PWM (pulse width modulation) dimming method and device for LED (light-emitting diode)
A technique of adjusting and adjusting coefficients, which is applied in the field of PWM dimming methods and devices, and can solve the problems of few PWM output ports of single-chip microcomputers.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
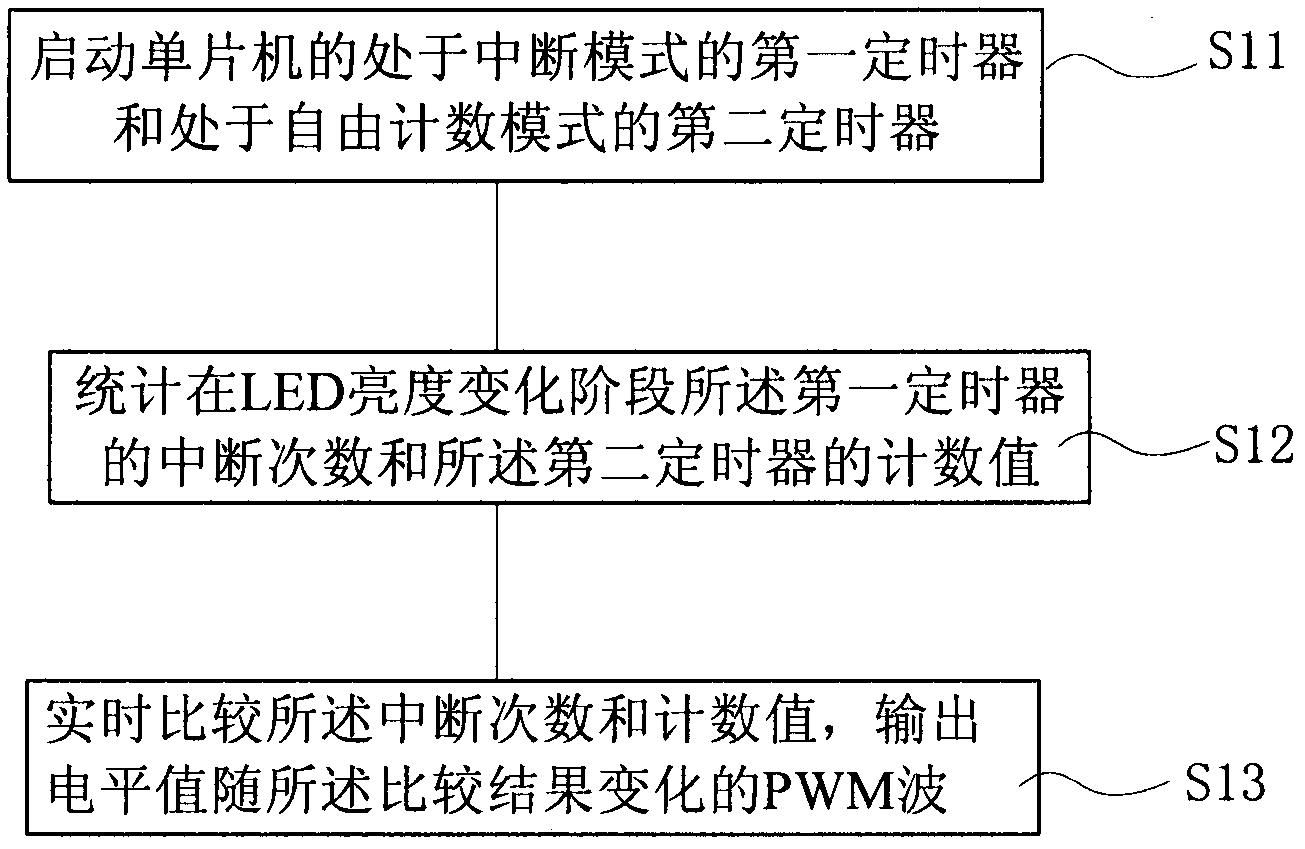
[0078] figure 2 It is a schematic flowchart of a PWM dimming method for controlling a single LED provided by the first embodiment of the present invention.
