Non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method and system
A technology of structured light illumination and microscopic imaging, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve problems such as limiting NL-SIM, high excitation light power density, biological tissue damage, etc., and achieve improved imaging resolution and imaging. Fast, damage-avoiding effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
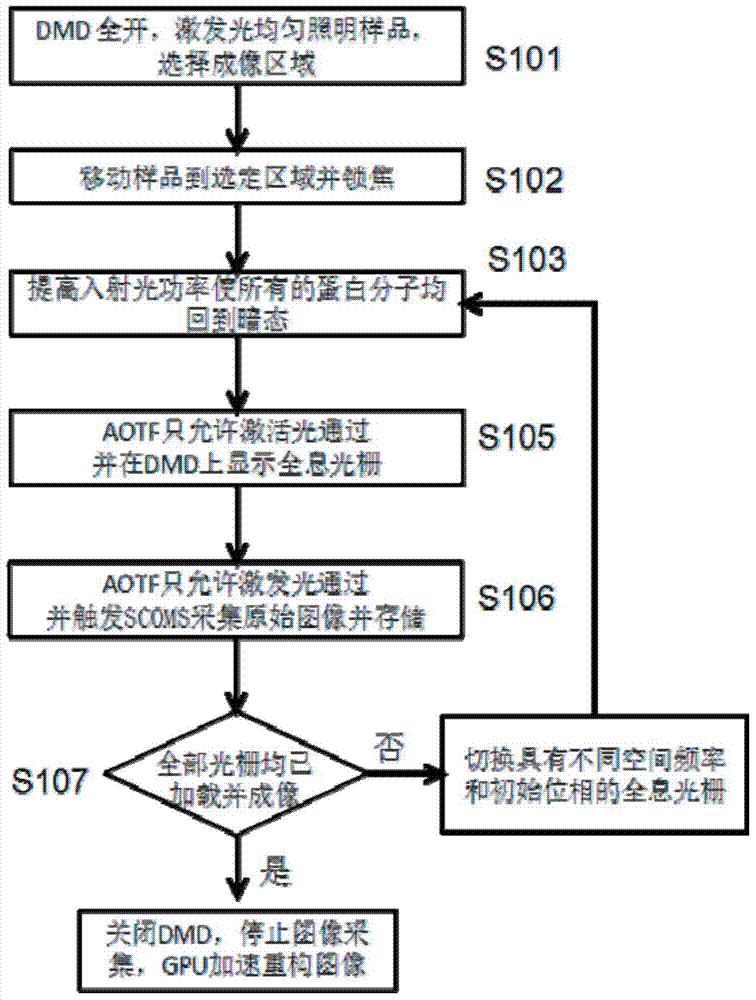
[0036] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a nonlinear structured light illumination super-resolution fluorescence imaging method. For the convenience of description, in this embodiment, the activation light specifically refers to a continuous