Adjustment method for dynamic stiffness of rubber joint with liquid damping, and rubber joint
A rubber joint, liquid damping technology, applied in the direction of shock absorber, spring, spring/shock absorber, etc., can solve problems such as changing dynamic stiffness, and achieve the effect of adjustable dynamic stiffness, easy implementation and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
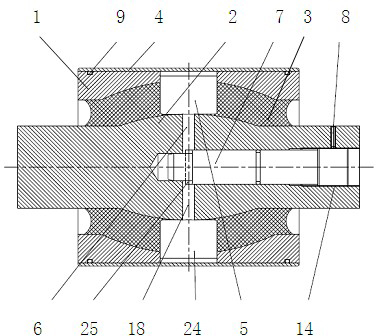
[0027] attached figure 1 An embodiment of the present invention is given, and it can be seen from the accompanying drawings that a rubber joint assembly with a liquid cavity and an adjustable flow channel inside includes a rubber joint jacket 1, a mandrel 2, and an elastic rubber 3; The rubber 3 is set on the mandrel 2; its characteristic is that there is a metal jacket 4 on the rubber joint jacket 1, and the rubber joint is pressed into the metal jacket; on the rubber joint jacket 1, two The independent liquid chambers 5 above communicate with each other through the throttling channel 6 arranged on the mandrel, and the throttling channel adjusting shaft 7 is set inside the mandrel 2 of the rubber joint and fixed by a set screw 8; Each part is sealed by an O-ring 9 to prevent leakage. The specific structure of the metal jacket 4 is a simple cylindrical tube, and rubber joints are press-fitted inside it.
[0028] attached figure 2 It is the specific structure of the rubber ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the throttling channel is formed in a different way (as attached Figure 5 shown), the throttling passage of embodiment one is formed by the step of the hole and the step of the shaft to form a channel with a square section, and the throttling passage of embodiment two is composed of the spherical end of the mandrel hole 28 and the spherical end of the adjustment shaft 27 The gap 26 between the mandrel hole 28 is composed of the spherical diameter of the end of the mandrel hole 28 and the spherical diameter of the end of the adjustment shaft 27. By adjusting the shaft 27 to move axially in the mandrel hole 28, the distance between the shaft and the hole can be adjusted. The clearance changes to achieve the purpose of damping adjustment.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that the damping force is not provided by the throttling passage, but by the throttling opening of the passage on the adjustment shaft, and the size of the throttling opening is adjustable.
[0036] attached Image 6 The implementation diagram of Embodiment 3 of another solution of the present invention is given. The structure is similar to Embodiment 1, the difference is that the adjustment shaft 29 is the optical axis in the mandrel hole, and the end of the shaft is not threaded; the adjustment shaft 29 An orifice 30 is added to itself, a spring 31 is added to the end of the adjustment shaft 29, and a positioning pin 32 is added to the mandrel 2 to prevent the adjustment shaft from swinging in the mandrel hole; The throttling hole 30 is combined with the throttling channel hole 32 on the mandrel 2 to form a throttling port, and at the same time, an axial stopper 54 is added to the outer end of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com