Method for detecting safety of insect-resistant transgenic corn on non-target organisms
An insect-resistant gene and safe technology, which is applied in the field of detecting whether transgenic insect-resistant corn is safe to non-target organisms, can solve the problems of impossible non-target biological safety, and achieve convenient, fast and accurate investigation and counting. The effect of judgment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1, the detection of whether transgenic Bt corn is safe to non-target organisms
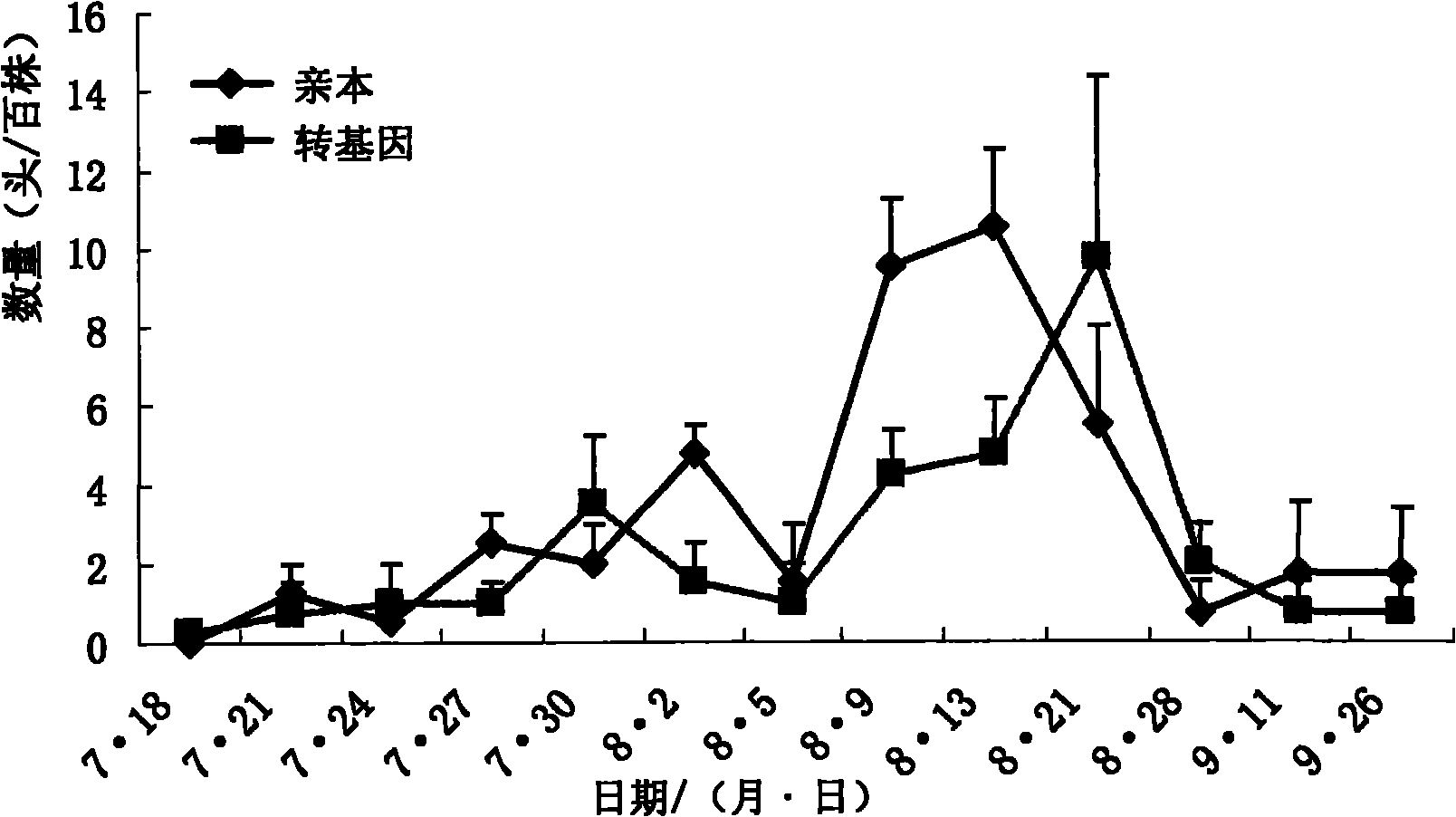
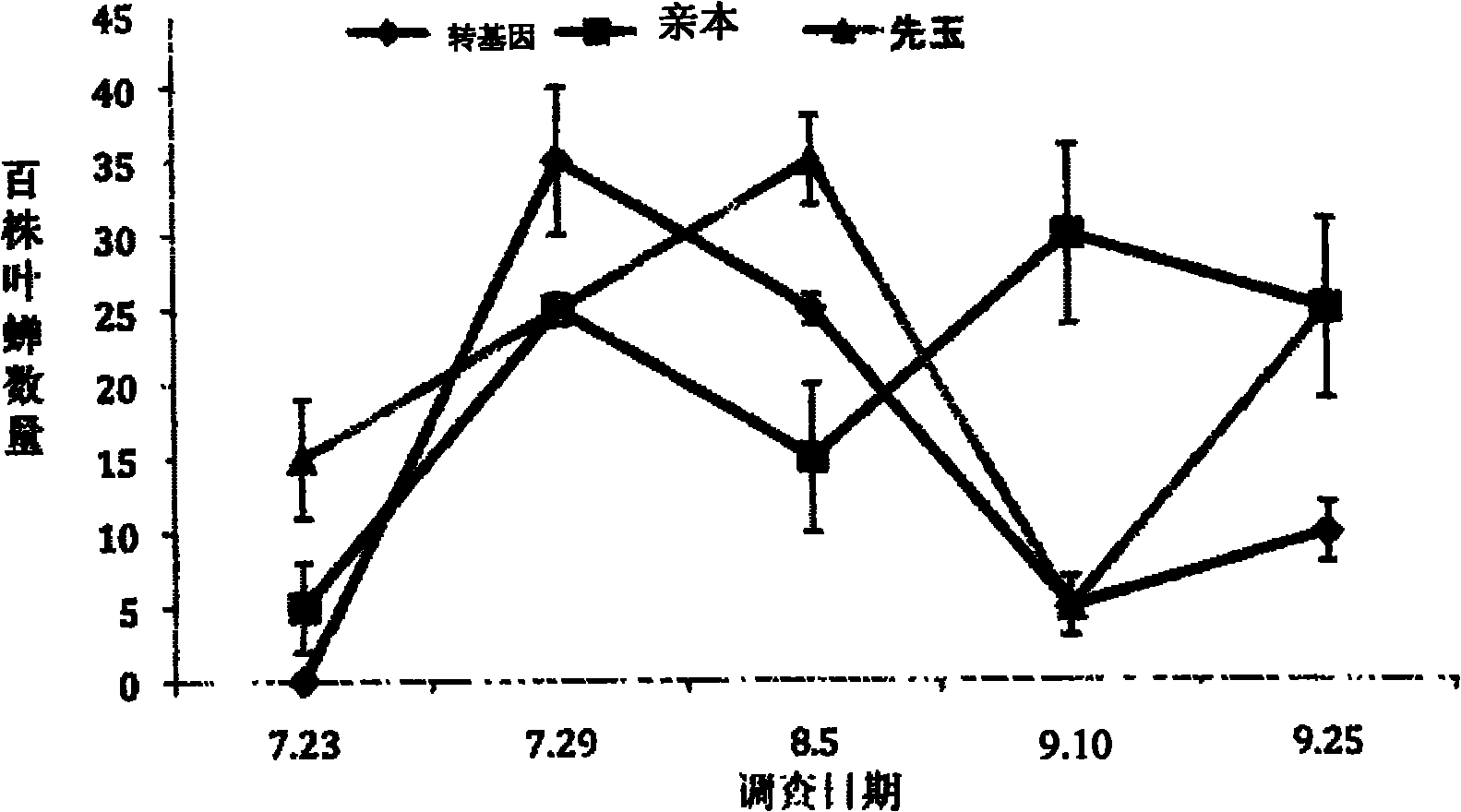
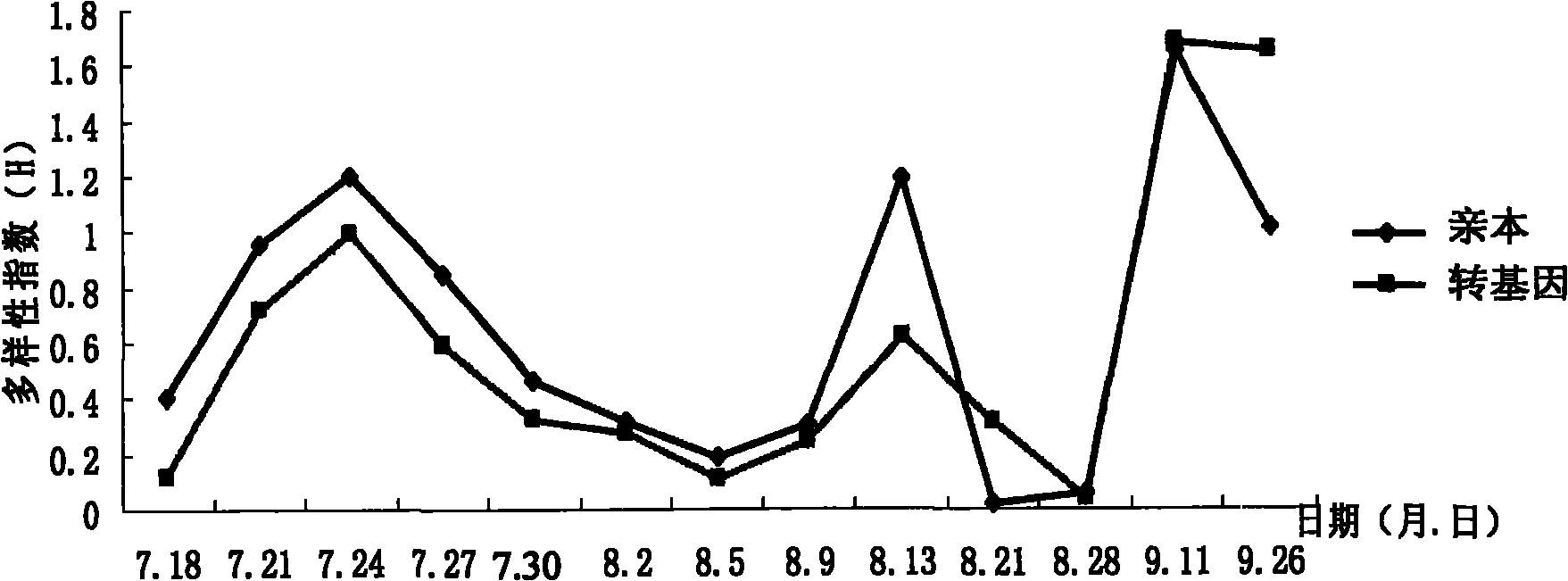
[0064] In 2009 and 2010, leafhoppers were used to study the effects of Cry1Ac transgenic maize on non-target organisms at the transgenic crop test base of China Agricultural University in Beijing.
