Purification method of indium back extraction solution
A stripping liquid and solution technology, which is applied in the field of comprehensive recovery of indium, can solve the problems of lower indium replacement efficiency and direct recovery rate, high consumption of zinc powder, and difficulty in removal, etc., so as to prevent the generation of arsine, low production cost, and effective Good for recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] In this example, the main components of indium stripping solution S1 (both in ionic state) are: In 87.62g / L, Fe 3.40g / L, Bi 1.58g / L, Sn 0.037g / L, As 5.61g / L L, Sb 1.60g / L.
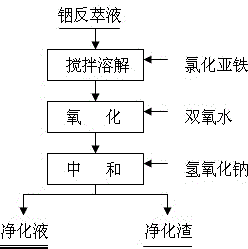
[0044] Step A: Add ferrous chloride to the purification tank equipped with indium stripping solution S1, stir continuously to dissolve it completely, and the amount of ferrous chloride added is the ferrous chloride required for the complete precipitation of arsenic and antimony in S1 1.0 times the theoretical amount.
[0045] Step B: Under stirring, slowly add hydrogen peroxide to the solution system of step A, and react for 0.5h under stirring to obtain an oxidation solution; wherein, the amount of hydrogen peroxide is oxidized Fe 2+ and Sn 2+ 1.1 times the required theoretical amount.
[0046] Step C: Add sodium hydroxide to the oxidizing solution prepared in step B, and carry out neutralization reaction under agitation. The neutralization reaction controls the end point pH=2.0, and keeps the e...
Embodiment 2
[0049] In this example, the main components of indium stripping solution S2 (both in ionic state) are: In 115.83g / L, Fe 6.07g / L, Bi 1.92g / L, Sn 0.042g / L, As 6.18g / L L, Sb 0.96g / L.
[0050] Step A: Add ferrous chloride to the purification tank equipped with indium stripping solution S2, stir continuously to make it completely dissolved, and the amount of ferrous chloride added is the ferrous chloride required for the complete precipitation of arsenic and antimony in S2 1.1 times the theoretical amount.
[0051] Step B: Under stirring, slowly add hydrogen peroxide to the solution system of step A, and react for 0.8h under stirring to obtain an oxidation solution; wherein, the amount of hydrogen peroxide is oxidized Fe 2+ and Sn 2+ 1.3 times the required theoretical amount.
[0052] Step C: Add sodium hydroxide to the oxidized solution prepared in step B, and carry out neutralization reaction under agitation. The neutralization reaction controls the end point pH=2.3, and keeps...
Embodiment 3
[0055] In this example, the main components of indium stripping solution S3 (both in ionic state) are: In 120.18g / L, Fe 4.19g / L, Bi 2.60g / L, Sn 0.051g / L, As 4.95g / L L, Sb 1.18g / L.
[0056] Step A: Add ferrous sulfate to the purification tank equipped with indium stripping liquid S3, stir continuously to make it completely dissolved, the amount of ferrous sulfate added is the theoretical amount of ferrous sulfate required for the complete precipitation of arsenic and antimony in S2 1.2 times.
[0057] Step B: Under stirring, slowly add hydrogen peroxide to the solution system in step A, and react for 1 hour under stirring to obtain an oxidation solution; wherein, the amount of hydrogen peroxide is oxidized Fe 2+ and Sn 2+ 1.5 times the required theoretical amount.
[0058] Step C: Add sodium hydroxide to the oxidizing solution prepared in step B, and carry out neutralization reaction under stirring conditions, and control the end point pH of the neutralization reaction to be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com