Method and system for controlling gait of robot
A robot and gait technology, which is applied in the direction of robots, program-controlled manipulators, manipulators, etc., can solve the problems of large number of sensors, difficulty in accurately determining the wearer's expected gait robot, and increased production costs, so as to achieve comfortable wearing feeling and avoid Low reliability and lower production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] Hereinafter, the method and system for controlling the gait of a robot according to preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
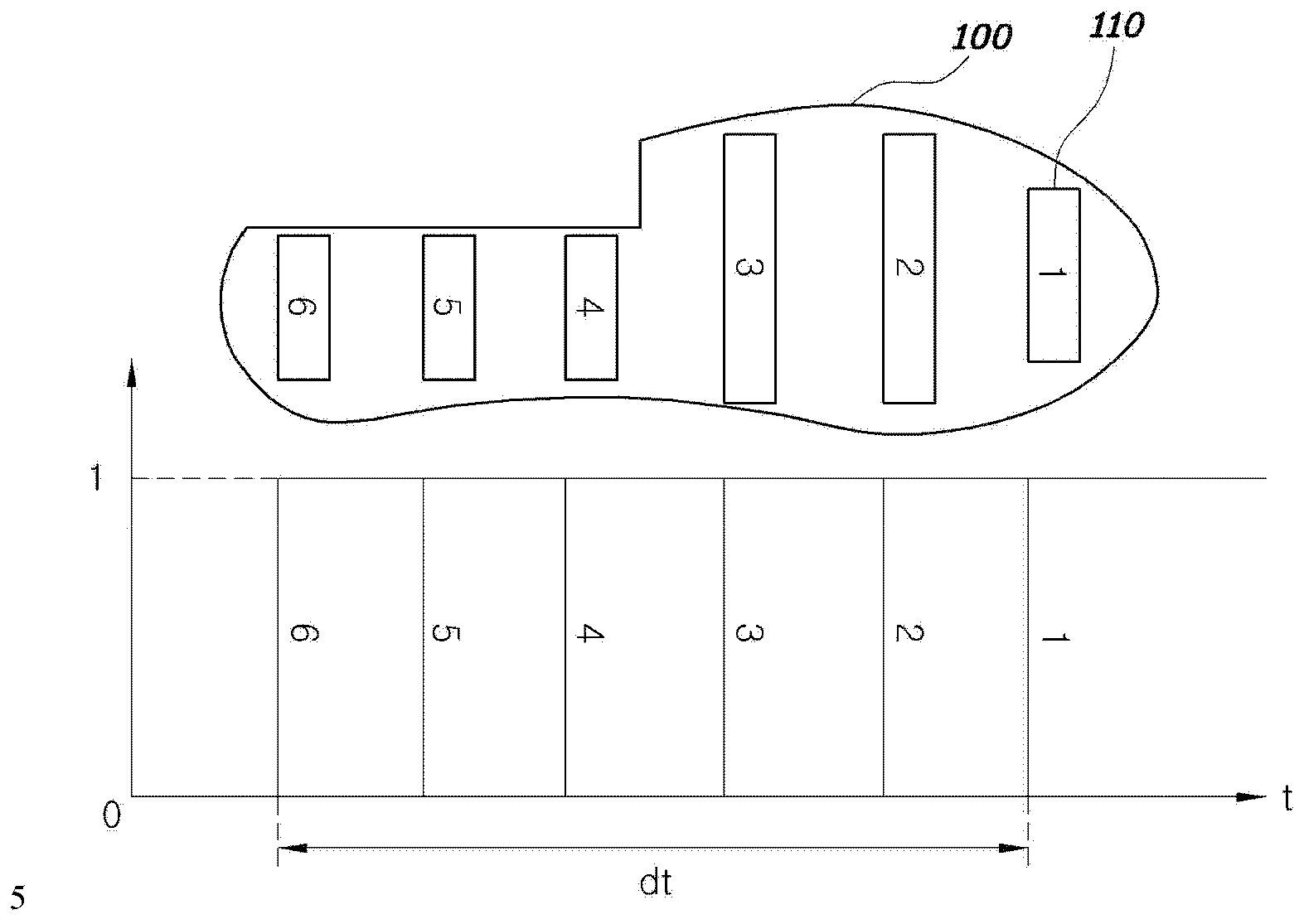
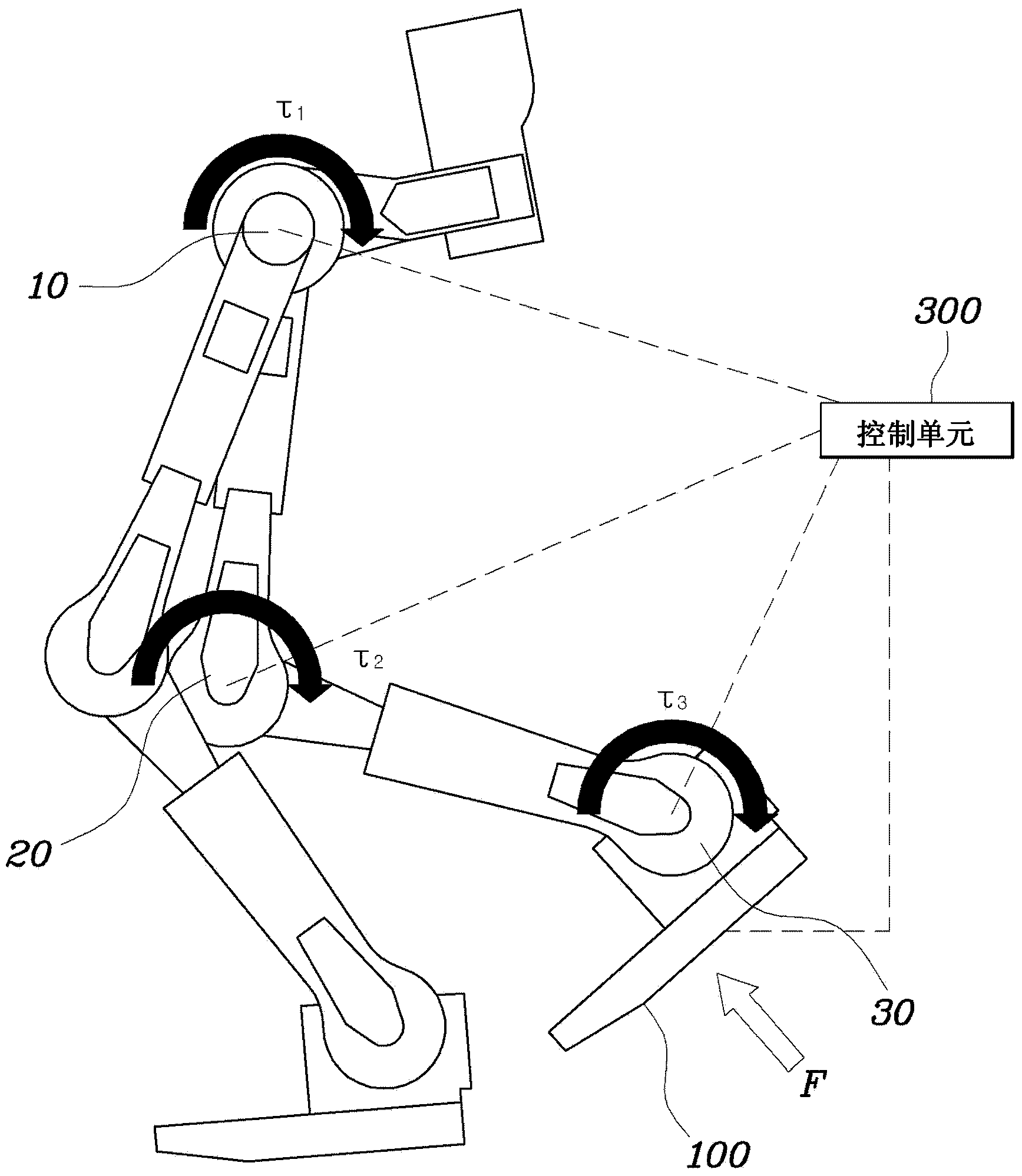
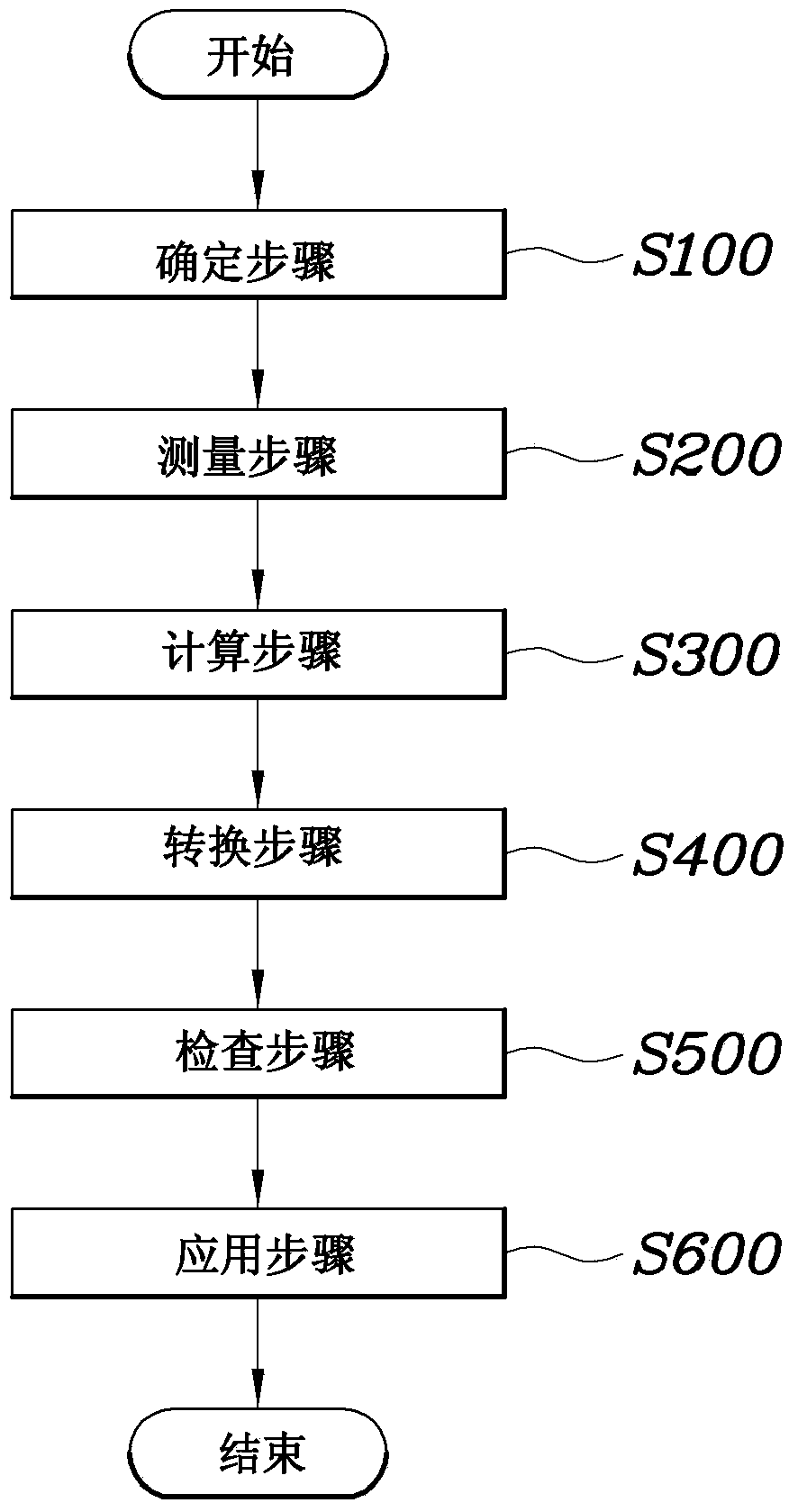
[0028] figure 1 is a diagram showing a surface contact sensor used in a method for controlling gait of a robot according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. figure 2 is a diagram showing the structure of a system for controlling gait of a robot according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. image 3 is a flowchart of an exemplary robot gait control method according to the present invention. Figure 4 is a graph showing trigonometric functions of the robot gait control method according to the present invention.
[0029] image 3 is a flowchart of an exemplary robot gait control method according to the present invention. The robot gait control method includes a determining step S100, determining whether the robot is in a walking sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com