Train fault recording device and method
A fault recording and train technology, applied in the field of rail transit vehicle communication, to achieve the effect of avoiding faults, enhancing reliability and safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
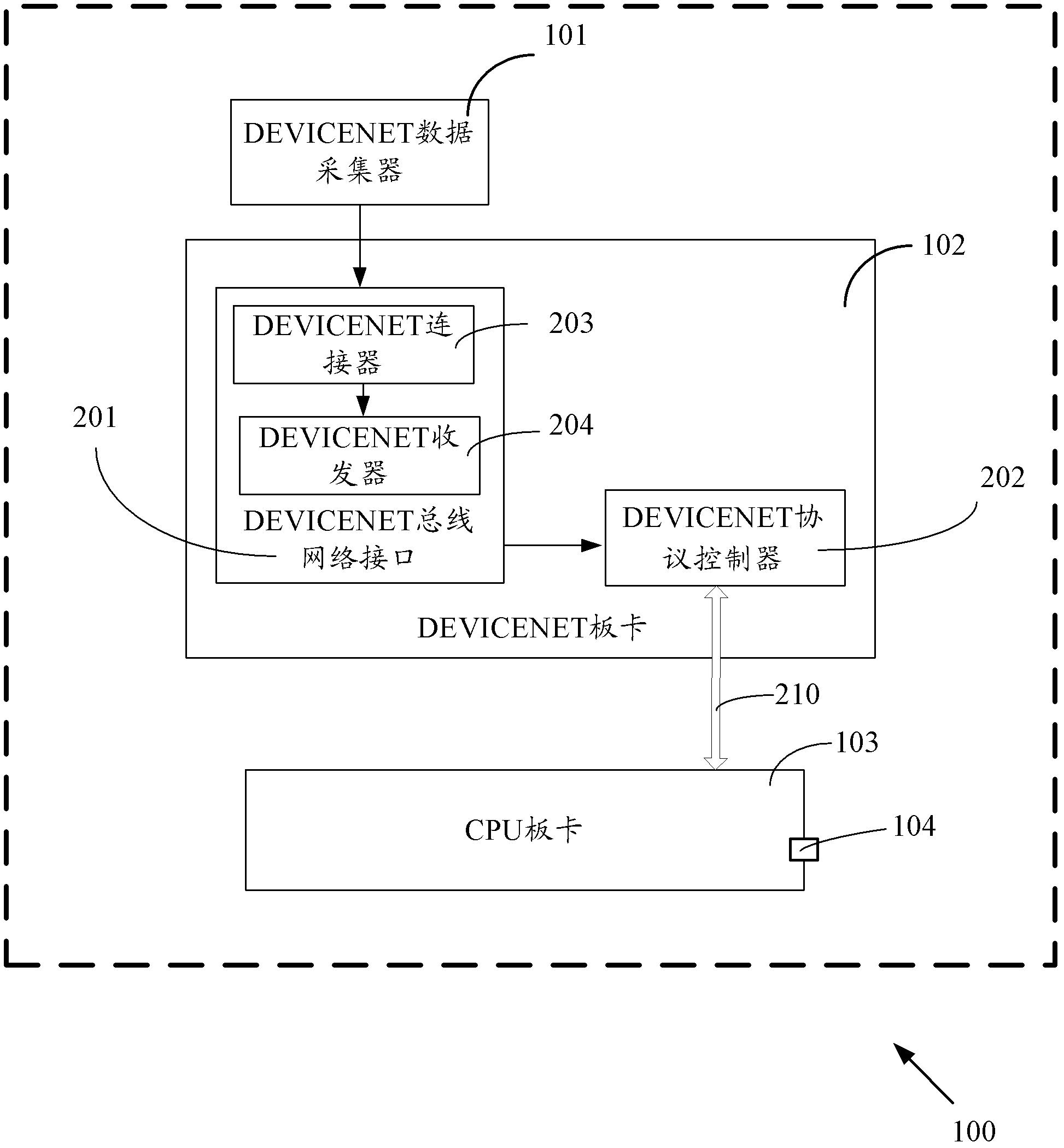
[0032] Embodiment 1 provides a train fault recording device. Such as figure 1 As shown, the train fault recording device 100 includes a DEVICENET data collector 101 , a DEVICENET board 102 and a CPU (Central Processing Unit, central processing unit) board 103 .
[0033] Wherein, DEVICENET data collector 101 is used for collecting the real-time monitoring data of train, and this real-time monitoring data is sent to DEVICENET board card 102; DEVICENET board card 102 is used for receiving the real-time monitoring data that DEVICENET data collector 101 sends and sends to CPU board The card 103 sends real-time monitoring data; the CPU board 103 includes an Ethernet port 104 for receiving and storing the real-time monitoring data, and calling the real-time monitoring data and sending the real-time monitoring data to the client through the Ethernet port 104 .
