Method and system using global and local catastrophes across sub-populations in parallel evolutionary computing
A group, local technology, applied in the field of evolutionary computing, can solve the problem of premature convergence of the execution instance of the evolutionary algorithm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
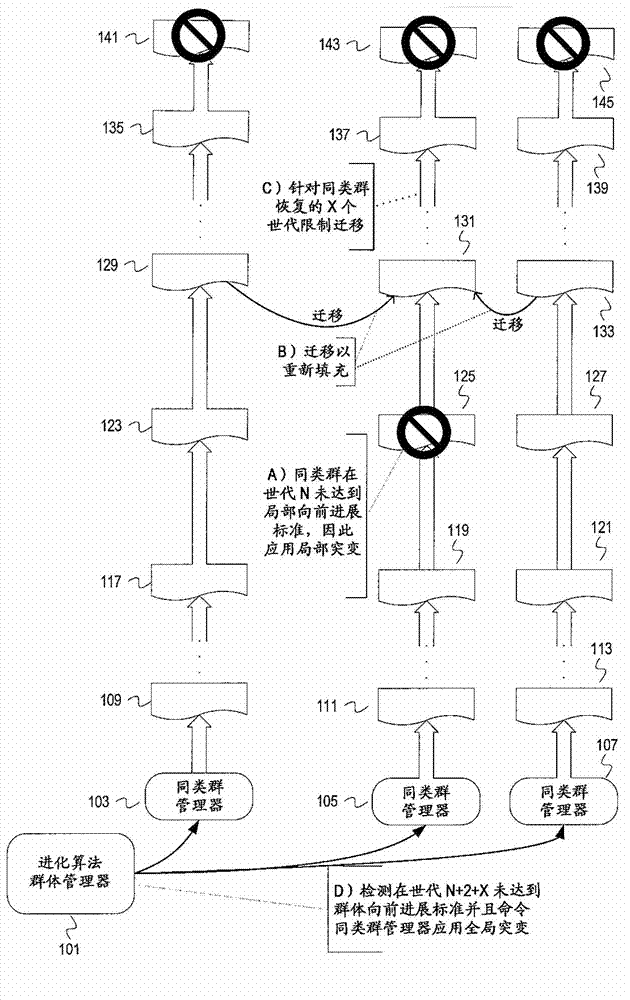
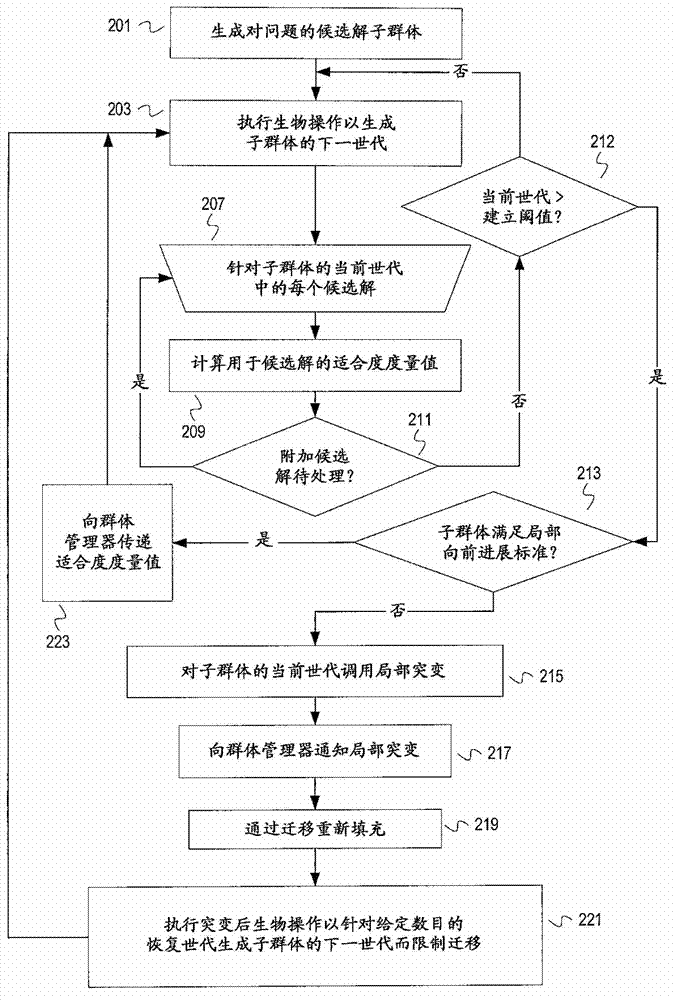
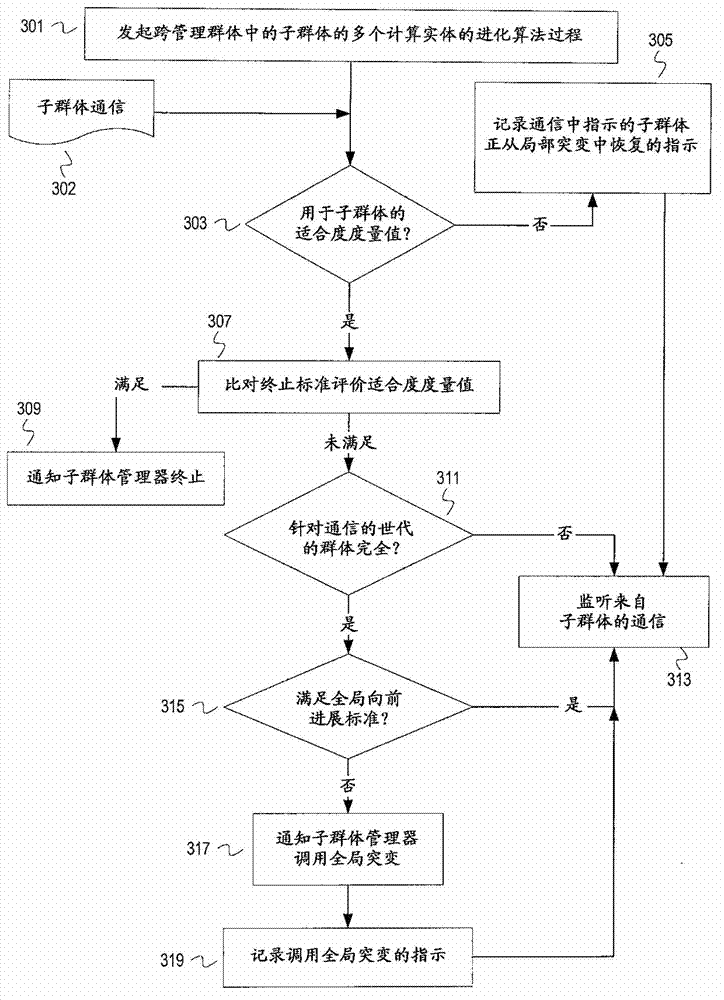
[0014] The following description includes example systems, methods, techniques, instruction sequences and computer program products that implement techniques of the inventive subject matter. However, it is understood that the described embodiments may be practiced without these specific details. For example, although the examples refer to machines, embodiments of the inventive subject matter can be practiced in a virtualized environment. For example, subpopulations can be assigned to different virtual machines supported by a single machine. As another example, subpopulations can be assigned to different cores in a multi-core environment. In other instances, well-known instruction instances, protocols, structures and techniques have not been shown in detail in order not to obscure the description.
[0015] the term
[0016] The literature on evolutionary computation uses a large variety of terms. In some cases, terms are used ambiguously. The genetic algorithm literature ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com