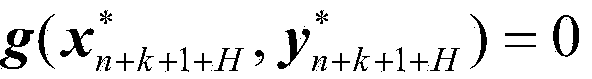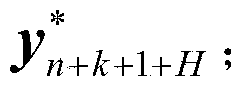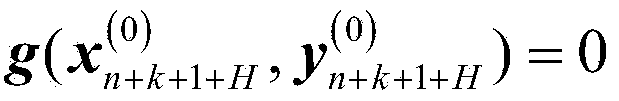Implicit-projection-based method for simulating stability of active power distribution system
An implicit projection algorithm and power distribution system technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult calculation speed and numerical stability limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example
[0096] For the linear integration algorithm, the linear constant coefficient differential equation The solution of and the scalar equation
[0097] x · = λx
[0098] The solutions are equivalent, where λ is the characteristic root of the matrix A, so the above formula is also called the scalar test equation. For a given numerical integration algorithm, its numerical stability domain refers to the s domain, and the algorithm satisfies the numerical stability condition when solving the scalar test equation
[0099] |σ(hλ)|≤1
[0100] The set of hλ.
[0101] This example takes the explicit fourth-order Runge-Kutta method (hereinafter referred to as RK4 algorithm) as an example for the internal integrator of the implicit projection algorithm. According to the numerical stability conditions, the implicit projection algorithm, the traditional RK4 algorithm and the explicit The numerically stable region of the for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com