Organic light emitting device and method for manufacturing organic light emitting device
A technology of organic light-emitting devices and organic light-emitting layers, which is applied in the manufacture of semiconductor/solid-state devices, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., and can solve the problems of diffuse reflection, OLED appearance influence, coupling-out efficiency limitation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0166] In the exemplary embodiments and figures, elements that are identical, of the same type or have the same effect can each be provided with the same reference numerals. The illustrated elements and their mutual size relationships are not to be regarded as to scale, rather individual elements such as layers, Components, devices and areas.
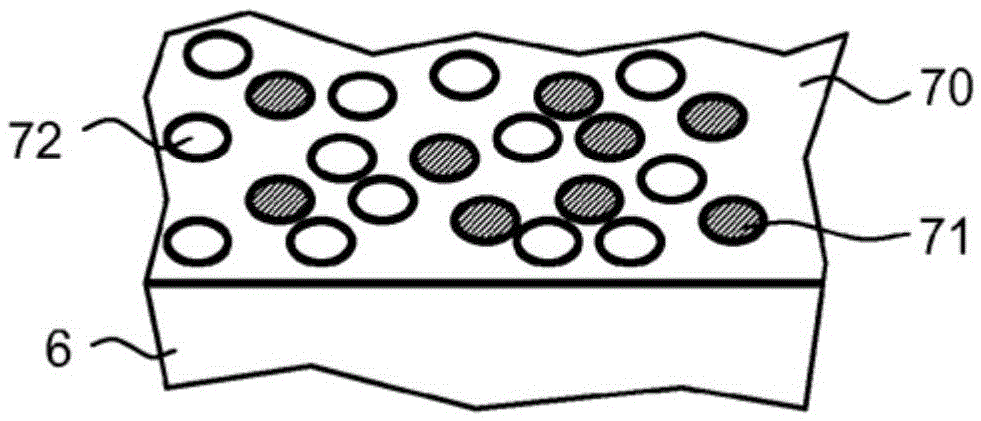
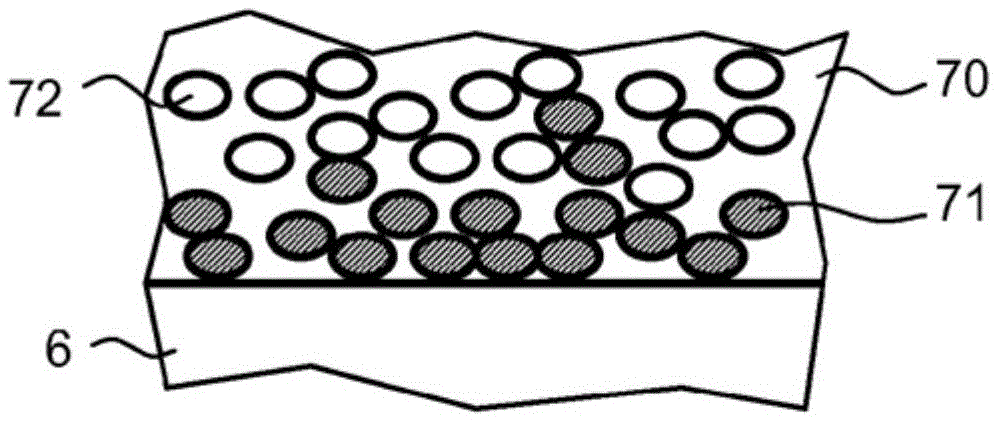
[0167] exist figure 1 An example of an organic light-emitting component 100 having a functional layer stack 10 is shown in FIG.
[0168] The functional layer stack 10 has a substrate 1 on which an organic functional layer stack 4 is arranged between a first electrode 2 and a second electrode 3 . The organic functional layer stack 4 has an organic emitting layer 5 .
[0169] In the exemplary embodiment shown, the substrate 1 is transparent, for example in the form of a glass pane or glass layer. A first electrode 2 is applied above the substrate, which first electrode comprises, for example, a transparent conductive oxide such as ITO...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com