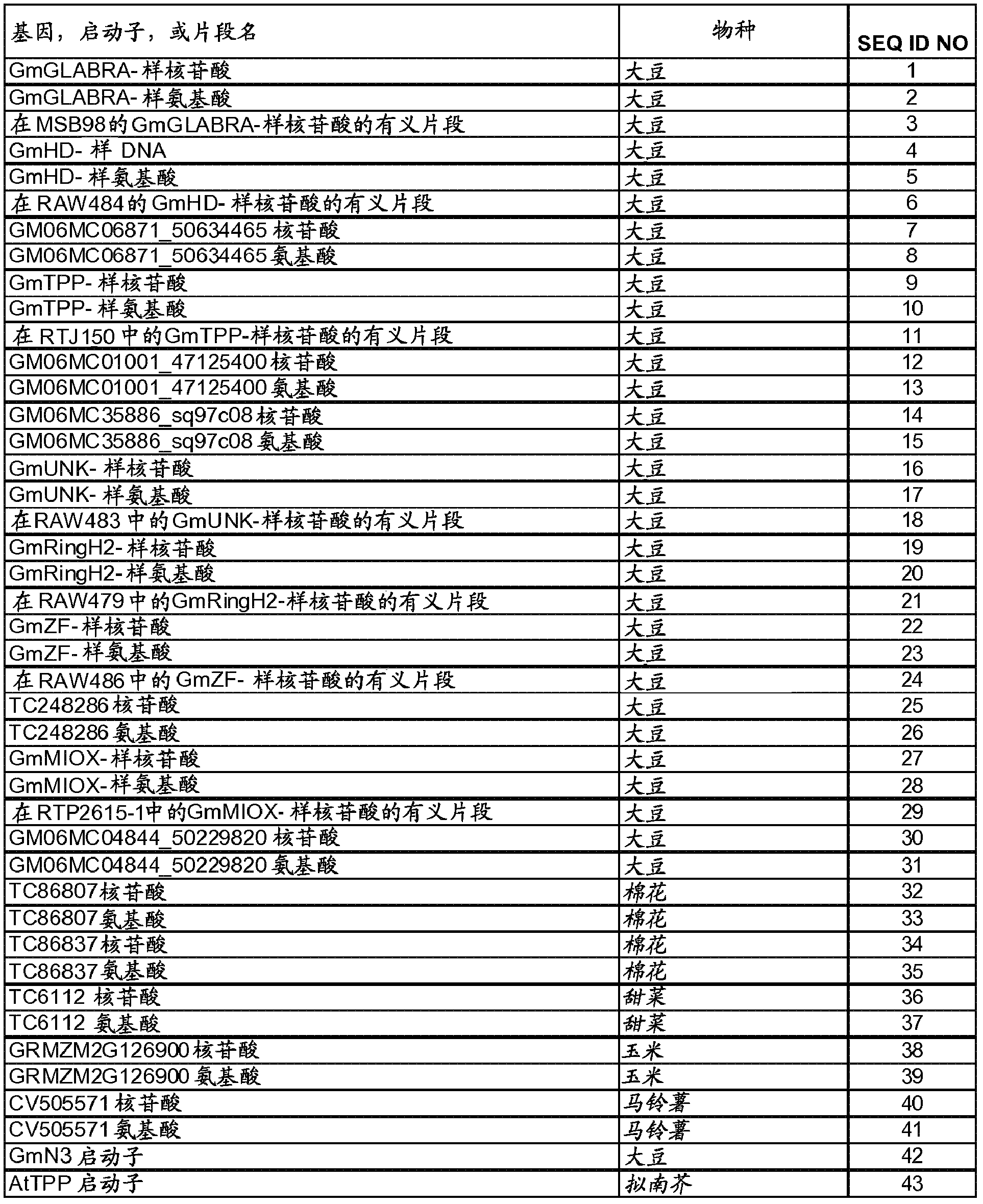
Nematode-resistant transgenic plants
A technology of transgenic plants and plants, applied in the directions of genetic engineering, biochemical equipment and methods, introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, etc., can solve the problems of plant regulation without removing the resistance of transgenic nematodes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1: Target gene cloning and vector construction
[0083] Using the available soybean target gene cDNA clone sequences, DNA fragments approximately 200-500 bp in length were isolated by PCR, which were used to construct the binary vectors described in Table 1 and discussed in Example 2. This PCR product was cloned into TOPO Pcr2.1 vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and the insert was confirmed by sequencing. This method was used to isolate target gene GmTPP-like, GmGLABRA-like, and GmMIOX-like gene fragments. Alternatively, available cDNA clone sequences of soybean target genes were used to identify DNA fragments approximately 200-300 bp in length that were used to construct the binary vectors described in Table 1 and discussed in Example 2. The DNA sequences of the identified soybean target genes were synthesized, cloned into pUC19 (Invitrogen) vector, and verified by sequencing. DNA synthesis was used to isolate target gene GmHD-like, GmRingH2 finger-like, GmUN...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Example 2 Bioassay of Double-stranded RNA Targeting Soybean Target Gene
