DES (data encryption standard) encryption method of resisting differential power analysis based on random offset
A technology of differential power analysis and encryption method, which is applied in the direction of encryption devices with shift registers/memory, etc., and can solve problems such as aligning power consumption curves, difficulty for attackers, and difficulty in blinding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
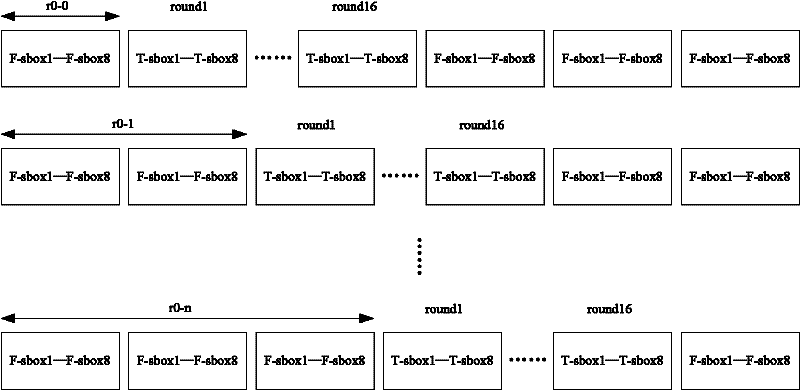
[0023] see figure 1 and figure 2 , the present invention provides an embodiment of a DES encryption method based on random offset and anti-differential power consumption analysis.
[0024] The DES encryption operation in Embodiment 1 calculates the round function every 8 clock cycles. The round function mainly includes a permutation operation and 8 Sbox operations. The permutation operation is calculated in the first and last clock cycle of the round function, and one Sbox operation is calculated in each clock cycle. The calculation sequence of the Sbox operation is determined by a random number. The entire encryption or decryption needs to calculate 16 rounds of functions, so a total of 128 clock cycles are needed to complete the DES operation. In addition, due to the need to insert fake DES to cover up the running position of the real DES, it is also necessary to add the calculation time of the fake DES. Therefore, the attacker will not be able to determine the operation...
Embodiment 2
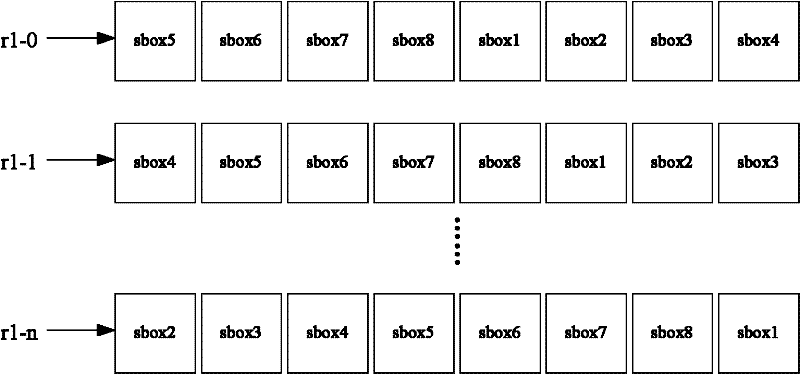
[0034] see image 3 and Figure 4 , the present invention provides another embodiment of a random offset-based anti-differential power analysis DES encryption method.
[0035] The DES encryption operation in Embodiment 2 calculates the round function every 8 clock cycles. The round function mainly includes a permutation operation and 8 Sbox operations. The permutation operation is calculated in the first and last clock cycle of the round function, and one Sbox operation is calculated in each clock cycle. The calculation sequence of the Sbox operation is determined by a random number. The entire encryption or decryption needs to calculate 16 rounds of functions, so a total of 128 clock cycles are needed to complete the DES operation. In addition, due to the need to insert fake DES to cover up the running position of the real DES, it is also necessary to add the calculation time of the fake DES. Therefore, the attacker will not be able to determine the operation position and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com