[0034] Specifically, the real-time monitoring data is mainly the train operation status collected in real time, such as the...
Embodiment 2
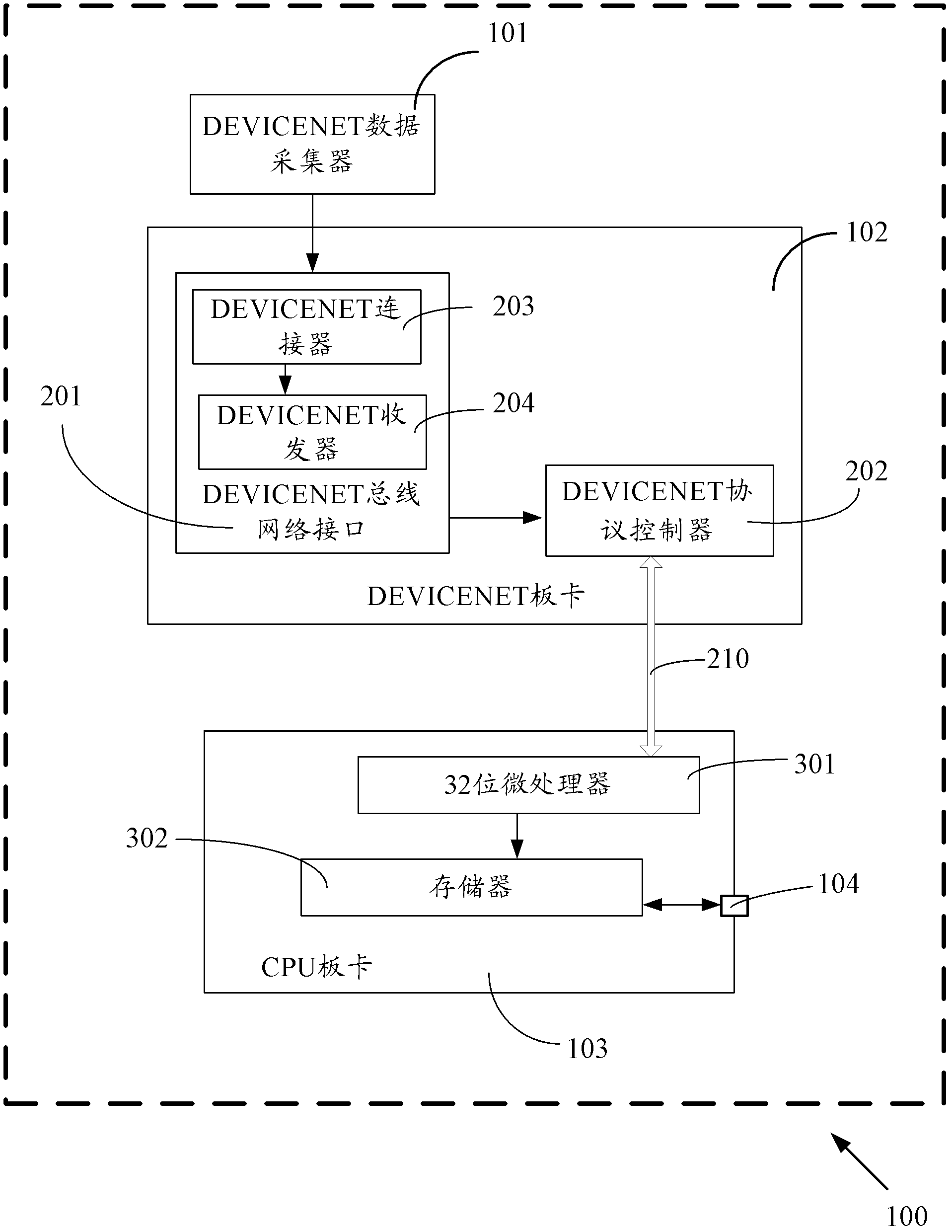
[0040] The second embodiment further explains in detail the CPU board in the train fault recording device of the first embodiment, and other structures are consistent with the above-mentioned embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
[0041] Such as figure 2 As shown, the CPU board 103 in the train fault recording device 100 of this embodiment also includes a 32-bit microprocessor 301 and a memory 302 .
[0042]Specifically, the 32-bit microprocessor 301 is used to receive real-time monitoring data and process the real-time monitoring data, and send the processed real-time monitoring data to the memory 302; the memory 302 is used to receive and store the data sent by the 32-bit microprocessor 301 The processed real-time monitoring data.
[0043] In this way, when the user needs to read the stored historical real-time monitoring data from the memory 302 , it can be directly read from the memory 302 through the Ethernet port 104 . The faulty train can be analyzed through th...
