A kind of water-based gel chromatography medium and method for detection
A chromatographic medium and water-based glue technology, applied in the field of medical detection, can solve the problems of reducing incubation time, cumbersome, complex antibodies, etc., and achieves the effects of low production technical requirements, improved detection efficiency, and simplified operation steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
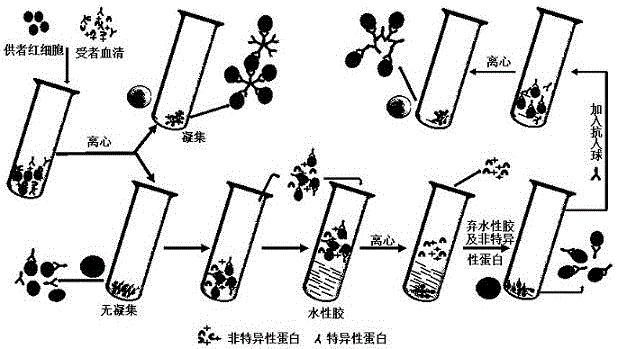
[0021] see figure 1 , providing a method for detecting incomplete antibodies by erythrocyte-aqueous gel chromatography anti-human globulin, comprising the steps of: (1) sensitization of erythrocytes: adding whole blood O-type RhD(+) and RhD(-) erythrocytes with normal saline Dilute to a volume percentage of 5%, take anti-D with a titer of 64 diluted with human serum, mix the two in equal volumes, and incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes;
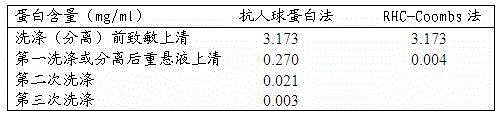
[0022](2) Add 1 mL of hydrocolloid to the two test tubes, then add 100 μL RhD(+) and 100 μL RhD(-) red blood cells respectively, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 1 min, discard the hydrocolloid, add 100 μL HG, and centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 1 min , observe the agglutination result. Add 1 drop of sensitized red blood cells to the test tube with negative results, and centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 1 min to verify the effectiveness of AHG.
[0023] At the same time, the test tube anti-human globulin test was used as a parallel control test, and the consiste...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Provide a erythrocyte-water gel chromatography direct antiglobulin test:
[0027] Mix 5% type O erythrocytes with equal volume of anti-D with a titer of 64 diluted with human serum, and incubate at 37°C for 30 min. Add 1 mL of hydrocolloid to a test tube, then dropwise add 100 μL of the sensitized erythrocytes obtained in Example 1, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 1 min, discard the hydrocolloid, then add 100 μL of LAHG dropwise, mix well, and centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 1 min. Observe for agglutination.
[0028] Provide a red blood cell-water gel chromatography indirect anti-human globulin test:
[0029] Add 1mL of hydrocolloid to a test tube, mix 5% type O red blood cells with equal volume of anti-D with a titer of 64 diluted with human serum, take 100μL of the mixture and place it on the upper layer of hydrocolloid, and incubate at 37°C for 30min Finally, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 1min, discard the hydrocolloid, add 100μLAHG dropwise, mix well, centrifuge at 1000rpm for ...
Embodiment 3
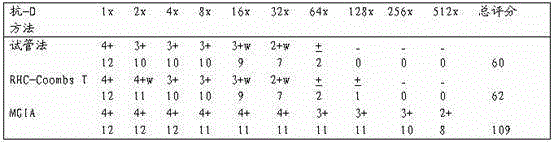
[0032] Provide a sensitivity comparison of anti-human globulin method, MGIA method and erythrocyte-water gel chromatography anti-human globulin method for detection of incomplete antibodies:
[0033] Erythrocyte sensitization: Dilute anti-D to 1:512 with 1% (w / v) BSA saline solution by mass volume percentage, wash 4 times with normal saline and dilute to 6% volume ratio, both Equal volumes were mixed, incubated at 37°C for 30 min, and mixed twice in between.
[0034] Test tube antihuman globulin method: wash all the sensitized red blood cells with normal saline 4 times, make a volume ratio of 3% for later use, mark the test tubes, add 50 μL of red blood cells dropwise to each tube, and then add 100 μL of AHG with a titer of 64 , centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 1 min, and observe the agglutination strength of different dilutions.
[0035] MGIA method: take a commercial MGIA anti-human globulin card, mark it well, add 50 μL of sensitized unwashed red blood cells with a volume ratio ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com