A deadlock-free adaptive routing algorithm in a Torus network
A deadlock-free, self-adaptive technology, applied in the field of distributed networks, can solve problems such as network delay reduction, achieve the effect of avoiding deadlocks and improving data transmission efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
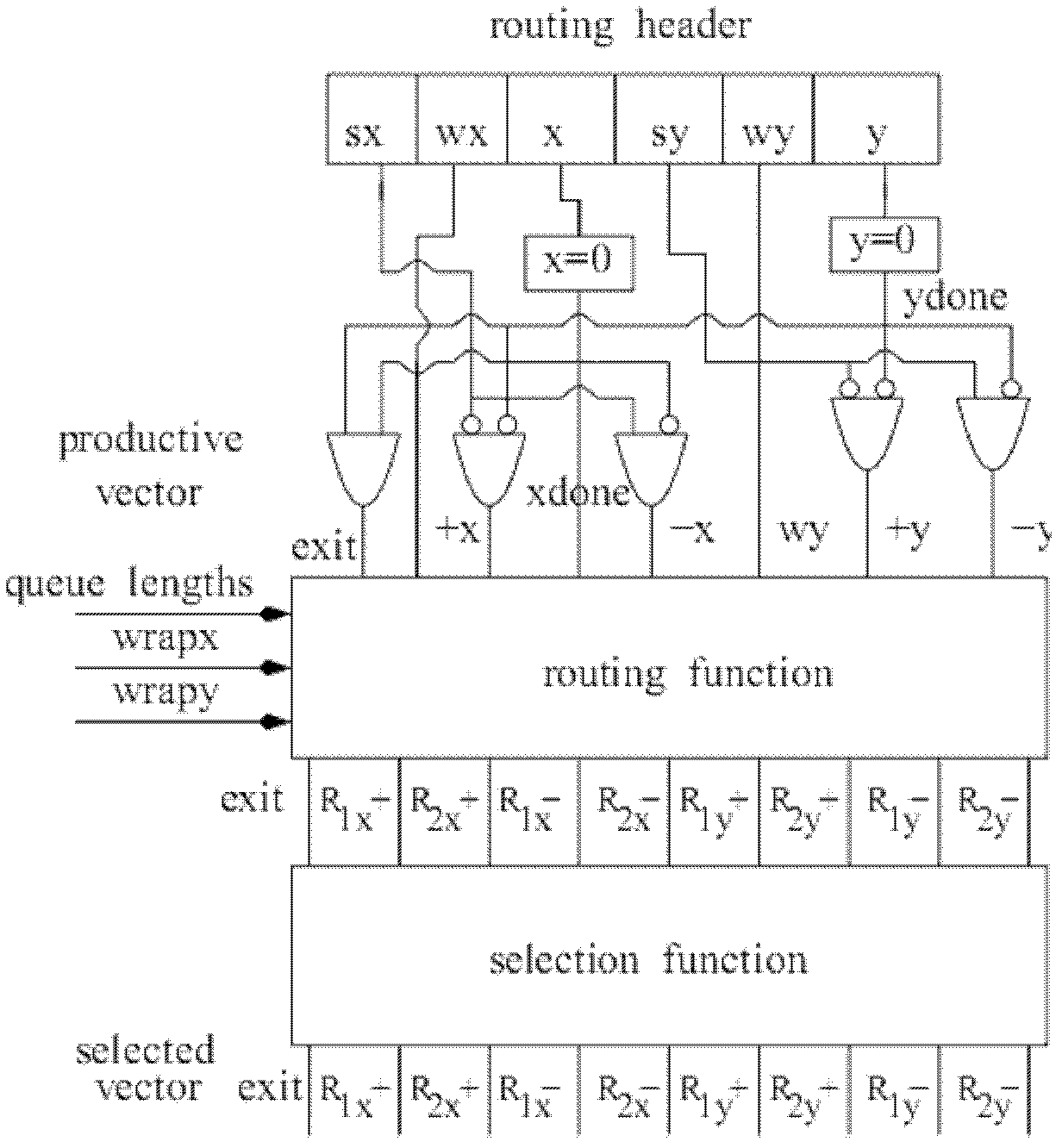
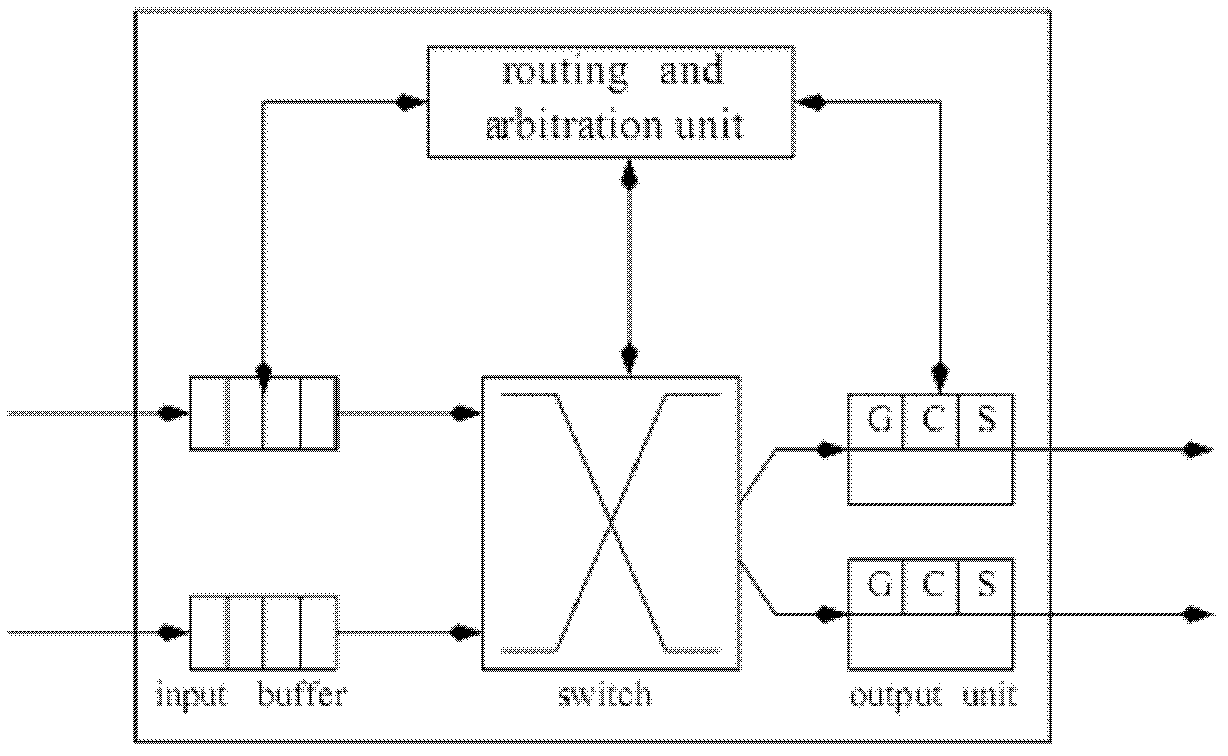
[0045] The Torus network adopts the virtual cut-through switching method without flow control. The algorithm is implemented as follows:
[0046] 1) The R1 channel is fully adaptive, and data packets can request the R1 channel at any time;
[0047] 2) If the data packet is already in the Mesh subnet, that is, the data packet no longer needs to go through any turnaround link to reach the destination, the data packet can request the R2 channel, and the data packet should follow the Mesh network when using the R2 channel Deadlock-free routing algorithms in , such as dimension order algorithm, turn model (TurnModel), etc.;
[0048] 3) If the next hop of the data packet is through a turnaround link, and the dimension of the turnaround link is the lowest dimension among the turnaround links that the data packet needs to pass through to reach the destination, then on that turnaround link , the packet can request the R2 channel.
[0049] For a Torus network with n dimensions and k no...
Embodiment 2
[0099] The Torus network adopts the virtual cut-through switching mode and uses flow control, so it is necessary to first define the secure data packet and the non-secure data packet:
[0100] 1) If the data packet is already in the Mesh subnet, that is, the data packet does not need to go through any turnaround link to reach the destination, and the next hop of the data packet follows the deadlock-free routing algorithm in the Mesh network, then for the next The node on one hop, the data packet is a security data packet;
[0101] 2) If the next hop of the data packet is through a turnaround link, and the dimension of the turnaround link is the lowest dimension in the turnaround link that the data packet needs to pass through to reach the destination, for the node on the next hop, The packet is a security packet;
[0102] A data packet that does not meet any of the above conditions is a non-secure data packet,
[0103] After giving the definitions of secure and non-secure da...