solid-state laser with a wavelength of 405 nm, and the excitation light specifically refers to a continuous solid-state laser with a wavelength of 488 nm. The output power of the two laser beams is adjustable between 0 and 100 mW.
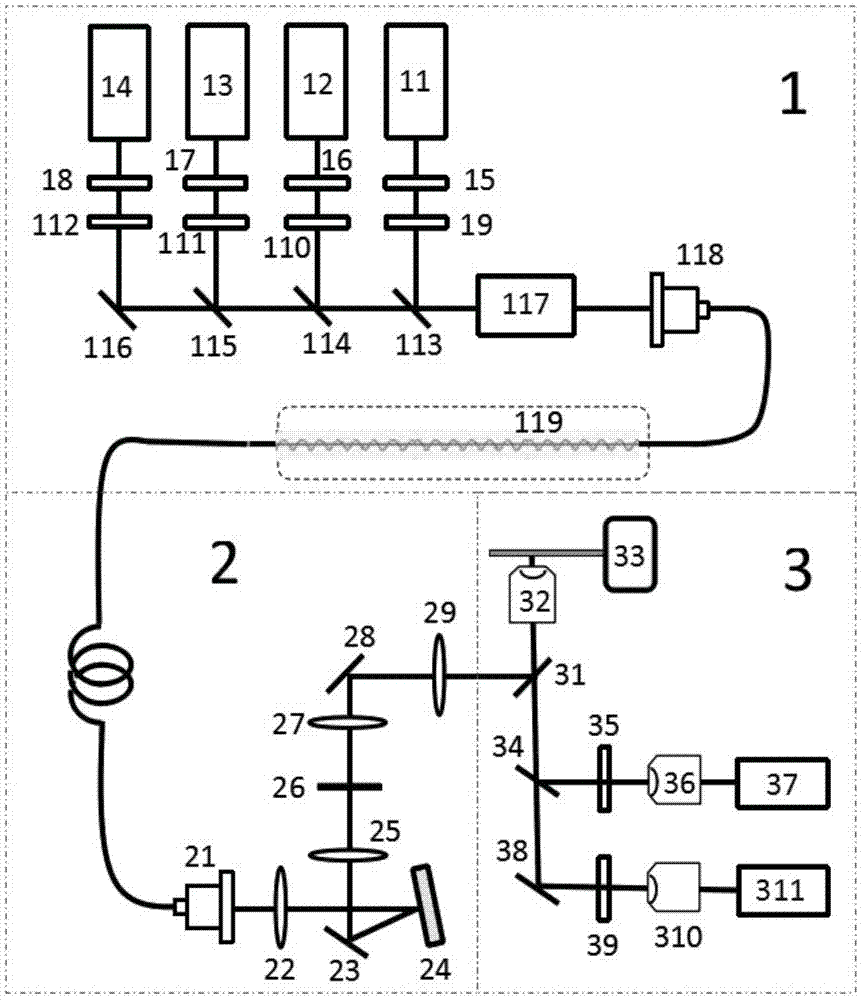
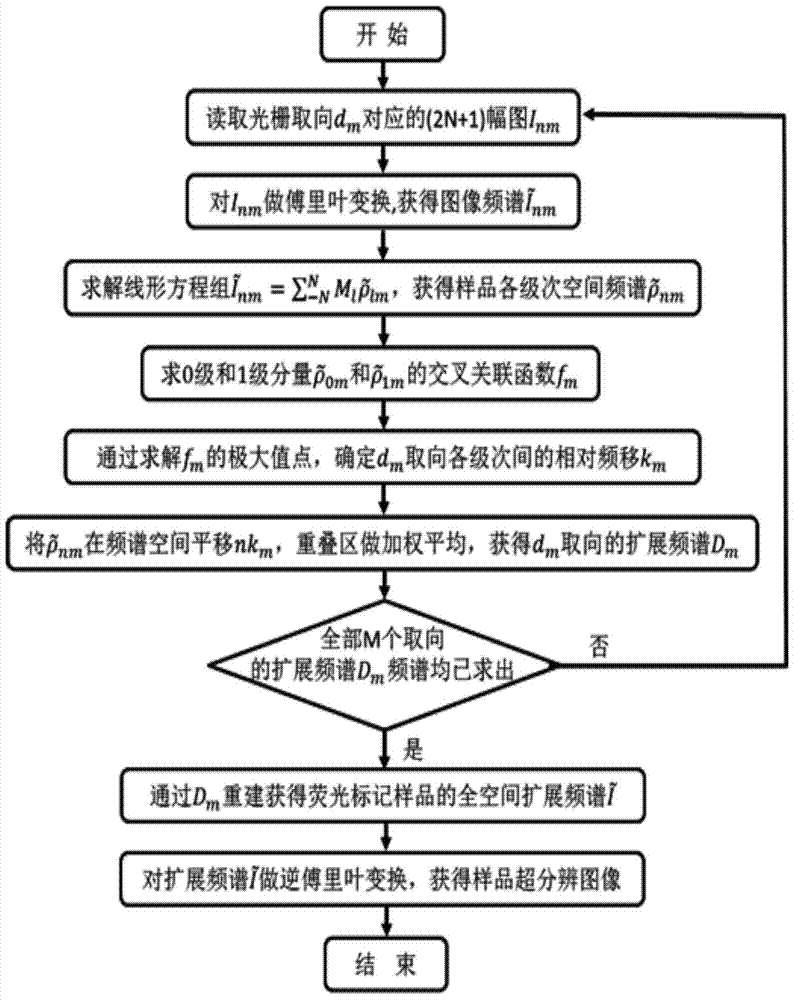
[0037] In order to achieve the purpose of the present invention, as figure 1 and 3 As shown, in some embodiments of the nonlinear structured illumination microscopy imaging method of the present invention, it includes the steps of:
[0038] Step S101: Uniformly illuminate the sample with excitation light, collect traditional wide-field illumination imaging images through SCOMS,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com