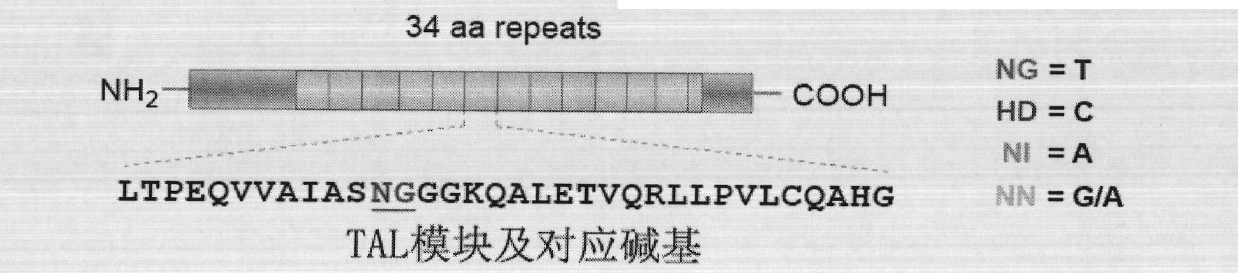
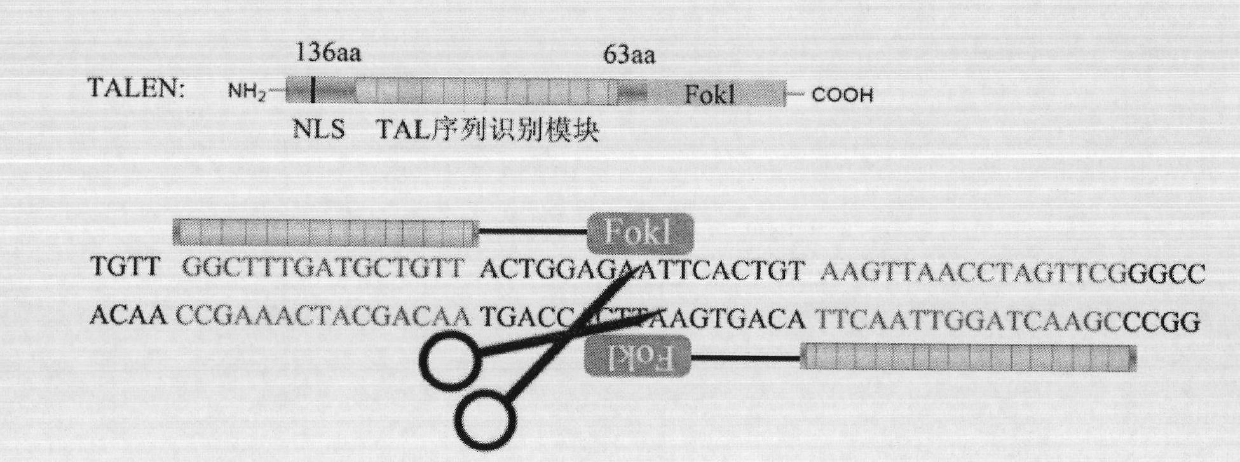
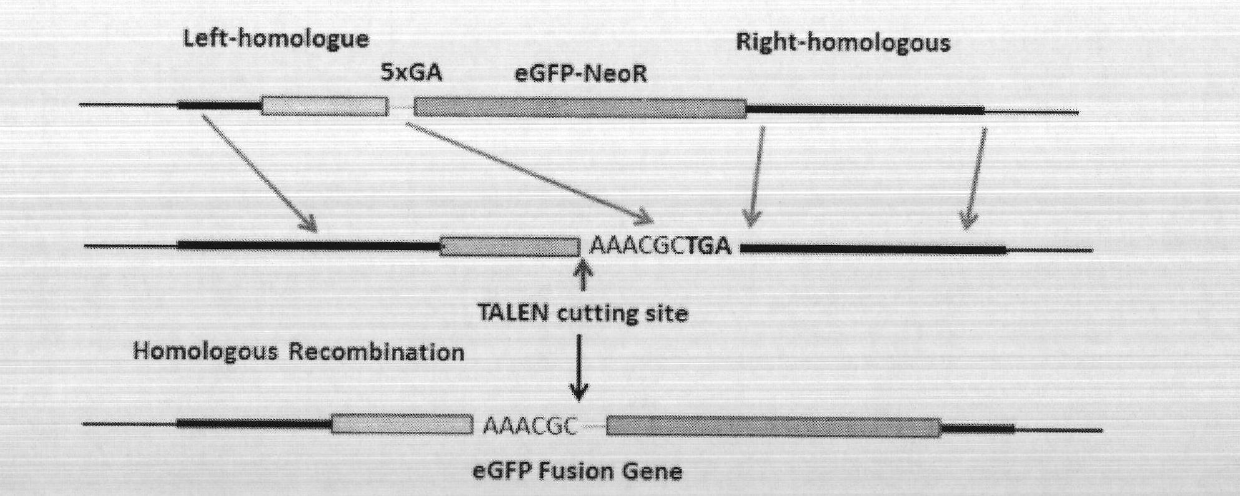
Solid-phase synthesis method of transcription activator-like effector
A transcriptional activation and effector technology, applied in peptide preparation methods, microbial-based methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems that are not suitable for large-scale applications, time-consuming, and labor-intensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1. TALE 5-connected sub-unit assembled from 1 TALE unit (1-connected sub-unit)
[0070] The DNA linker sequence, the 5 TALE linker unit sequences, the DNA sequence to be combined with the 5-linker and the final assembled TALE 5-linker unit sequence are shown in Attached Table 1.
[0071] First, before DNA immobilization, mix the 5-terminal modified biotin DNA linker with the first linking unit digested by BbsI, and connect in solution; secondly, after treating the linking unit immobilized on the magnetic beads with BbvI enzyme digestion , wash the magnetic beads 3 times; moreover, before adding the second TALE linking unit, digest it with BbsI, purify it, and connect it to the magnetic beads under the action of T4 DNA ligase; repeat the above digestion and purification , connection and other steps 3 times, you can get 5 consecutive pieces.
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2 TALE 10-connected sub-unit assembled from 1 TALE unit (1-connected sub-unit)
[0073] The DNA linker sequence, the 5 TALE linker unit sequences, the DNA sequence to be combined with the 5-linker and the final assembled TALE 5-linker unit sequence are shown in Attached Table 2.