Embodiment 3
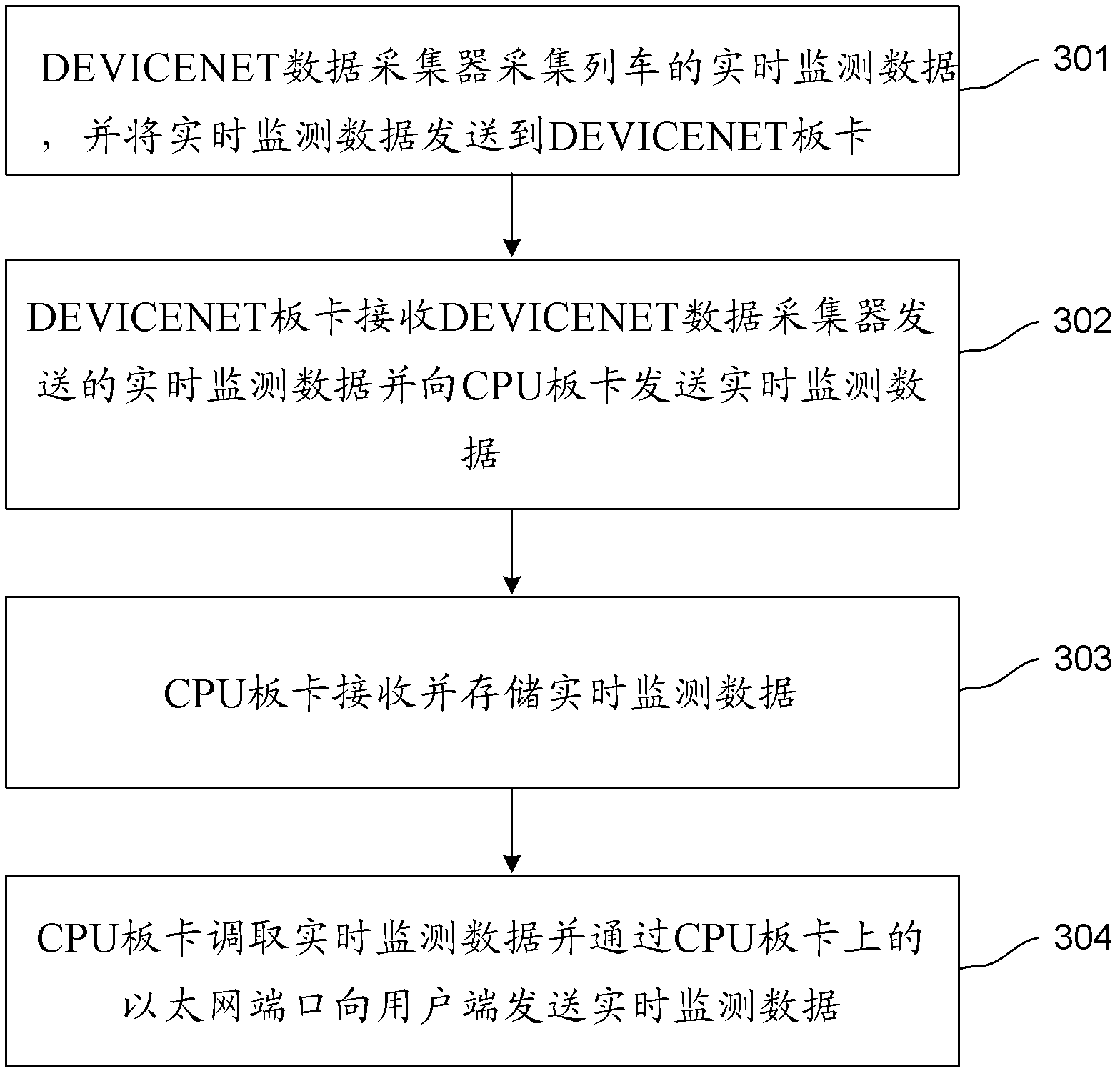
[0046] The third embodiment provides a train failure recording method, such as image 3 As shown, it is a schematic flow chart of the train fault recording method in the third embodiment. The train failure recording method can be executed by the train failure recording device of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2.
[0047] Step 301, the DEVICENET data collector collects real-time monitoring data of the train, and sends the real-time monitoring data to the DEVICENET board.
[0048] Step 302, the DEVICENET board receives the real-time monitoring data sent by the DEVICENET data collector and sends the real-time monitoring data to the CPU board.
[0049] Step 303, the CPU board receives and stores real-time monitoring data.
[0050] Step 304, the CPU board retrieves the real-time monitoring data and sends the real-time monitoring data to the client through the Ethernet port on the CPU board.
[0051] According to the train fault recording method of the present embodiment 3, the real...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com