Web page cross-domain communication method and device
A cross-domain communication and webpage technology, applied in the field of webpage processing, can solve the problem of lost cross-domain data transmission convenience, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing mutual nesting problems and reducing development costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] refer to figure 1 , shows a flow chart of a webpage cross-domain communication method according to an embodiment of the present invention, the method may specifically include the following steps:
[0075] Step 11. The first page with the first root domain name loads the second page with the second root domain name in an embedded manner in the first page.
[0076] In the embodiment of the present invention, the first page and the second page are webpages of different sources, that is, their webpage addresses have different root domain names. For example, the webpage address of the first page is www.so.com, and the corresponding first The root domain name is so.com, the webpage address of the second page is www.i.so.com, and the corresponding second root domain name is i.so.com.
[0077] Loading the second page in an embedded manner in the first page can be in any achievable manner, for example, by embedding an iframe frame, inserting "" statement; or use Scriptlets comp...
Embodiment 2
[0125] refer to figure 2 , showing a flow chart of a web page cross-domain communication method according to another embodiment of the present invention, the method may specifically include the following steps:
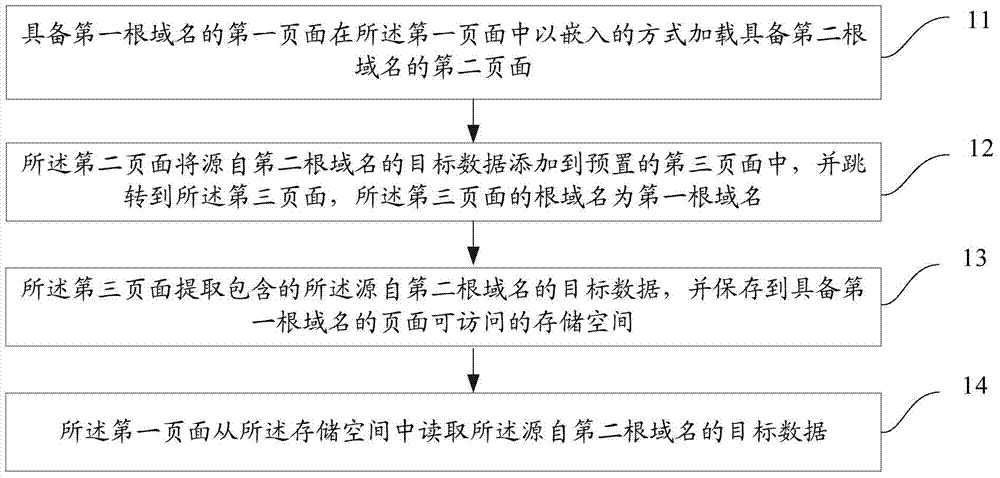
[0126] Step 21: The first page with the first root domain name loads the second page with the second root domain name in an embedded manner in the first page.
[0127] Step 22, the second page adds the target data from the second root domain name to the preset third page, and jumps to the third page, the root domain name of the third page is the first root domain name.
[0128] Step 23, the third page extracts the included target data originating from the second root domain name, and saves it in a storage space accessible to pages with the first root domain name.
[0129] Step 24: After the target data is saved in the storage space accessible by the page with the first root domain name, or after the loading of the third page is completed, the third page triggers an...
Embodiment 3
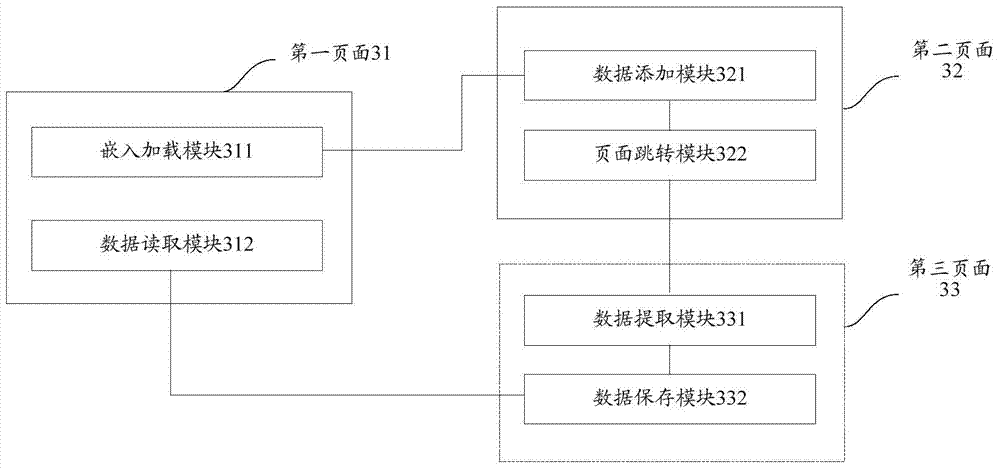
[0143] refer to image 3 , which shows a structural block diagram of an apparatus for webpage cross-domain communication according to an embodiment of the present invention, which may specifically include a first page 31 , a second page 32 and a third page 33 .
[0144] The first page 31 includes an embedded loading module 311;
[0145] The embedded loading module 311 is configured to load a second page with a second root domain name in an embedded manner in the first page on the first page with the first root domain name;
[0146] The second page includes a data adding module 321 and a page jump module 322;
[0147] The data adding module 321 is used for the second page to add the target data originating from the second root domain name to the preset third page, where the root domain name of the third page is the first root domain name;
[0148] The page jump module 322 is configured to jump to the third page;
[0149] The third page 33 includes a data extraction module 33...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com