[0074] First, before DNA immobilization, mix the 5-end biotin-modified DNA linker with the first linking unit digested by BbsI, and connect in solution; secondly, treat the linking unit immobilized on the magnetic beads with BbvI enzyme digestion , wash the magnetic beads 3 times; moreover, before adding the second TALE linking unit, digest it with BbsI, purify it, and connect it to the magnetic beads under the action of T4 DNA ligase; repeat the above digestion and purification , connection and other steps 8 times, you can get 10 consecutive pieces.
Embodiment 3
[0075] Embodiment 3 is assembled into TALE 16 linker by 4 TALE quadruple linker units
[0076] The DNA sequence to be combined with the DNA linker, the 16-linker, and the sequence of each TALE linking unit are shown in Attached Table 3.
[0077] On the basis of TALE quadruplets, 4-step assembly can be carried out on the magnetic beads, and finally assembled into 16 TALE linkers. In the first step, the biotinylated ds-DNA linker (Biotinylated ds-DNA linker) has a SpeI restriction site, so it will produce sticky ends after digestion. After purification, it will be incubated with magnetic beads and will be fixed to the surface of the magnetic beads. The second step is to purify and amplify the TALE4 linker. In the third step, the TALE 4-linkage was digested with SpeI. In the fourth step, add the enzyme-digested first 4-linker to the magnetic bead solution with the DNA linker, connect for 15 minutes to 1 hour, and wash 3 times. In the fifth step, use NheI to digest the magnetic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com