Bitterness-improving agent for bitter food and beverages and astringency-improving agent for astringent food and beverages
A technology for improving agents and food and beverage products, applied in the field of bitter taste improving agents and astringent taste improving agents, can solve the problems of increased astringency and unsatisfactory fragrance and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1 (covering of the bitterness of carbonated water)
[0043] According to the concentration shown in the following table 1, add sedanolactone as the bitter taste improving agent (bitter taste masking agent) of the present invention to fully degassed pure water, then charge into carbon dioxide with the internal pressure of 294KPa in the bottle to obtain the present invention carbonated water.
[0044] flavor comparison
[0045] Table 1 shows the comparative evaluation of the flavor of carbonated water containing or not containing the product of the present invention by 10 professional evaluators.
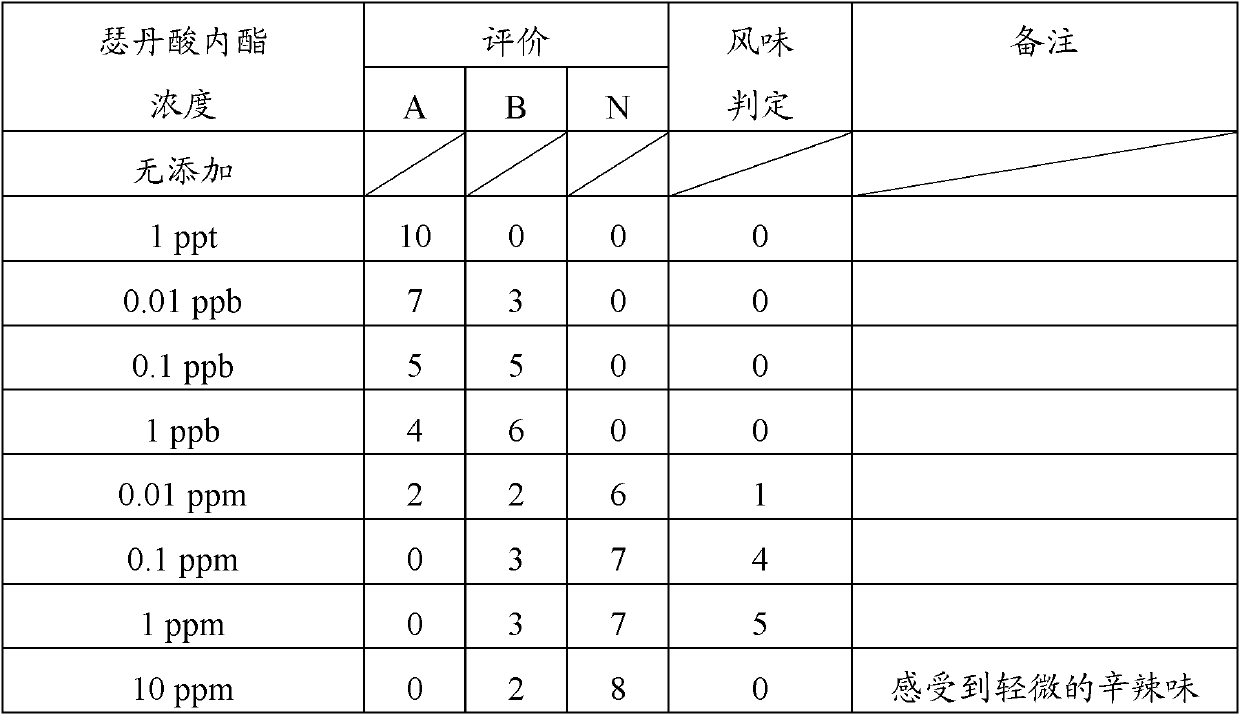
[0046] Table 1 Bitterness evaluation of carbonated water
[0047]
[0048] Evaluation
[0049] A: The number of people who thought there was no difference from the case where no sedanolactone was added
[0050] B: The number of people who think that the bitterness is somewhat weakened
[0051] N: Number of people who hardly feel bitterness
[0052] Flavor Ju...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 (masking of the bitterness of grapefruit juice)
[0055] Grapefruit juice was obtained by adding 3-n-butylphthalide as the bitterness improving agent (bitterness masking agent) of the present invention to commercially available grapefruit juice at the concentrations shown in Table 2 below.
[0056] flavor comparison
[0057] Table 2 shows the comparative evaluation of the flavor of grapefruit juice containing or not containing the product of the present invention by 10 professional evaluators.