[0065] 1. Method
[0066] 1. Material selection
[0067] 2009: (1) transgenic maize group (denoted as transgenic); (2) parental control group (denoted as parent).
[0068] 2010: (1) Transgenic corn group (denoted as transgenic); (2) parental control group (denoted as parent); (3) conventional hybrid varieties (denoted as Xianyu).
[0069] 2. Location selection
[0070] The test site is more than 500 meters away from other corn fields, and the fertility conditions of the test plots are basically the same. Each plot is about 25×30 meters, divided into 15 plots, and each variety has 5 replicates. The area of each plot is set at 45m 2 (5m×9m), 15 rows are planted in each plot, 20 ...
Embodiment 2
[0157] Embodiment 2, the influence of transgenic corn on the growth and development of Heterochromia
[0158] Toxicology experiment: every 30 newly hatched ladybug larvae is a group, a total of 8 groups. Among them, 4 groups were fed with transgenic Bt corn pollen and aphids at a ratio of 2:1 (weight ratio) as treatment; 4 groups were fed with non-transgenic corn pollen and aphids at a ratio of 2:1 as a control. Ladybug larvae were single-headed in finger tubes, and their growth and development were observed every day, and the developmental periods of ladybugs at different ages were recorded. They were weighed every other day from larvae to early adult stages, and were weighed at the adult stage (45 days, Counting from the 1st instar) for the last weighing to evaluate the impact of transgenic insect-resistant corn pollen on ladybugs.
[0159] The result is as Figure 9 shown. The results showed that the GM corn was not toxic to Heterochromia.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com