Power save mode for lightpaths
An optical path and node technology, applied in the field of optical communication network, can solve problems such as increasing the overall cost of optical network
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] summary
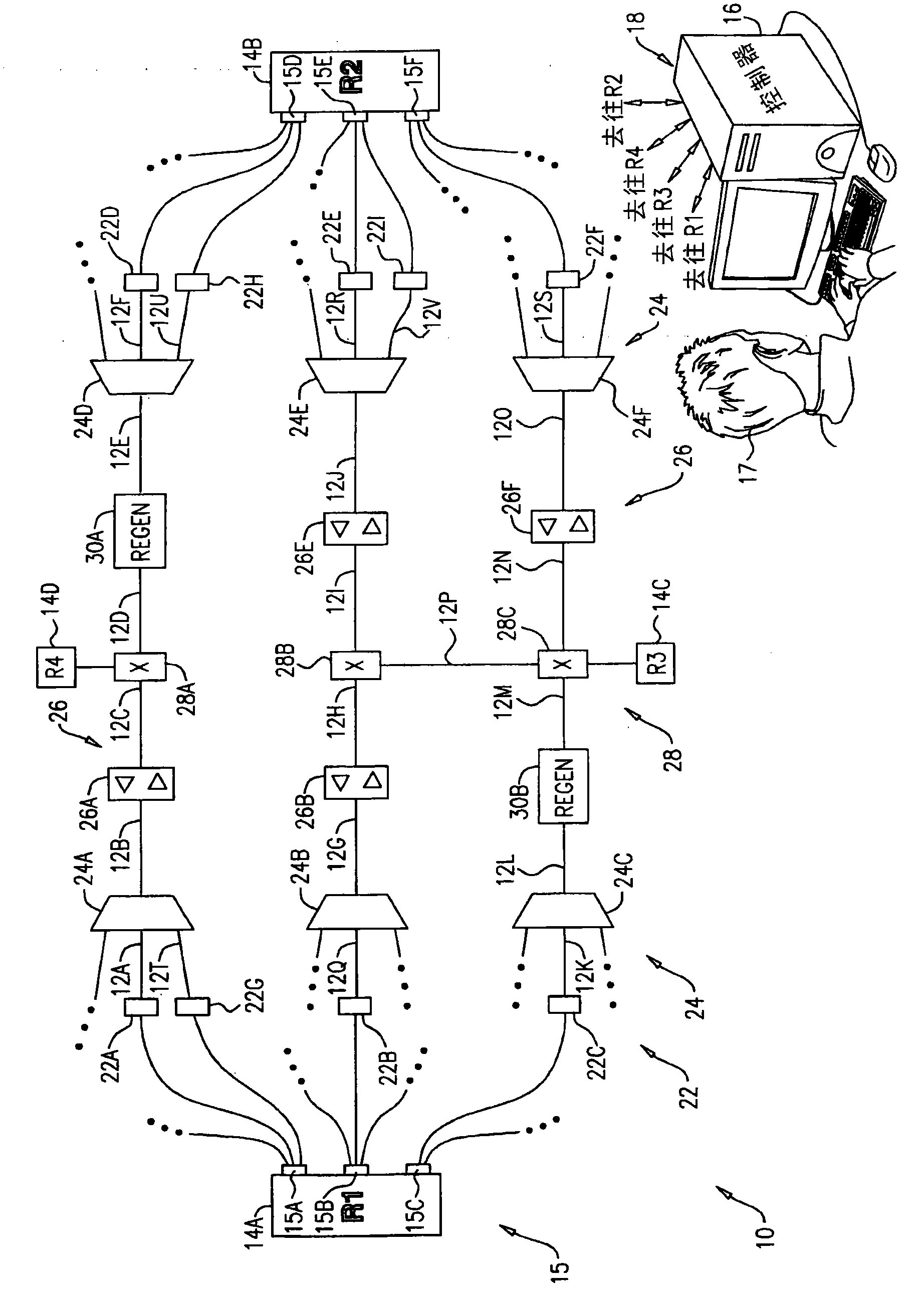
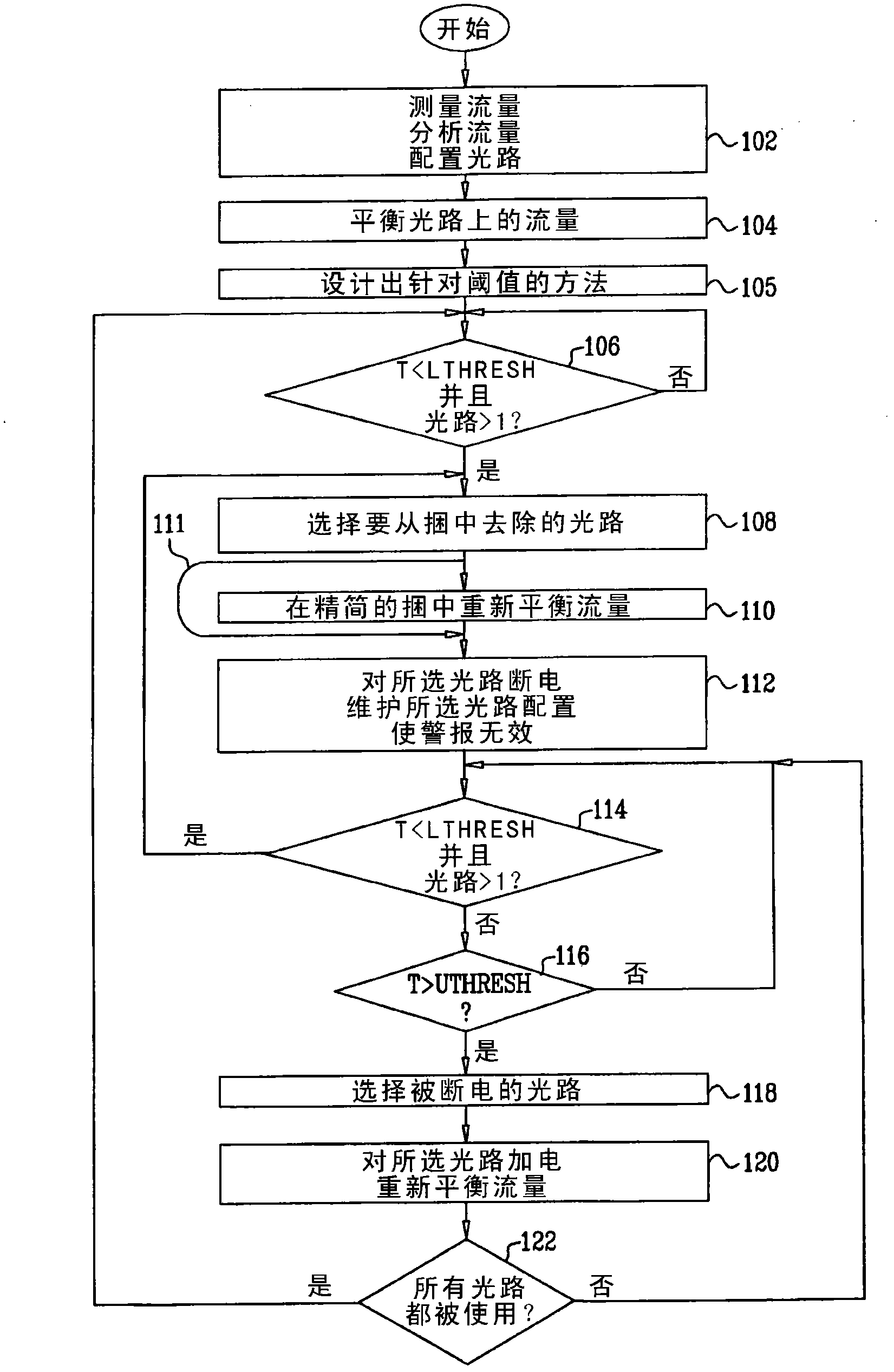
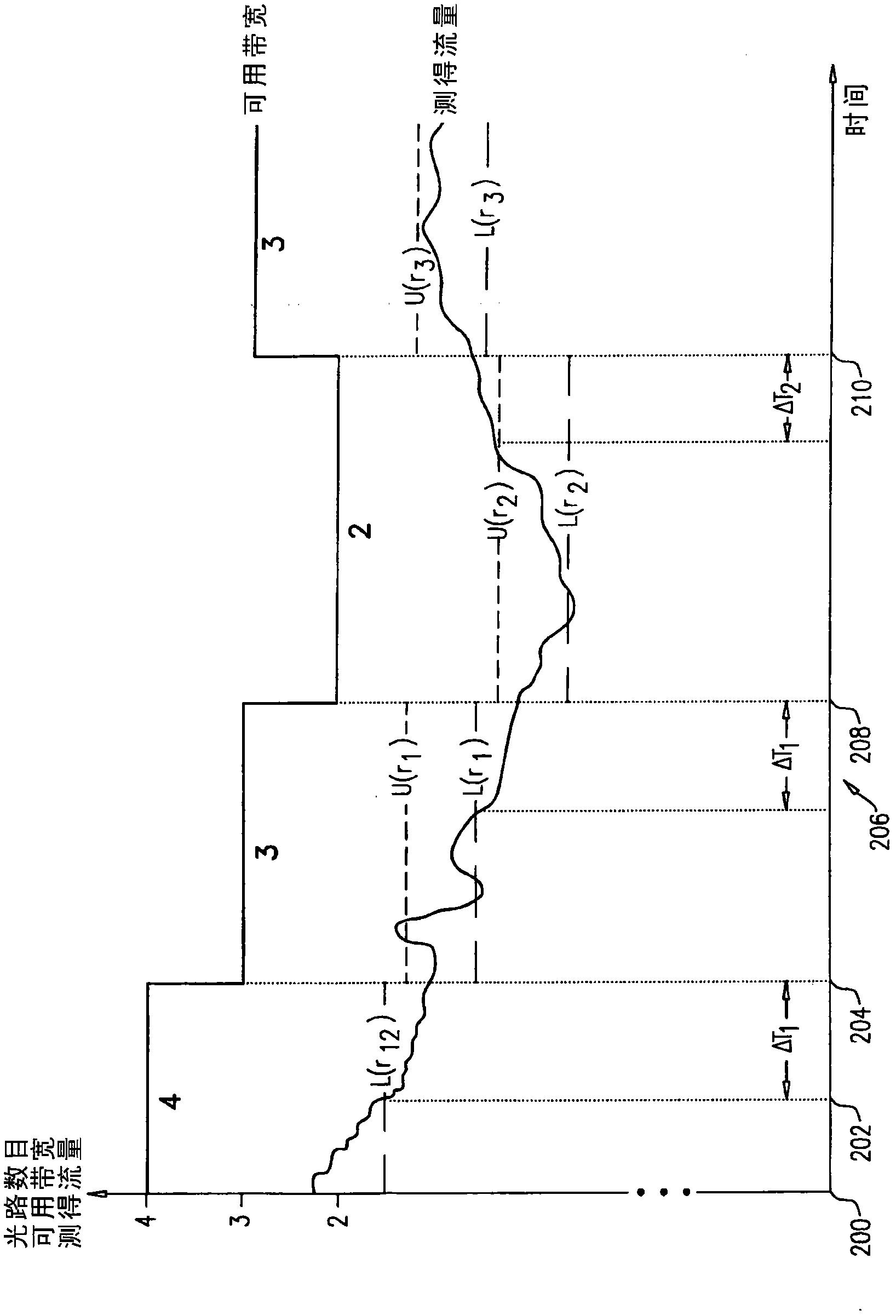
[0026] Embodiments described herein are intended to provide a method for optical communication between nodes of an optical network. In one embodiment, a set of lightpaths is formed between the first node and the second node of the network, each lightpath in the set having a respective configuration. Communication traffic is communicated between the first node and the second node via the set of lightpaths. In response to a determination that a communication traffic level associated therewith for the set of lightpaths is less than a predetermined threshold, lightpaths having a given configuration are removed from the set of lightpaths to form a reduced set of lightpaths. between said first node and said second node via said reduced set of lightpaths while reducing the level of power consumption in the removed lightpaths and while maintaining said given configuration in the removed lightpaths The communication traffic is transmitted.
[0027] describe
[0028] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com