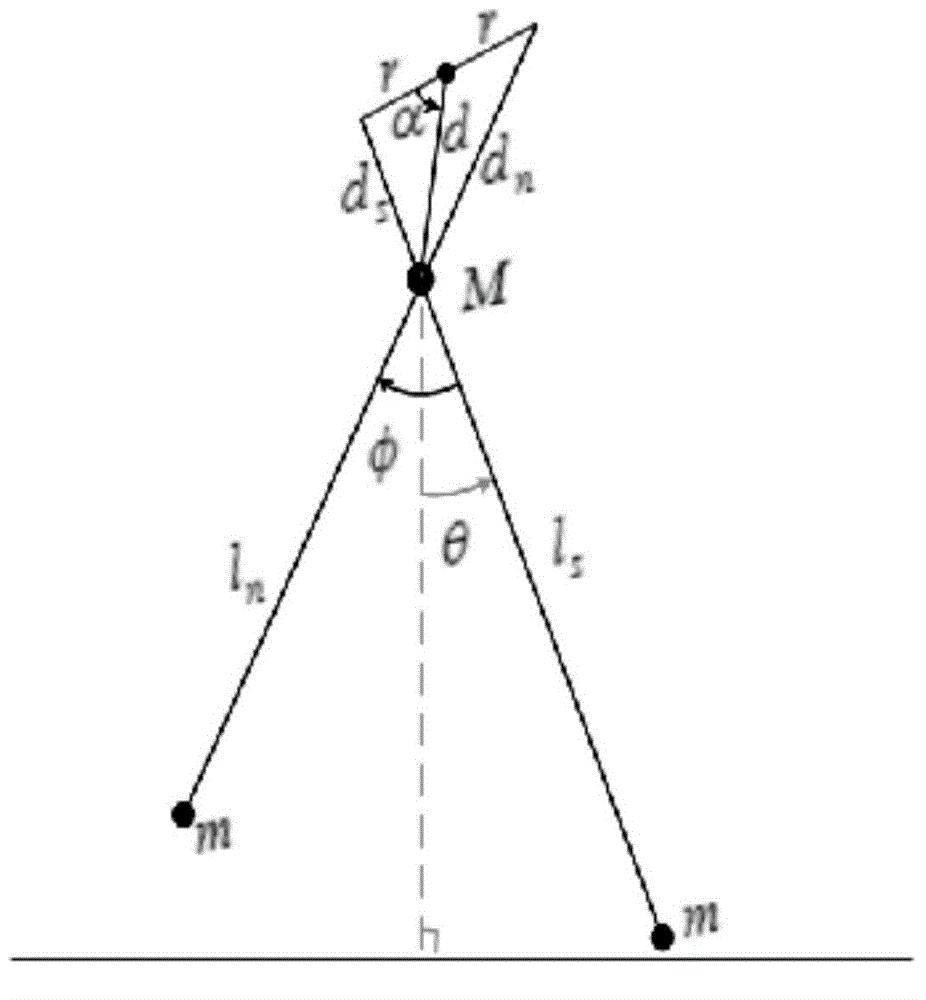
[0020] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, the telescopic leg underactuated walking device includes a hip, a driving device, a data acquisition device and a main control device 12 . Described hip comprises left hip 1 and right hip, each hip (left hip 1) connects inside and outside two straight legs (left outer straight leg 5, left inner straight leg 6) by crank rocker, each The straight leg is fixedly connected with a foot 7; the hip is composed of two parts that are left and right completely symmetrical, and the left (right) hip is used ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com