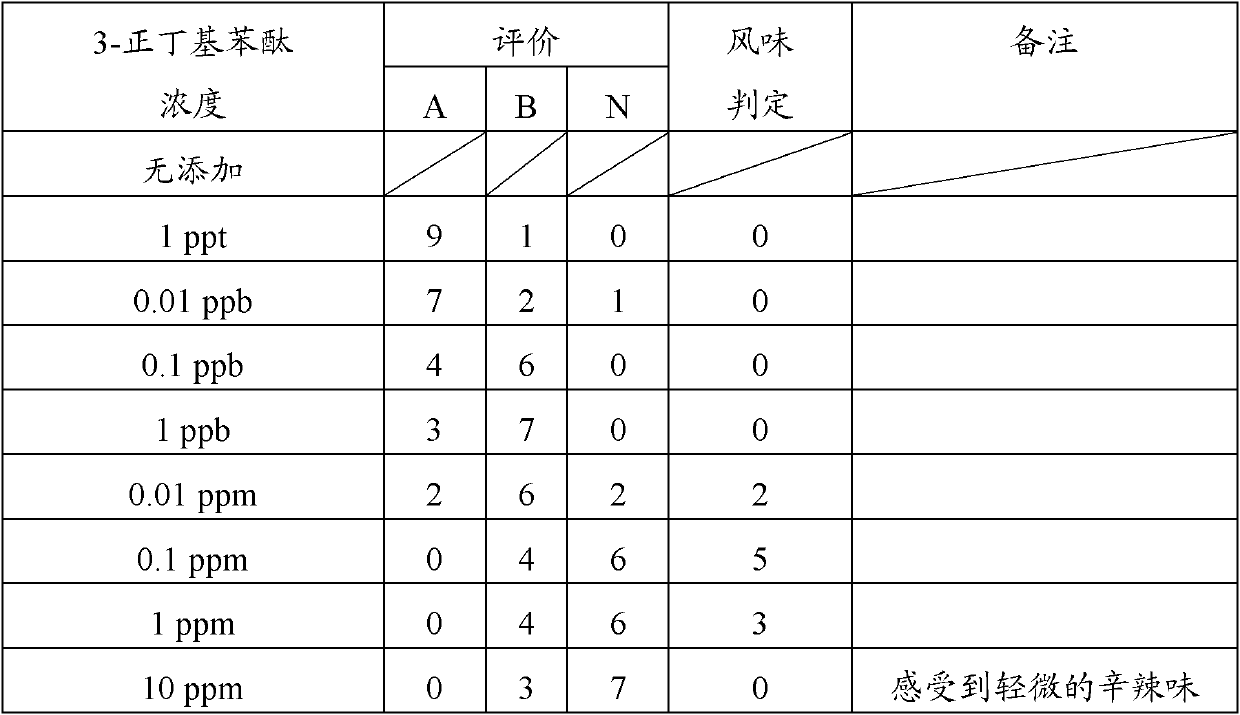
[0058] Table 2 Bitterness evaluation of grapefruit juice
[0059]
[0060] Evaluation
[0061] A: The number of people who thought there was no difference from the case where 3-n-butylphthalide was not added
[0062] B: The number of people who think that the bitterness is somewhat weakened
[0063] N: Number of people who hardly feel bitterness
[0064] Flavor Judgment: The number of people who judged the most suitable bitterness.
[0065] As shown in Table 2...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3 (masking of the bitterness of green tea beverage)
[0067] Add 5000g of warm water (containing 0.03% sodium ascorbate) at 60°C to 100g of green tea (Ercaicha) produced by the steaming method (heat treatment with steam) produced in China, and then extract for 5 minutes with occasional stirring. Then, solid-liquid separation was carried out with a filter cloth to obtain 4500 g of extract (B×0.6°). 0.04 g of tannase (manufactured by Kikkoman, 5000 U / g) was added to the extract. The resulting mixture was left standing at 40°C for 1 hour to decompose the gallic acid catechol into the non-gallic acid catechol (the gallic acid catechin has a strong astringent taste, while the non-gallic acid catechol has a strong bitter taste), and then heated at 90°C for 1 minute to inactivate the enzyme. After cooling to 20°C, the extract was adjusted to B×0.5° with ion-exchanged water to obtain a bitter green tea extract. A green tea drink was obtained by adding seltan lacto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com