Systems and methods of storing data
A data and data page technology, applied in information storage, read-only memory, static memory, etc., can solve the problem that logical pages affect flash memory access methods and performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
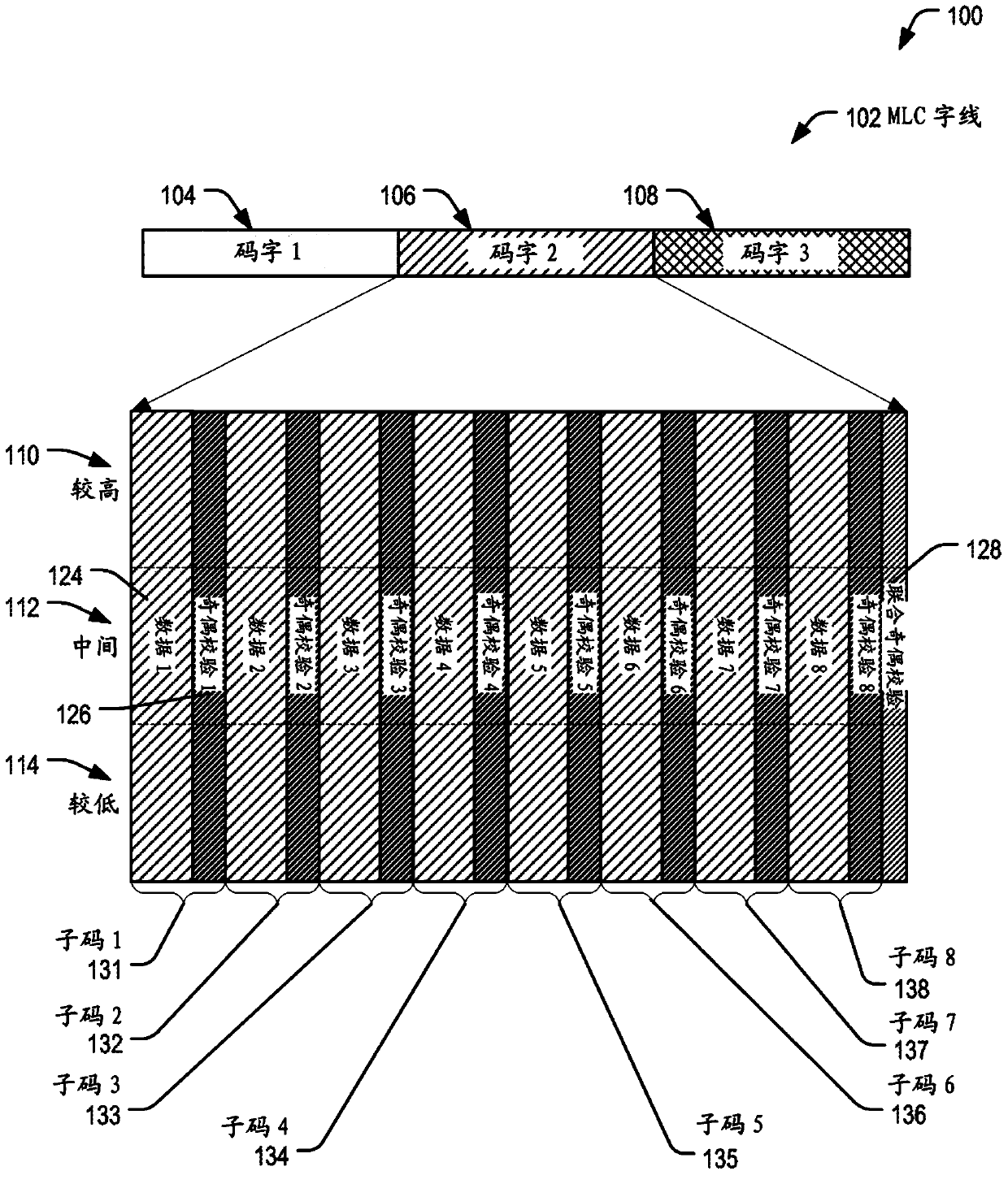
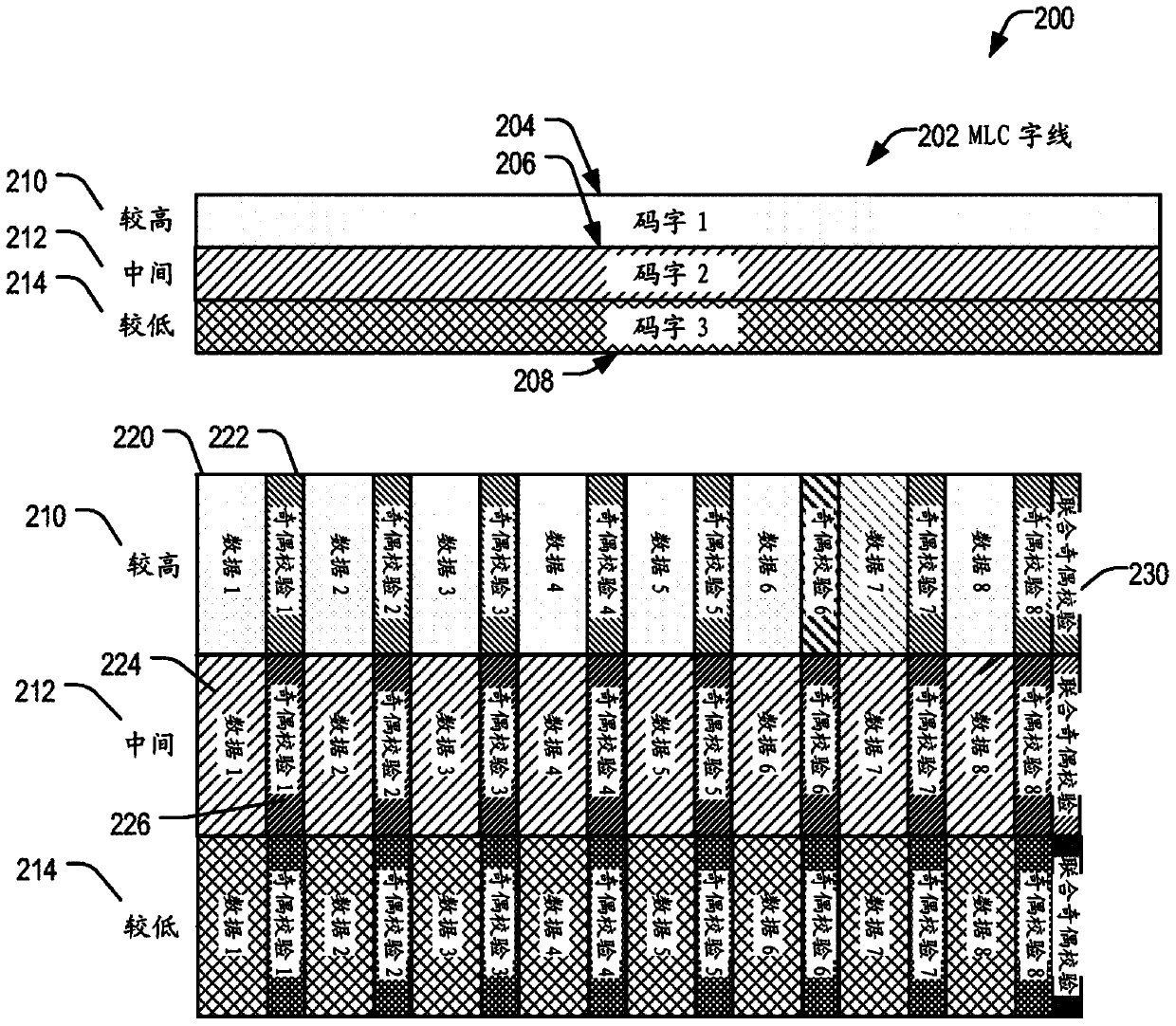
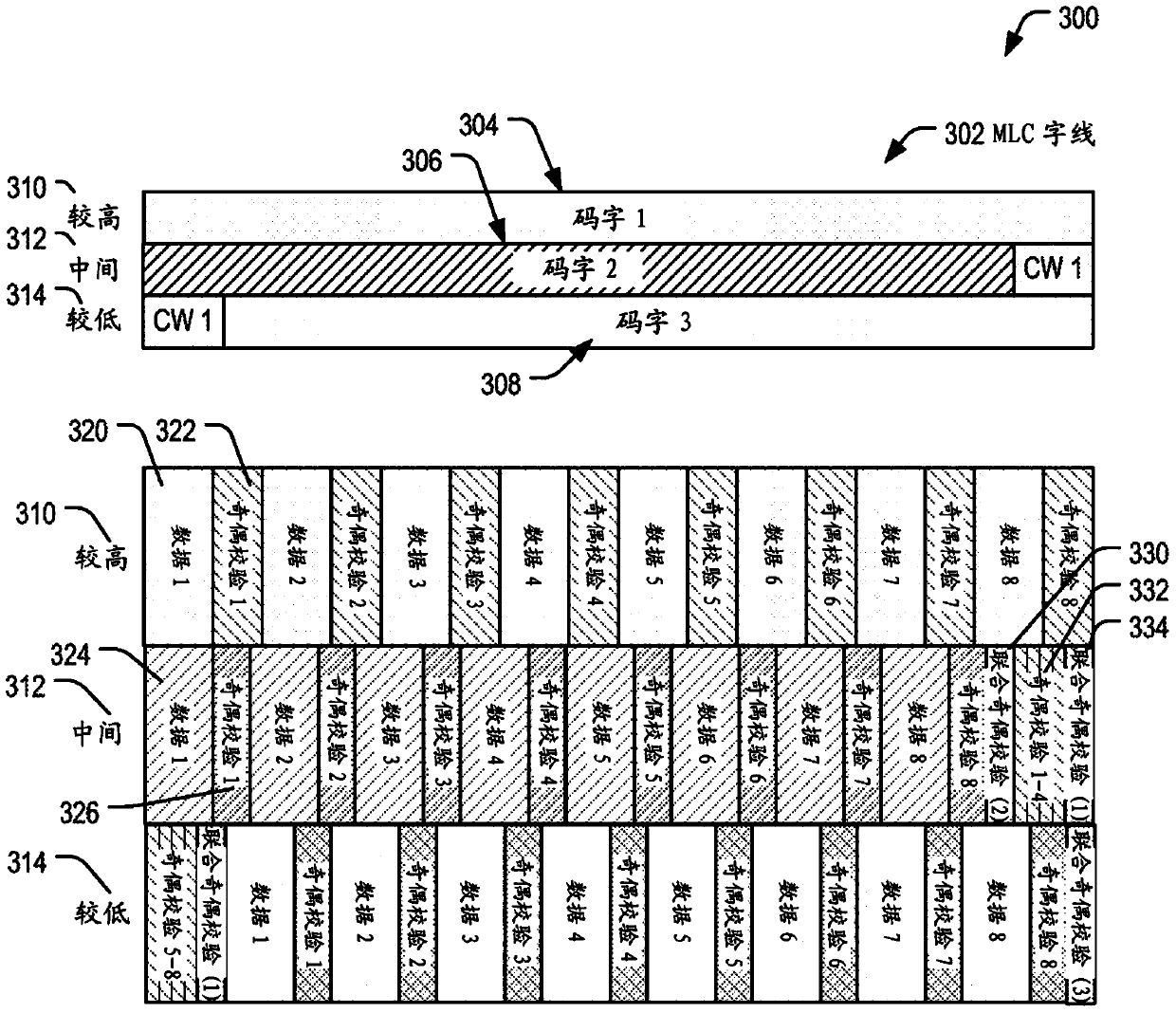
[0041] By using a multi-stage decoding concatenated code construction, an efficient encoding scheme that provides a good trade-off between reliability, access time and complexity can be implemented at flash memory. Such a code construction enables efficient access to small amounts of data by individually protecting each small amount of data using word codes stored as short sub-words in flash memory. A subcode may include data and parity bits that provide redundancy to protect the data. The subword can later be read from flash, passed to the flash controller, and decoded to retrieve the data for that subcode. Reading the subwords individually and decoding the subcodes enables faster read performance for random read requests of the flash memory compared to reading and decoding the entire codeword to access the data. If decoding a subcode fails because there are too many errors in the subword, a longer codeword can be read from flash memory, passed to the controller and decoded ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com