[0091] The binary vectors described in Table 1 were used in the rooting plant assay system disclosed in commonly-owned co-pending US Patent Publication 2008 / 0153102. Transgenic roots were generated after transformation with the binary vector described in Example 1. Multiple transgenic root lines were subcultured and inoculated with surface decontaminated race 3SCN second stage larvae (J2) at a level of approximately 500 J2 / well. Four weeks after nematode inoculation, the number of cysts in each well was counted. For each transformation construct, the number of cysts for each line was calculated to determine the average cyst number and standard error for the construct. The cyst counts for each transformation construct were compared to the cyst counts for the empty vector control tested in parallel to determine whether the tested construct resulted in a reduction in cyst number. Bioassay results ...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3: Identification of additional soybean sequences targeted by binary constructs
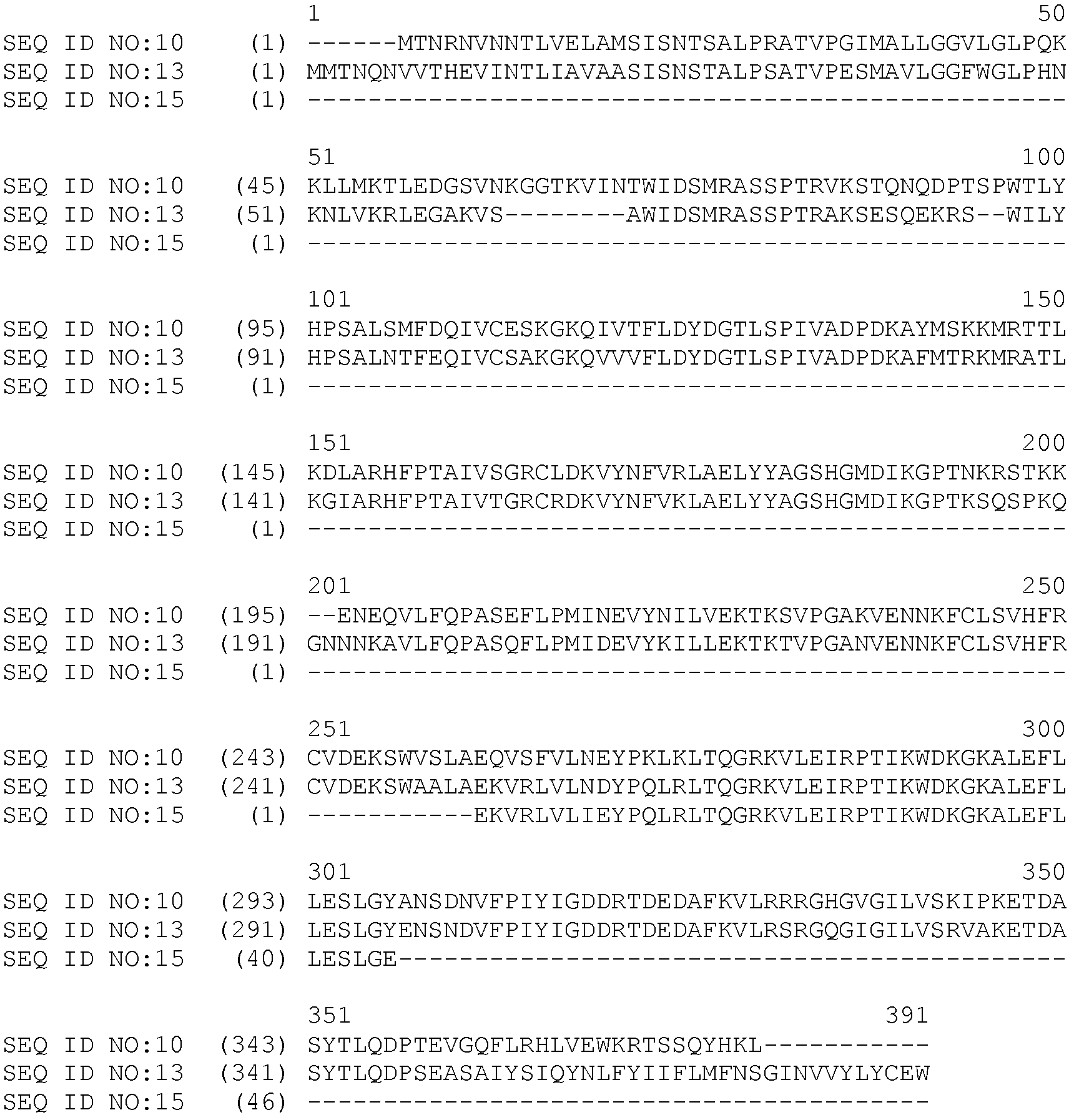
[0093] As disclosed in Example 2, construct RAW484, when operably linked to an SCN-inducible promoter and expressed in soybean roots, resulted in the expression of a double-stranded RNA molecule targeting SEQ ID NO: 4 and reduced cyst counts. The sense fragment of the GmHD-like gene contained in RAW484 described by SEQ ID NO:6 corresponds to nucleotides 592-791 of the GmHD-like sequence described by SEQ ID NO:4. At least one 21-mer obtained from processing of a double-stranded RNA molecule expressed from RAW484 can target another soybean sequence described by SEQ ID NO:7. Figure 2 shows the amino acid alignment of the identified target of the double-stranded RNA molecule expressed from RAW484 described by the GmHD-like target gene SEQ ID NO:5 and GM50634465 described by SEQ ID NO:8. Figure 6 shows the identified target of the double-stranded RNA molecule expressed from RAW484 desc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com