Method for training scout bees and letting scout bees fly
A technology for reconnaissance bees and bees, applied in the field of training and flying scout bees, can solve the problems of few successful cases, inability to estimate the best timing for releasing bees to find targets, low efficiency, etc., to achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
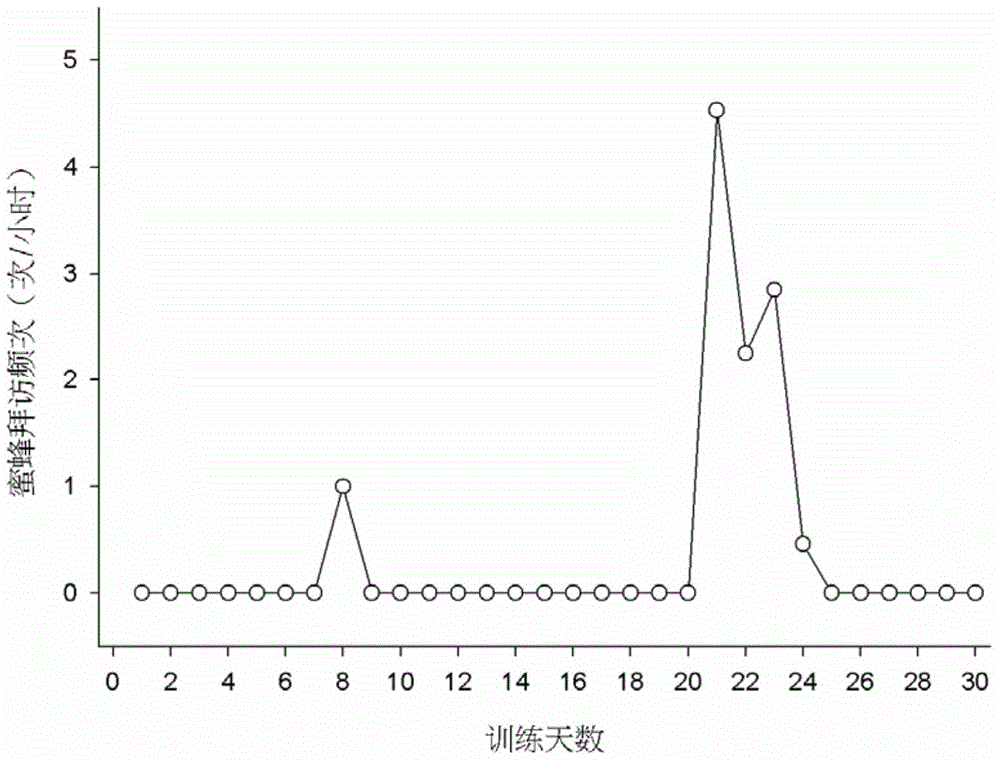
[0019] ①Choose a group of bees, intercept 15-20 worker bees at the door of the hive, put them into a small glass bottle (usually only 1-2 in each small glass bottle), and cover it tightly with a cap with a small hole Small glass jars. Add 150ml of cold water to a 250ml beaker, and put some ice cubes in the cold water, then insert the small glass bottle into it, let the body temperature of the bees drop gradually, after about 10 minutes, the bees start to freeze, take out the bees, Strap them to metal brackets designed for training bees. During the binding process, the whole body of the bee is bound up, and only the head and antennae of the bee can move freely.
[0020] ②After the bound bees wake up, use the needle of a 1ml syringe to tap the bee's antennae to induce the bees to kiss, then push the syringe to overflow the syrup, let the bees suck the syrup until the bees are full and withdraw their kisses. Put the fed bees into the cardboard box, cover the lid, and place in a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com