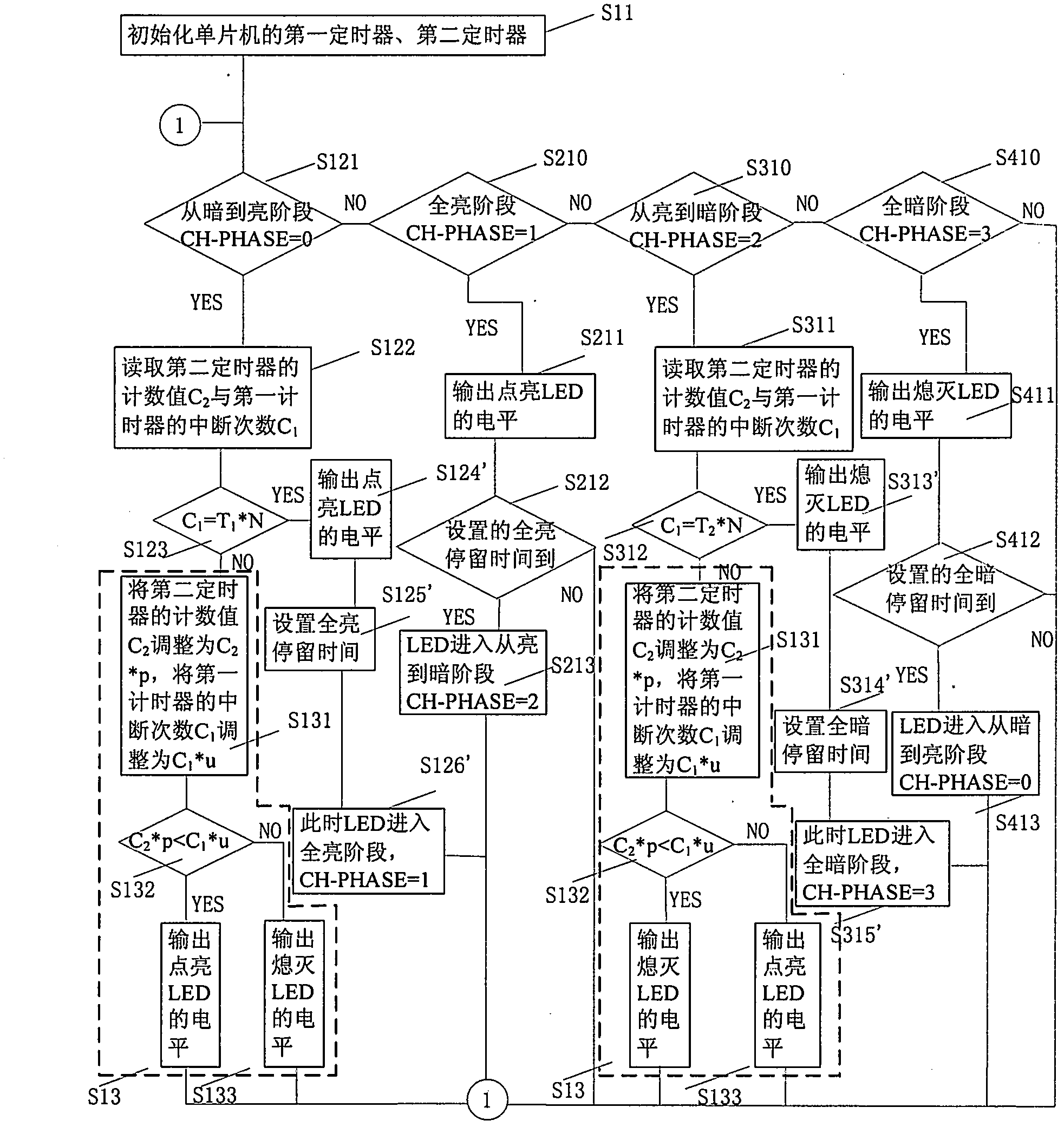
[0079] combine figure 1 and figure 2 , execute S11, initialize the first timer and the second timer of the single-chip microcomputer;
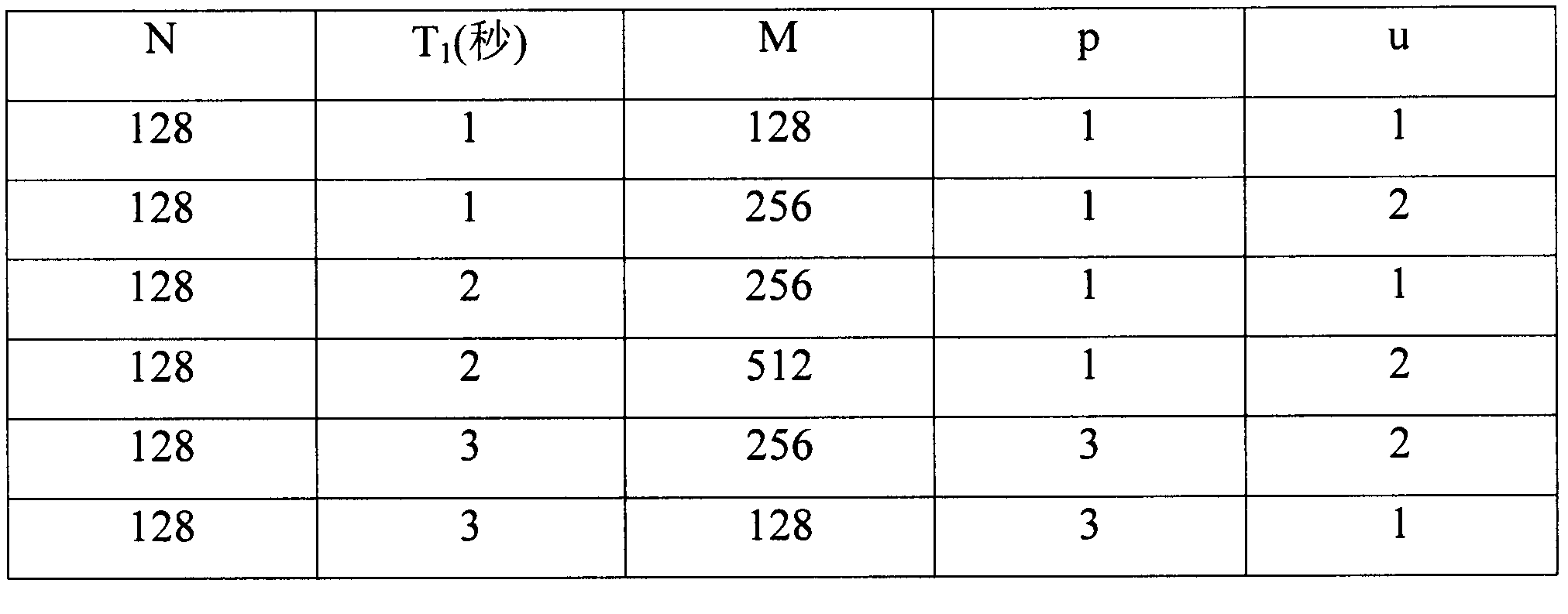
[0080] The first timer is set to interrupt mode, N times per second; the second timer is set to free counting mode.
[0081] Then execute S12, count the number of interruptions of the first timer and the count value of the second timer in the LED brightness change stage, including: LED is in the process of changing from dark to bright or from bright to dark, counting all The number of interruptions of the first timer mentioned above, and cleared when the first clear value is counted, the second timer starts to count freely and every first time T 3 The count is increased by 1, and the second timer is cleared when the count reaches the first value M;
[0082] When the LED changes fro...
Embodiment 2
[0130] If it is necessary to control the PWM dimming of two LEDs, and the brightness and dimming methods of the two LEDs and the required time are the same, then apply PWM to the LEDs of the two LEDs.
[0131] If the lighting and dimming methods or required time of the two LEDs are different, the dimming method and device provided in the second embodiment can be used.
[0132] In Figure 8(a), use CH1-PHASE=0 to mark the phase from dark to bright of the first LED, CH1-PHASE=1 to mark the phase when the first LED is fully bright, and CH1-PHASE=2 to mark the phase from the first LED to bright In the dark stage, CH1-PHASE=3 marks the full-dark stage of the first LED. The first LED starts from dark to bright by default, ie CH1-PHASE=0.
[0133] In Figure 8(b), use CH2-PHASE=0 to mark the stage from dark to bright for the second LED, CH1-PHASE=2 to mark the full-bright stage of the second LED, and CH2-PHASE=2 to mark the second LED from bright In the dark stage, CH2-PHASE=3 marks ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com