Novel OLED display architecture
A technology of organic light-emitting devices and light-emitting materials, which is applied in semiconductor devices, electric solid-state devices, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as negative work function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
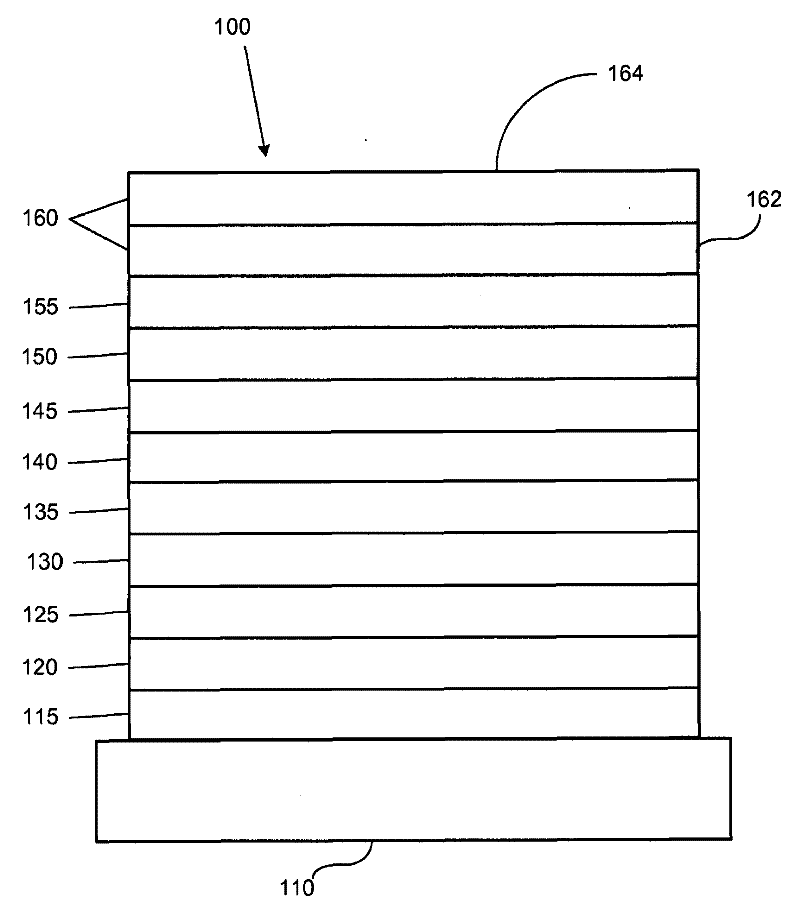
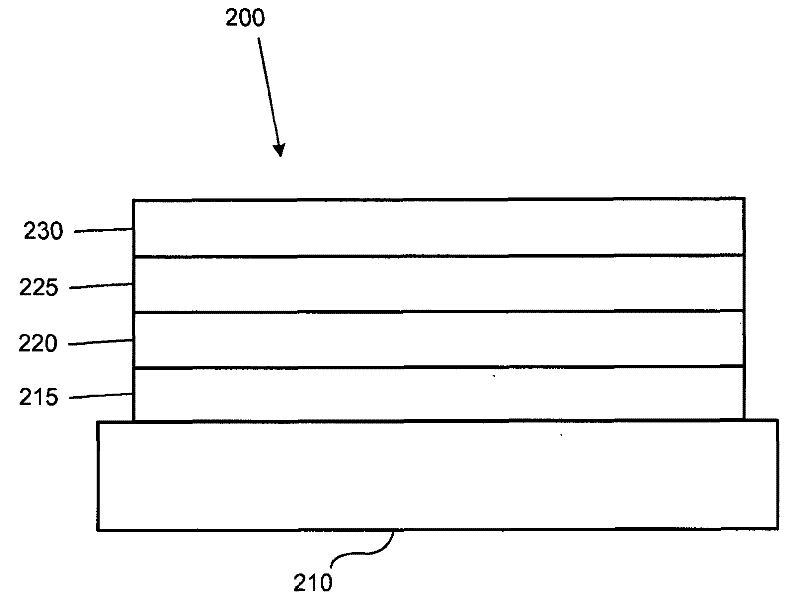
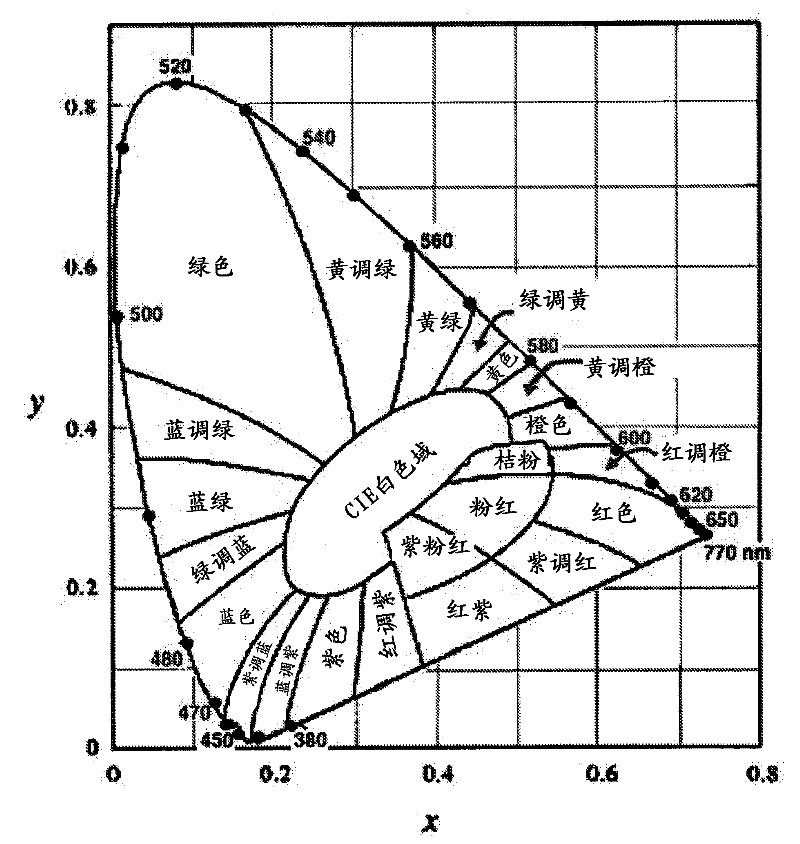
[0029] Typically, an OLED comprises at least one organic layer disposed between and electrically connected to an anode and a cathode. When a current is applied, the anode injects holes into the one or more organic layers and the cathode injects electrons into the one or more organic layers. Each of the injected holes and electrons migrates toward the oppositely charged electrode. When an electron and a hole localize on the same molecule, an "exciton" is formed, which is a localized electron-hole pair with an excited energy state. Light is emitted when the excitons relax through a photoemission mechanism. In some cases, the excitons can be localized to excited excimers or exciplexes. Non-radiative mechanisms also occur, such as thermal relaxation, but are generally considered unnecessary.
[0030] Initial OLEDs used light-emitting molecules that emitted light ("fluorescence") from their singlet states, as disclosed in US Patent No. 4,769,292, which is incorporated herein by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com