Embodiment 3
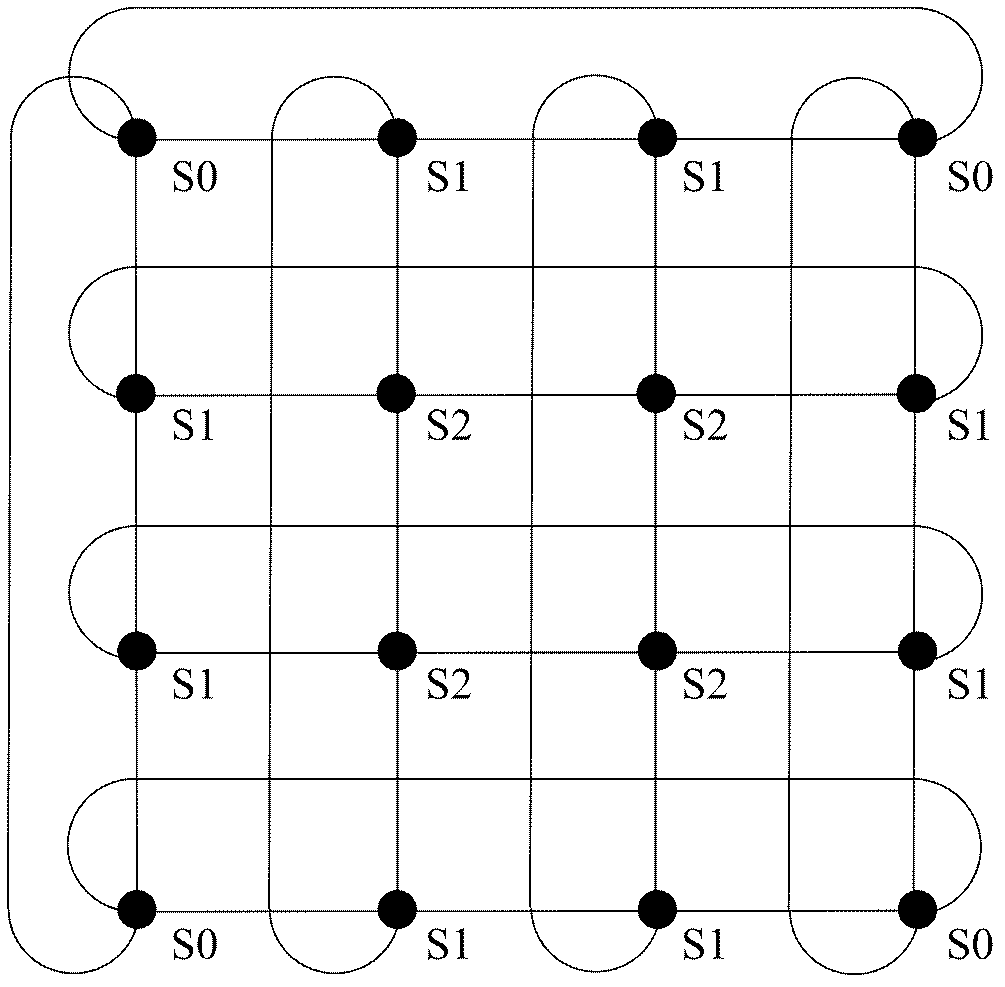
[0110] If the Torus network adopts the wormhole exchange method, according to the distance from each node to the vertex in the Torus network, all nodes are divided into different sets Si, the set S0 contains all vertices, and the minimum path from the nodes in the set Si to all vertices , the shortest distance is i, the implementation of the algorithm is as follows:
[0111] 1) When the data packet needs to pass through the turnaround link, it can only apply for the R1 channel from the node in the set Si to the node in the set Sj, where j≤i, when the data packet does not need to pass through the turnaround link, the data packet There is no limit to request R1 channel;
[0112] 2) If the data packet is already in the Mesh subnet, that is, the data packet does not need to go through any turnaround link to reach the destination, then the data packet can request the R2 channel, and the data packet should follow the Mesh when using the R2 channel Deadlock-free routing algorithms i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com