Face recognition method and device
A face recognition and face testing technology, applied in the field of face recognition, can solve the problems of not satisfying rotation invariance, long calculation time, poor recognition rate, etc., to reduce redundancy, improve recognition performance, and reduce complexity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Such as figure 1 The flow chart of the face recognition method provided by the present invention is shown, and for the convenience of description, only the parts related to the embodiment of the present invention are shown.
[0023] In step S101, the test image is generated into a plurality of test sub-images through circular symmetric Gabor transformation.
[0024] In the embodiment of the present invention, the test image is subjected to circular symmetric Gabor transformation to generate a plurality of corresponding test sub-images. For example, the test image can correspondingly generate 5, 6, or 7 test sub-images. Preferably, it is better to generate five test sub-images after the test image is subjected to circular symmetric Gabor transform.
[0025] In the embodiment of the present invention, since the ring-symmetric Gabor transform is invariant to rotation, the problem of discretization of directions in the traditional Gabor wavelet transform is avoided. Moreo...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Such as figure 2 Shown is the flow chart of the method for subjecting the sample images in the sample library to the circular symmetric Gabor transform and calculating the corresponding sample face feature space through PCA provided by the present invention. The method provided in the second embodiment can be compared with that in the first embodiment The method is used in combination, but not limited to the method provided in this example. For ease of description, only parts related to the embodiments of the present invention are shown.
[0040] In step S201, N sample images are subjected to Circular Symmetrical Gabor Transformation (CSGT) to generate multiple sample sub-images.
[0041] In the embodiment of the present invention, there may be N sample images in the sample image library, and N is a positive integer. Each sample image is subjected to circular symmetric Gabor transformation to generate multiple corresponding sample sub-images, and the test image is sub...
Embodiment 3
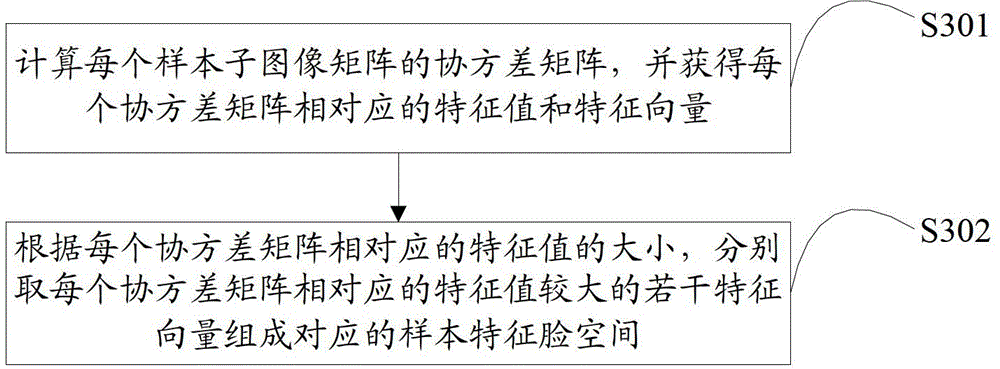
[0060] Such as image 3 Shown is the method flowchart of step S203 in the second embodiment of the present invention, which is a refinement of step S203 in the first embodiment, therefore, the method provided in the third embodiment can be combined with the methods in the first and second embodiments Use, but not limited to the method provided in this example. For ease of description, only parts related to the embodiments of the present invention are shown.
[0061] In step S301, the covariance matrix of each sample sub-image matrix is calculated, and the eigenvalues and eigenvectors corresponding to each covariance matrix are obtained.
[0062] In step S302, according to the size of the eigenvalues corresponding to each covariance matrix, several eigenvectors corresponding to each covariance matrix with larger eigenvalues are respectively selected to form a corresponding sample eigenface space.
[0063] In the embodiment of the present invention, the eigenvalues c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com